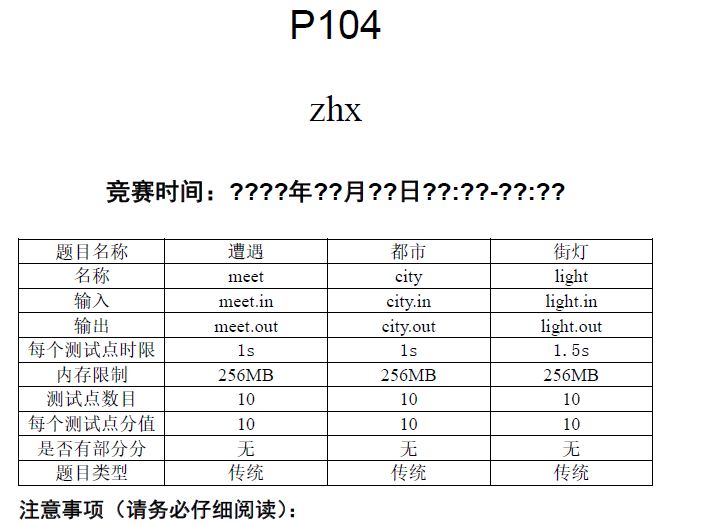
2017-10-29-morning-清北模拟赛
T1 遭遇


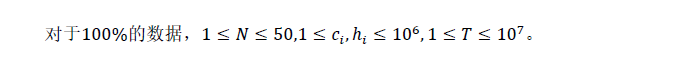

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 inline void read(int &x) 6 { 7 x=0; register char ch=getchar(); 8 for(; ch>'9'||ch<'0'; ) ch=getchar(); 9 for(; ch>='0'&&ch<='9'; ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; 10 } 11 const int T(1e7+5); 12 const int N(55); 13 int n,t,ans; 14 struct Node { 15 int h,c; 16 }a[N]; 17 18 bool cmp1(Node a,Node b) 19 { 20 return a.h<b.h; 21 } 22 bool cmp2(Node a,Node b) 23 { 24 return a.c<b.c; 25 } 26 27 bool fc,fh; 28 inline void Judge() 29 { 30 if(a[1].c) fc=1; 31 int pre=a[1].h; 32 for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i) 33 { 34 if(a[i].c) fc=1; 35 if(pre!=a[i].h) fh=1; 36 if(fc&&fh) return ; 37 } 38 } 39 40 inline void work1() 41 { 42 std::sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp1); 43 int pre=a[1].h;ans++; 44 for(int i=2; i<=n&&t>=abs(a[i].h-pre); ) 45 ans++,t-=abs(a[i].h-pre),pre=a[i++].h; 46 printf("%d\n",ans); 47 } 48 inline void work2() 49 { 50 std::sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp2); 51 for(int i=1; i<=n&&t>=a[i].c; ++i) 52 ++ans,t-=a[i].c; 53 printf("%d\n",ans); 54 } 55 56 bool vis[N]; 57 void DFS(int now,int cnt,int tt) 58 { 59 ans=ans>cnt?ans:cnt; 60 if(cnt==n+1) return ; 61 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) 62 { 63 if(vis[i]) continue; 64 if(tt+abs(a[i].h-a[now].h)+a[i].c>t) continue; 65 vis[i]=1; 66 DFS(i,cnt+1,tt+abs(a[i].h-a[now].h)+a[i].c); 67 vis[i]=0; 68 } 69 } 70 inline void work3() 71 { 72 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) 73 vis[i]=1,DFS(i,1,a[i].c),vis[i]=0; 74 printf("%d\n",ans); 75 } 76 77 int Presist() 78 { 79 freopen("meet.in","r",stdin); 80 freopen("meet.out","w",stdout); 81 // freopen("1.txt","r",stdin); 82 read(n); 83 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) read(a[i].c); 84 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) read(a[i].h); 85 Judge();read(t); 86 if(!fc) { work1(); return 0; } 87 if(!fh) { work2(); return 0; } 88 work3(); 89 return 0; 90 } 91 92 int Aptal=Presist(); 93 int main(int argc,char**argv){;}
贪心:以c为第一关键字,枚举跳楼的集合,可以发现对于一个集合里的楼房,高度的消耗为hmax-hmin(可以发现,从最高向最低或从最低向最高调最优,那么sum=h1-h2+h2-h3+h3-h4,设h1=hmax,h4=min),确定集合的最高最低楼房,n^3枚举

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 #define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b) 6 #define min(a,b) (a<b?a:b) 7 8 inline void read(int &x) 9 { 10 x=0; register char ch=getchar(); 11 for(; ch>'9'||ch<'0'; ) ch=getchar(); 12 for(; ch>='0'&&ch<='9'; ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; 13 } 14 const int T(1e7+5); 15 const int N(55); 16 int n,t,ans; 17 struct Node { 18 int h,c; 19 bool operator < (const Node&x)const 20 { 21 return c<x.c; 22 } 23 }a[N]; 24 25 int Presist() 26 { 27 freopen("meet.in","r",stdin); 28 freopen("meet.out","w",stdout); 29 // freopen("1.txt","r",stdin); 30 read(n); 31 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) read(a[i].c); 32 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) read(a[i].h); 33 read(t); std::sort(a+1,a+n+1); 34 for(int l=1; l<=n; ++l) 35 for(int r=l+1; r<=n; ++r) 36 { 37 int tot=t,tmp; 38 int max_=max(a[l].h,a[r].h); 39 int min_=min(a[l].h,a[r].h); 40 tot-=(max_-min_+a[l].c+a[r].c); 41 if(tot<0) continue; tmp=2; 42 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) 43 { 44 if(i==l||a[i].h>max_) continue; 45 if(i==r||a[i].h<min_) continue; 46 if(tot-a[i].c<0) continue; 47 tot-=a[i].c,tmp++; 48 } 49 ans=max(ans,tmp); 50 } 51 if(ans==0&&a[1].c<=t) ans=1; 52 printf("%d\n",ans); 53 return 0; 54 } 55 56 int Aptal=Presist(); 57 int main(int argc,char**argv){;}
DP: f[i][j]表示跳了i座楼房,现在在j号的最小花费,以h为第一关键字,确定当前楼房j,枚举下一个楼房,
在满足话费小于t的情况下,更新ans

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 4 const int N = 105; 5 6 struct Building 7 { 8 int h, c; 9 bool operator<(const Building &x)const 10 { 11 return h < x.h; 12 } 13 }B[N]; 14 int n,f[N][N]; 15 int main() 16 { 17 freopen("meet.in", "r", stdin); 18 freopen("meet.out", "w", stdout); 19 scanf("%d",&n); 20 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) 21 scanf("%d", &B[i].c); 22 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) 23 scanf("%d",&B[i].h); 24 int T;scanf("%d",&T); 25 std::sort(B,B+n); 26 int ans=0; 27 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) 28 if((f[1][i]=B[i].c)<=T) ans = 1; 29 for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i) 30 for(int j=0, minv = T + 1; j < n; ++j) 31 { 32 if((f[i][j]=minv+B[j].h+B[j].c)<=T) ans=i; 33 minv=std::min(minv,f[i-1][j]-B[j].h); 34 } 35 printf("%d\n",ans); 36 return 0; 37 }
T2 都市



设b1,b2,……,bn为一组答案,那么给出的n*(n-1)/2个数中,最小的一定等于b1+b2,
次小的一定等于b1+b3,为了确定b1 b2 b3我们还需要b2+b3的值。
由于b1+b4可能小于b2+b3,所以我们不能确定b2+b3的值,那么由于数据范围挺小的,枚举b2+b3是n*(n-1)/2中的哪一个就好了。
确定了b2+b3之后我们发现b1 b2 b3的值就都有了,然后b1+b4一定是剩下中最小的,依次类推一个一个解出剩下的数就搞定了。

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 4 inline void read(int &x) 5 { 6 x=0; register char ch=getchar(); 7 for(; ch>'9'||ch<'0'; ) ch=getchar(); 8 for(; ch>='0'&&ch<='9'; ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; 9 } 10 const int M(1e8+5); 11 const int N(323); 12 int now,t,it,vis[N*N]; 13 int n,m,a[N*N],b[N]; 14 int ans[N][N],cnt; 15 bool flag; 16 17 int Presist() 18 { 19 freopen("city.in","r",stdin); 20 freopen("city.out","w",stdout); 21 read(n),m=n*(n-1)>>1; 22 for(int i=1; i<=m; ++i) read(a[i]); 23 std:: sort(a+1,a+m+1); 24 for(int i=3; i<=n&&a[i]<a[1]+a[2]; ++i) 25 { 26 if((a[1]+a[2]-a[i])&1) continue; 27 if(i>3&&a[i] ==a[i-1]) continue; 28 b[1]=a[1]+a[2]-a[i]>>1; 29 b[2]=a[1]-b[1], b[3]=a[2]-b[1]; 30 vis[1]=vis[2]=vis[i]=i; 31 flag=1; now=1; 32 for(int j=4; j<=n; ++j) 33 { 34 for(; vis[now]==i; ) now++; 35 b[j]=a[now]-b[1]; 36 for(int t,k=1; k<j; ++k) 37 { 38 t=b[j]+b[k]; 39 it=std::lower_bound(a+1,a+m+1,t)-a; 40 for(; a[it]==t&&vis[it]==i; ) it++; 41 if(a[it]!=t) { flag=0; break; } 42 vis[it]=i; 43 } 44 if(!flag) break; 45 } 46 if(!flag) continue; cnt++; 47 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j) ans[cnt][j]=b[j]; 48 } 49 printf("%d\n",cnt); 50 for(int i=1; i<=cnt; ++i) 51 { 52 for(int j=1; j<n; ++j) 53 printf("%d ",ans[i][j]); 54 printf("%d\n",ans[i][n]); 55 } 56 return 0; 57 } 58 59 int Aptal=Presist(); 60 int main(int argc,char**argv){;}
T3 街灯


做法的核心思想是按p的大小分不同的做法,首先注意到p>10000是没有什么意义的,所以我们按照sqrt(10000)=100进行分块来做。
对于p<=100的,我们发现对于p<=100,总共的可能的询问也就只有100*(100-1)/2=4950种(p,v)的取值,所以我们可以预处理这一部分。
我们枚举一个p和一个v,对一个(p,v)开一个vector,将所有模p等于v的数全部放到这个vector里面来,那么每次询问的时候,只需要直接在这个vector里面二分区间内有多少个在这个vector里面即可。
对于p>100的,情况就比较多了没法预处理了,但是注意到可能被统计到答案里面的数,只有v,p+v,2p+v…………之类的数,这样可能的数只有sqrt(n)个,所以我们提前对每一个v开一个vector,把所有等于v的数全部放到这个vector里面。之后每一次询问的时候,我们去v,p+v,2p+v……这每一个vector里面二分即可。
这样总的复杂度就是O(nlognsqrt(n))了,就可以过了。vector常数比较大,也可以直接用数组或者链表实现。

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 inline void read(int &x) 8 { 9 x=0; register char ch=getchar(); 10 for(; ch>'9'||ch<'0'; ) ch=getchar(); 11 for(; ch>='0'&&ch<='9'; ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; 12 } 13 const int N(1e5+5); 14 const int V(10000); 15 16 vector<int>vc1[105][105],vc2[N]; 17 18 int a[N]; 19 20 int Presist() 21 { 22 freopen("light.in","r",stdin); 23 freopen("light.out","w",stdout); 24 int n,m; read(n),read(m); 25 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) 26 read(a[i]),vc2[a[i]].push_back(i); 27 for(int i=1; i<=100; ++i) 28 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j) 29 vc1[i][a[j]%i].push_back(j); 30 int L,R,L_,R_,Mid,ans; 31 for(int l,r,v,p; m--; ) 32 { 33 read(l),read(r),read(p),read(v); 34 if(p<=100) 35 { 36 L=0, R=vc1[p][v].size()-1; 37 for(L_=-1; L<=R; ) 38 { 39 Mid=L+R>>1; 40 if(vc1[p][v][Mid]>=l) 41 R=Mid-1,L_=Mid; 42 else L=Mid+1; 43 } 44 if(L_==-1) { puts("0"); continue; } 45 46 L=L_, R=vc1[p][v].size()-1; 47 for(R_=-1; L<=R; ) 48 { 49 Mid=L+R>>1; 50 if(vc1[p][v][Mid]<=r) 51 L=Mid+1, R_=Mid; 52 else R=Mid-1; 53 } 54 if(R_==-1) { puts("0"); continue; } 55 printf("%d\n",R_-L_+1); 56 } 57 else 58 { 59 ans=0; 60 for(int i=v; i<=V; i+=p) 61 { 62 vector<int>::iterator l_=lower_bound(vc2[i].begin(),vc2[i].end(),l); 63 vector<int>::iterator r_=upper_bound(vc2[i].begin(),vc2[i].end(),r); 64 ans+=r_-l_; 65 } 66 printf("%d\n",ans); 67 } 68 } 69 return 0; 70 } 71 72 int Aptal=Presist(); 73 int main(int argc,char**argv){;}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号