Codeforces 512D. Fox And Travelling 题解
Fox And Travelling
题面翻译
- 给定一张
- 一个点只有当与它直接相连的点中最多只有一个点未被选择过时才可被选择。
- 询问对于每个
题目描述
Fox Ciel is going to travel to New Foxland during this summer.
New Foxland has
There is one important rule in New Foxland: you can't visit an attraction if it has more than one adjacent attraction that you haven't visited yet.
At the beginning Fox Ciel haven't visited any attraction. During her travelling she may move aribtrarly between attraction. After visiting attraction
She wants to know how many different travelling plans she can make. Calculate this number modulo
输入格式
First line contains two integers: 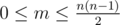 ), the number of attractions and number of undirected roads.
), the number of attractions and number of undirected roads.
Then next
输出格式
Output
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3 2
1 2
2 3
样例输出 #1
1
2
4
4
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
4 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
样例输出 #2
1
0
0
0
0
样例 #3
样例输入 #3
12 11
2 3
4 7
4 5
5 6
4 6
6 12
5 12
5 8
8 9
10 8
11 9
样例输出 #3
1
6
31
135
483
1380
3060
5040
5040
0
0
0
0
样例 #4
样例输入 #4
13 0
样例输出 #4
1
13
156
1716
17160
154440
1235520
8648640
51891840
259459200
37836791
113510373
227020746
227020746
提示
In the first sample test for
In the second sample test Ciel can't visit any attraction in the first day, so for
In the third sample test Foxlands look like this:

题目
给定一张 n 个点 m 条边的无向图。一个点只有当与它直接相连的点中最多只有一个点未被遍历过时才可被遍历。询问对于每个 k ∈ [0, n],遍历 k 个点的方案数。约束条件如下:
- n ≤ 100
- m ≤ (n-1)^2
- 答案对 10^9 + 9 取模
题解
首先,在环中的点一定不会被遍历。
用类似拓扑排序的过程可以把环上的点全部扔掉,剩下的点会构成若干个有根树和无根树,其中有根树的根是树中唯一与环中的点相连的点。
每棵树求出答案后,01 背包合并即可,中间只需要乘上一个组合数。
对于有根树,设 fi,j 为 i 的子树中选 j 个的方案数,那么就是树上背包,同样需要乘上一个组合数。
对于无根树,以树中每个点为根做一次有根树的树上背包,这样会发现每种选择 i 个点的方案会被多算 s-i 次,其中 s 为这棵无根树的大小,那么除掉即可。
总时间复杂度 O(n^3),其中背包经过了上下界优化,原理简单来说就是「每对点只会在 LCA 处合并一次」。
、
const int N = 107;
int n, m, d[N], w[N], b[N], s[N], S;
vi e[N];
modint p[N], v[N], vp[N], f[N][N], ans[N];
inline modint C(int a, int b) {
return p[a] * vp[b] * vp[a-b];
}
void dfs(int x, int o, int &s) {
b[x] = o, ++s;
for (ui i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++) {
int y = e[x][i];
if (!d[y] && !b[y]) dfs(y, o, s);
}
}
void dp(int x, int fa) {
s[x] = 1, f[x][0] = 1;
for (ui i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++) {
int y = e[x][i];
if (b[x] != b[y] || y == fa) continue;
dp(y, x);
for (int j = 0; j < s[y]; j++) f[x][s[x]+j] = 0;
for (int j = s[x] - 1; ~j; j--)
for (int k = 1; k <= s[y]; k++)
f[x][j+k] += f[x][j] * f[y][k] * C(j + k, j);
s[x] += s[y];
}
f[x][s[x]] = f[x][s[x]-1];
}
void get(int x) {
dp(x, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= s[x]; i++) f[0][i] += f[x][i];
}
int main() {
rd(n), rd(m);
p[0] = v[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = p[i-1] * i;
vp[n] = p[n] ^ -1;
for (int i = n; i; i--) v[i] = p[i-1] * vp[i], vp[i-1] = vp[i] * i;
for (int i = 1, x, y; i <= m; i++) rd(x), rd(y), e[x].pb(y), e[y].pb(x), ++d[x], ++d[y];
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (d[i] <= 1) w[i] = 1, q.push(i);
while (q.size()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (ui i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++) {
int y = e[x][i];
if (--d[y] <= 1 && !w[y]) w[y] = 1, q.push(y);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (d[i] == 1) dfs(i, i, s[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (!d[i] && !b[i]) dfs(i, i, s[i]);
ans[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (i == b[i]) {
int o = s[i];
if (d[i] == 1) get(i);
else {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (b[j] == i) get(j);
for (int j = 0; j <= o; j++) f[0][j] *= v[o-j];
}
for (int j = S; ~j; j--)
for (int k = 1; k <= o; k++)
ans[j+k] += ans[j] * f[0][k] * C(j + k, j);
for (int j = 0; j <= o; j++) f[0][j] = 0;
S += o;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) print(ans[i]);
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!