Mybatis学习笔记(一)-环境配置-语句查询
1.环境配置
创建一个项目后需要导入Mybaits的依赖,直接用MAVEN依赖就好
但是在POM文件中需要在build配置一个资源获取插件
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
要不会出现找不到配置文件的异常
2.Mybaits的代码结构
-
实体类
-
DAO接口
-
实现DAO接口的配置文件
-
主配置文件
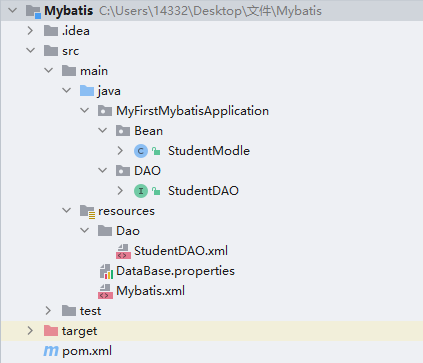
我的目录结构
3.实现第一个Mybatis程序
1.编写实体类
要求:
- 实体类成员变量要和数据库中字段保持一致
- 为成员变量实现GET/SET方法
数据库Student表

实体类:
package MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean;
public class StudentModle {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Integer age;
public StudentModle() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student记录{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2.编写DAO接口
要求:
- 需要使用实体类对象接收数据
package MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO;
import MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle;
public interface StudentDAO {
StudentModle SelectStudentinfo(Integer id);
}
3.编写对应的DAO配置文件
要求:
- 要引入DTD约束文件
- mapper中的namespace中填写对应接口的全限命名
- select中的id填写对应的方法名称
- resultType中填写对应的实体类的全限命名
- 在接口中定义的函数原型的参数用#{} 一 一对应起来
<!--#DTD约束文件-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--DAO配置-->
<mapper namespace="MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO">
<select id="SelectStudentinfo" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select * from student where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
4.配置主配置文件
-
environments
在编码中可能有不同的生产环境,比如在生产中使用的数据库和测试的数据库不一样,那么我们在指定环境时候将会用到下面的标签
-
environment
在这个标签内可以指定不同的数据库,使用id区分,那么有了数据库之后就有数据库事务方案有下面这个指定
-
transactionManager
一般是JDBC
-
dataSource
指定是否使用连接池 在里面property指定数据库的连接信息 那些name值是固定的
-
mappers
用于注册其他配置文件统一管理
<!--DTD约束文件-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--主配置文件设置-->
<configuration>
<!--选择环境-->
<environments default="development">
<!--环境ID-->
<environment id="development">
<!--事务解决方案-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc_test?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--对其它的配置文件的注册-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="Dao/StudentDAO.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
5.编写实现类
方法一:获取对应的Mapper,让映射器通过命名空间和方法名称找到对应的SQL
注意点:
- 使用接口类型接受sqlSession.getMapper(接口.class)
public void test1() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
//把配置文件信息加载到流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//读取配置信息,创建出工厂
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//创建出sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession对象=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取对应的Mapper,让映射器通过命名空间和方法名称找到对应的SQL,发送给数据库执行后返回结果
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
//动态代理对象
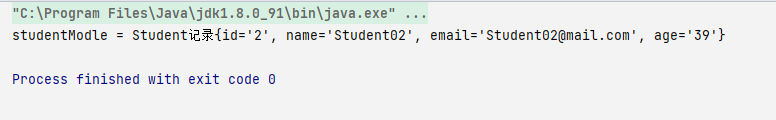
StudentModle studentModle= studentDAO.SelectStudentinfo(2);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
方法二:直接使用SqlSession,通过命名信息去执行SQL返回结果,该方式是IBatis版本留下的
注意点:
- SqlSession的指定是接口定义的方法名
- selectOne是SqlSession的方法,还有很多
public void test2() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 直接使用SqlSession,通过命名信息去执行SQL返回结果,该方式是IBatis版本留下的
String SQLID1="MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO.SelectStudentinfo";
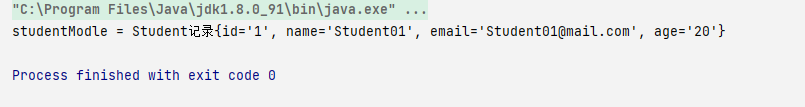
StudentModle studentModle= sqlSession.selectOne(SQLID1,1);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
执行结果
方法一
方法二
3.对其他查询结果的探究
1.多参数的查询
在StudentDAO中加入一个SelectStudentNameAndAge方法如下:
StudentModle SelectStudentNameAndAge(@Param(value = "name") String name,@Param(value = "age") Integer age);
在进行多个参数操作时需要绑定参数,使用@Param,里面的value = " "就代表了这个参数
在对应DAO配置文件中如下实现
- select中的id填写对应的方法名称
- resultType中填写对应的实体类的全限命名
- 参数使用#
<select id="SelectStudentNameAndAge" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select name,age from student where name=#{name} and age=#{age}
</select>
实现类:
// 测试多个参数的查询
public void test3() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
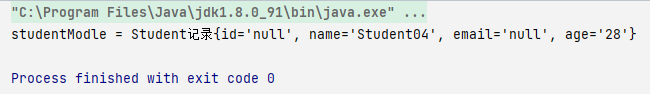
StudentModle studentModle= studentDAO.SelectStudentNameAndAge("Student04",28);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
结果
可以看到id email都没有赋值因为只查询了两个字段
对多条记录的查询
在StudentDAO中加入一个SelectAllStudentinfo()方法如下:
使用了LIst集合装返回的值,指定泛型为实体类
List<StudentModle> SelectAllStudentinfo();
对应DAO配置文件如下
<select id="SelectAllStudentinfo" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select * from student
</select>
实现类:
//获取多条数据
public void test4() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
List<StudentModle>FindAllinfos=studentDAO.SelectAllStudentinfo();
for (StudentModle studentModle:FindAllinfos) {
System.out.println(studentModle);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
结果:
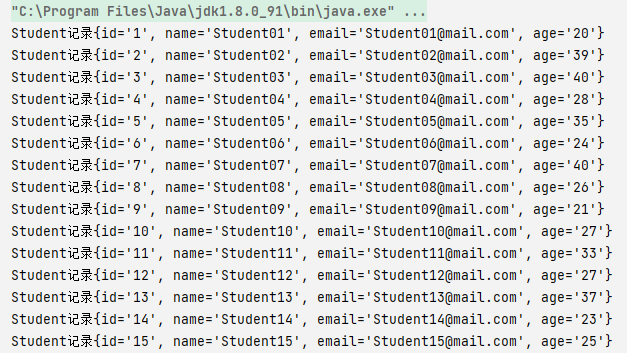
4.对如何创建出接口对象的思考
我们都知道接口要使用必须要有实现类,但是我并没有编写任何一个实现类,做的仅仅只是把接口对象的方法使用而已,那为什么呢?
我们先DEGUB一下看看
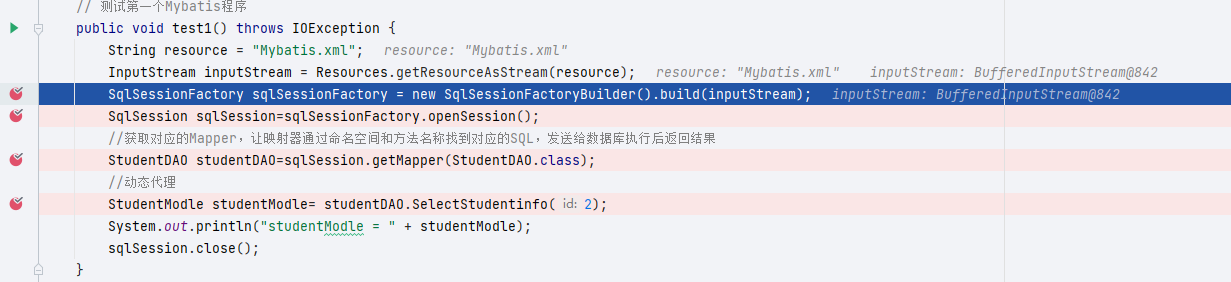
1我们看到流被创建出来了
2接着工厂被创建出来了
3接着Sqlsession出来了
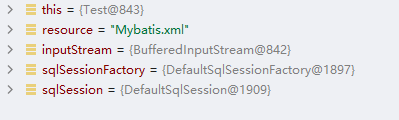
4接着发现了一个代理对象,看到接口对象被代理了
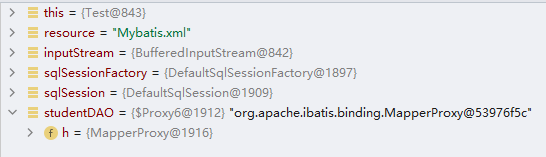
看见了接口对象被代理,再联想以接口为基础实现的代理技术,那就是JDK代理模式了
之前研究代理设计模式要有以下下要素
- 原始方法
- 实现原方法相同的接口
- 额外方法
那我们再分析JDBC代码,不难发现获取连接的代码,释放资源的代码是冗余的,那不同的DAO方法区别就在中间的那片代码,那这个像不像所谓的额外功能?
String dburl="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc_test?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=UTC";
String dbuser="root";
String dbpassword="atgxstuSf2<e";
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn =DriverManager.getConnection(dburl,dbuser,dbpassword);
Statement stat =conn.createStatement();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
String sqlString=
"select BOOKID,BOOKNAME,BOOKPRICE FROM T_book";
ResultSet rs =stat.executeQuery(sqlString);//结果集
while (rs.next()) {
String bookname =rs.getString("BOOKNAME");
String bookid =rs.getString("BOOKID");
String bookprice =rs.getString("BOOKPRICE");
System.out.println(bookid+""+bookname+""+bookprice);
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
rs.close();
stat.close();
conn.close();
}
}
那么原始方法呢?
不就是获取连接的代码,释放资源的代码
再看是否实现原方法相同的接口?
参考了https://www.cnblogs.com/demingblog/p/9544774.html#mapper接口的动态代理类的生成 的源码分析
看到了如下代码
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { //映射器代理工厂
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
// 删除部分代码,便于阅读
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//使用了JDK自带的动态代理生成映射器代理类的对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(否实现原方法相同的接口
mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),//--->传入了原方法相同的接口
new Class[] { mapperInterface },
mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
那问题也就大致解答了
那么继续观察对应接口的配置文件
<mapper namespace="MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO">
<select id="SelectStudentinfo" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select * from student where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
namespace指定了接口
id指定了方法
resultType指定了结果接受的对象(可以抽象到JDBC的那个while这段取数据的操作)
还指定了SQL语句
这些信息足够生成一个原始方法了还有额外功能
这样就解释了为什么Mybaits凭什么就一个配置文件能做出许多方法来,还不带实现类的。
5.完整代码
接口:
package MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO;
import MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDAO {
StudentModle SelectStudentinfo(Integer id);
StudentModle SelectStudentNameAndAge(@Param(value = "name") String name,@Param(value = "age") Integer age);
List<StudentModle> SelectAllStudentinfo();
}
对应配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO">
<select id="SelectStudentinfo" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select * from student where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="SelectStudentNameAndAge" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select name,age from student where name=#{name} and age=#{age}
</select>
<select id="SelectAllStudentinfo" resultType="MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle">
select * from student
</select>
</mapper>
测试类:
import MyFirstMybatisApplication.Bean.StudentModle;
import MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
// 测试第一个Mybatis程序
public void test1() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取对应的Mapper,让映射器通过命名空间和方法名称找到对应的SQL,发送给数据库执行后返回结果
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
//动态代理
StudentModle studentModle= studentDAO.SelectStudentinfo(2);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
@org.junit.Test
// 测试第一个Mybatis程序得不同实现方式
public void test2() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 直接使用SqlSession,通过命名信息去执行SQL返回结果,该方式是IBatis版本留下的
String SQLID1="MyFirstMybatisApplication.DAO.StudentDAO.SelectStudentinfo";
StudentModle studentModle= sqlSession.selectOne(SQLID1,1);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
@org.junit.Test
// 测试多个参数的查询
public void test3() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
StudentModle studentModle= studentDAO.SelectStudentNameAndAge("Student04",28);
System.out.println("studentModle = " + studentModle);
sqlSession.close();
}
@org.junit.Test
//获取多条数据
public void test4() throws IOException {
String resource = "Mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDAO studentDAO=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDAO.class);
List<StudentModle>FindAllinfos=studentDAO.SelectAllStudentinfo();
for (StudentModle studentModle:FindAllinfos) {
System.out.println(studentModle);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
}





