6. RDD综合练习:更丰富的操作
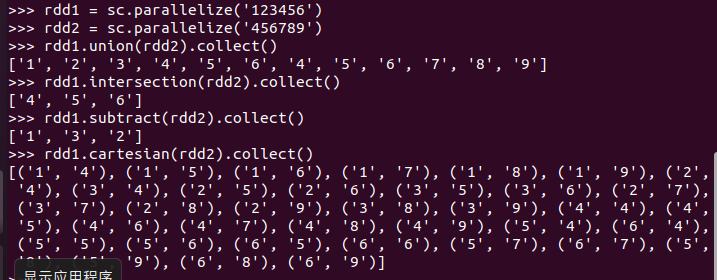
集合运算练习
union(), intersection(),subtract(), cartesian()
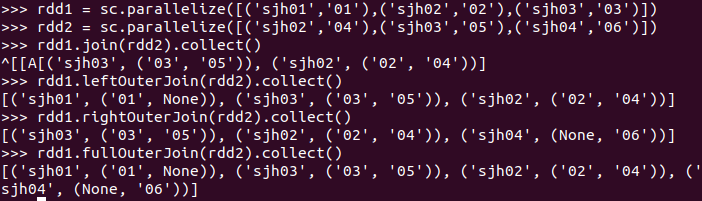
内连接与外连接
join(), leftOuterJoin(), rightOuterJoin(), fullOuterJoin()
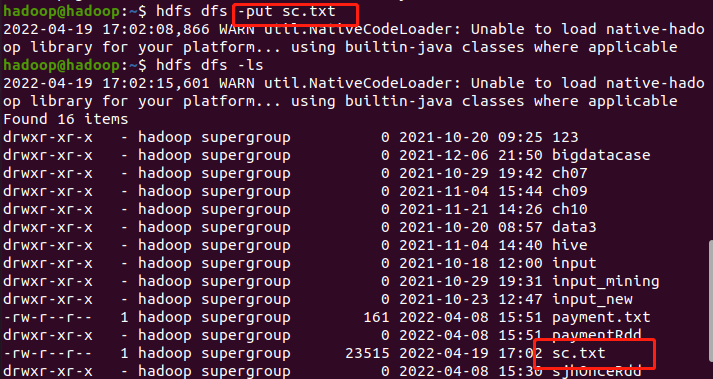
三、综合练习:学生课程分数
网盘下载sc.txt文件,通过RDD操作实现以下数据分析:
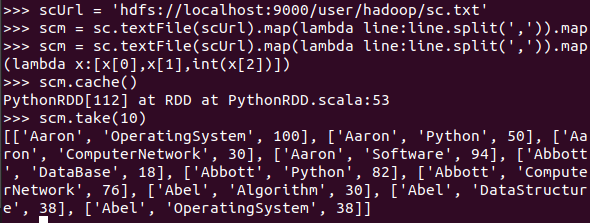
- 持久化 scm.cache()
![]()
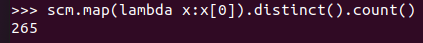
- 总共有多少学生?map(), distinct(), count()
![]()
- 开设了多少门课程?
![]()
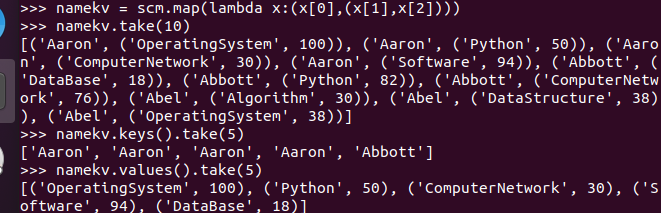
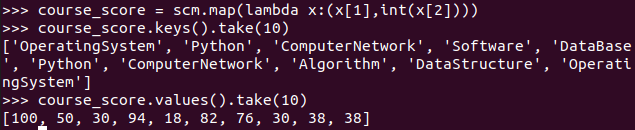
- 生成(姓名,课程分数)键值对RDD,观察keys(),values()
![]()
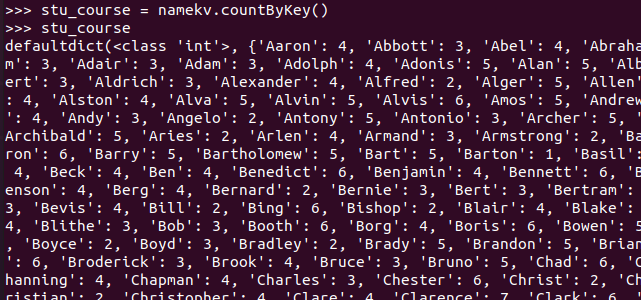
- 每个学生选修了多少门课?map(), countByKey()
![]()
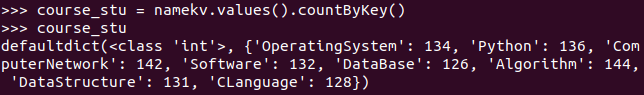
- 每门课程有多少个学生选?map(), countByValue()
![]()
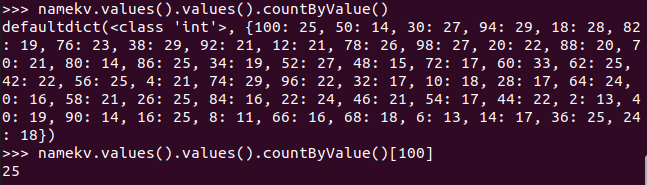
- 有多少个100分?
![]()
![]()
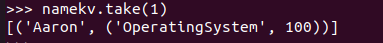
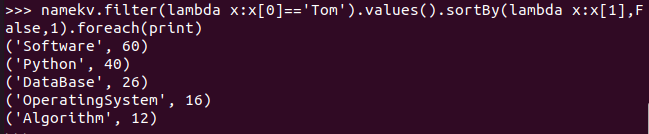
- Tom选修了几门课?每门课多少分?filter(), map() RDD
![]()
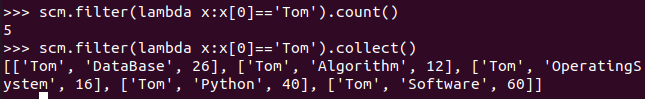
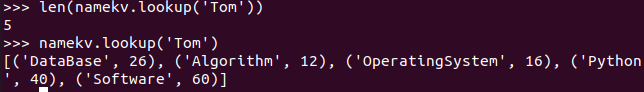
- Tom选修了几门课?每门课多少分?map(),lookup() list
![]()
- Tom的成绩按分数大小排序。filter(), map(), sortBy()
![]()
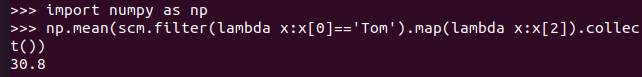
- Tom的平均分。map(),lookup(),mean()
![]()
![]()
![]()
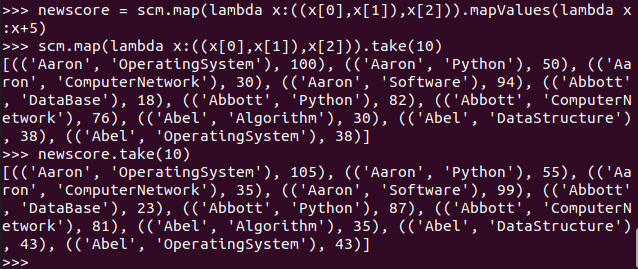
- 生成(课程,分数)RDD,观察keys(),values()
![]()
- 每个分数+5分。mapValues(func)
![]()
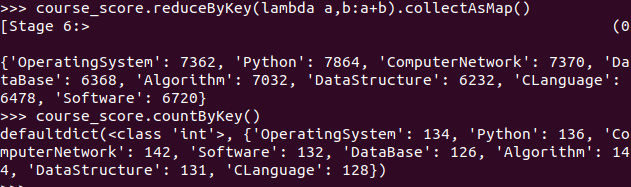
- 求每门课的选修人数及所有人的总分。combineByKey()
![]()
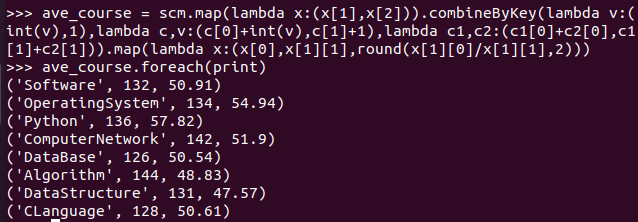
- 求每门课的选修人数及平均分,精确到2位小数。map(),round()
>>> ave_course = scm.map(lambda x:(x[1],x[2])).combineByKey(lambda v:(int(v),1),lambda c,v:(c[0]+int(v),c[1]+1),lambda c1,c2:(c1[0]+c2[0],c1[1]+c2[1])).map(lambda x:(x[0],x[1][1],round(x[1][0]/x[1][1],2)))
![]()
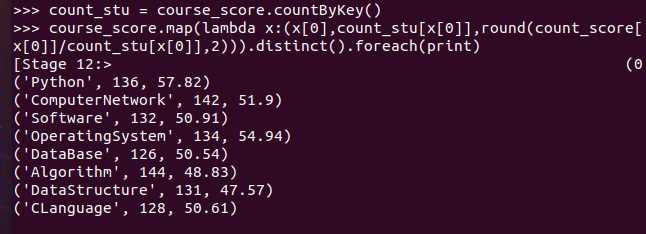
- 求每门课的选修人数及平均分。用reduceByKey()实现,并比较与combineByKey()的异同。
>>> count_stu = course_score.countByKey() >>> course_score.map(lambda x:(x[0],count_stu[x[0]],round(count_score[x[0]]/count_stu[x[0]],2))).distinct().foreach(print)
![]()
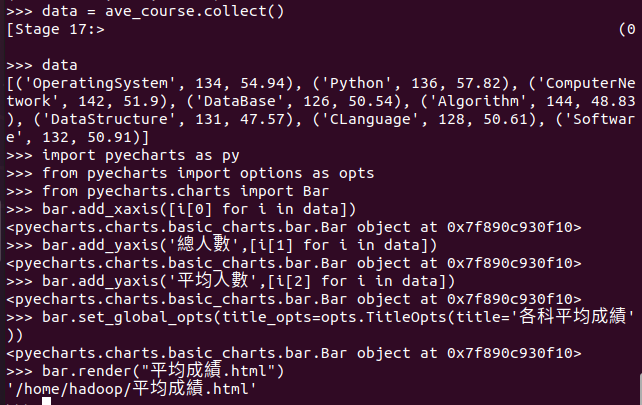
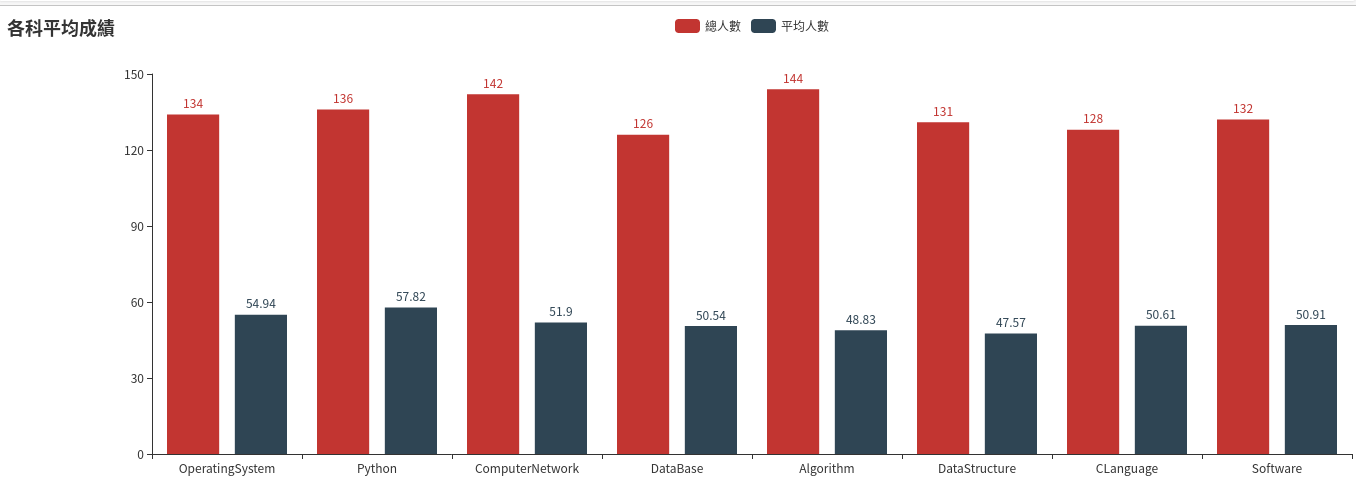
- 结果可视化。 pyecharts.charts,Bar()
>>> data = ave_course.collect() >>> data >>> import pyecharts as py >>> from pyecharts import options as opts >>> from pyecharts.charts import Bar >>> bar.add_xaxis([i[0] for i in data]) >>> bar.add_yaxis('總人數',[i[1] for i in data]) >>> bar.add_yaxis('平均人數',[i[2] for i in data]) >>> bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='各科平均成績')) >>> bar.render("平均成績.html") >>>
![]()
![]()
资源链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Hc9SxMLcsP9HVQLZ7eSVYA 提取码:tefr




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号