浅谈Apache Shiro CVE-2023-22602
一、漏洞描述
Apache Shiro 是一个可执行身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理的 Java 安全框架。
由于 1.11.0 及之前版本的 Shiro 只兼容 Spring 的ant-style路径匹配模式(pattern matching),且 2.6 及之后版本的 Spring Boot 将 Spring MVC 处理请求的路径匹配模式从AntPathMatcher更改为了PathPatternParser,当 1.11.0 及之前版本的 Apache Shiro 和 2.6 及之后版本的 Spring Boot 使用不同的路径匹配模式时,攻击者访问可绕过 Shiro 的身份验证。
- 影响范围
- org.apache.shiro:shiro-web@[1.0.0-incubating, 1.11.0)
- shiro@影响所有版本
二、相关分析
2.1 AntPathMatcher跟PathPattern
根据对应漏洞的描述,先简单看看Spring MVC两个处理请求的路径匹配模式:AntPathMatcher&PathPatternParser(根据官方文档的描述:Parser for URI path patterns producing PathPattern instances that can then be matched to requests.所以实际上需要关注的是PathPattern)。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration是Spring Boot中关于Spring MVC自动配置类,对比下2.6之前之后的两个版本,可以发现2.6及之后版本多了个PathPatternParser的实现:
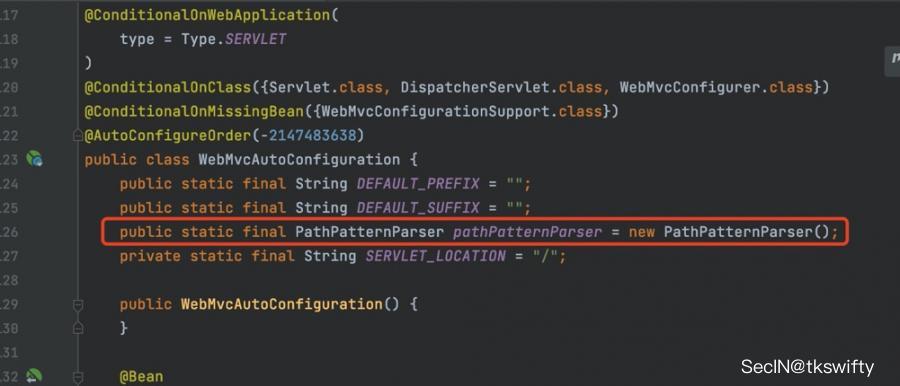
此外,WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置类中包含了一个静态类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter,通过这里加载的WebMvcProperties内容也可以看出来2.6前后版本具体的差异:
- 在 2.6之前,默认使用的是AntPathMatcher(具体配置在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcProperties.Pathmatch),查看具体的代码:
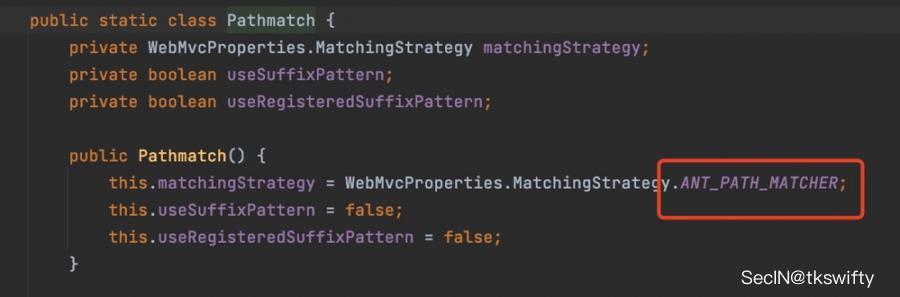
- 2.6.0及之后就变成了PathPattern了,具体代码如下
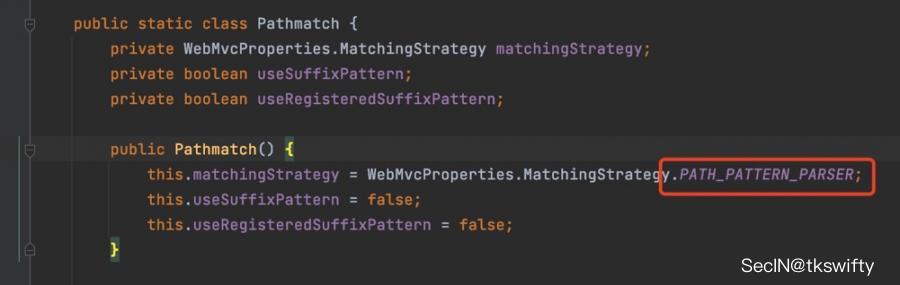
下面看看两者具体有什么区别:
2.1.1 AntPathMatcher
AntPathMatcher所属模块为spring-core,对应classorg.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher。一般用于类路径、文件系统和其它资源的解析。
查看官方文档,可以知道AntPathMatcher支持的Path匹配规则如下:
| ? | 匹配任意单字符 |
|---|---|
| * | 匹配0或者任意数量的字符 |
| ** | 匹配0或者任意层级的目录 |
| {spring:正则表达式} | 匹配到的path内容赋值给spring变量 |
2.1.2 PathPattern
PathPattern是Spring5新增的API,所属模块为spring-web,对应class org.springframework.web.util.pattern.PathPattern。
查看官方文档描述:
Representation of a parsed path pattern. Includes a chain of path elements for fast matching and accumulates computed state for quick comparison of patterns.
PathPattern matches URL paths using the following rules:
?matches one character*matches zero or more characters within a path segment**matches zero or more path segments until the end of the path{spring}matches a path segment and captures it as a variable named "spring"{spring:[a-z]+}matches the regexp[a-z]+as a path variable named "spring"{*spring}matches zero or more path segments until the end of the path and captures it as a variable named "spring"
Note: In contrast to AntPathMatcher, ** is supported only at the end of a pattern. For example /pages/{} is valid but /pages/{}/details is not. The same applies also to the capturing variant {*spring}. The aim is to eliminate ambiguity when comparing patterns for specificity.
根据官方文档的描述,其实 跟AntPathMatcher匹配规则区别不大,PathPattern在保持其匹配规则的基础上,新增了 {*spring} 的语法支持。
{*spring}表示匹配余下的path路径部分并将其赋值给名为spring的变量(变量名可以根据实际情况随意命名,与@PathVariable名称对应即可),例如如下例子:
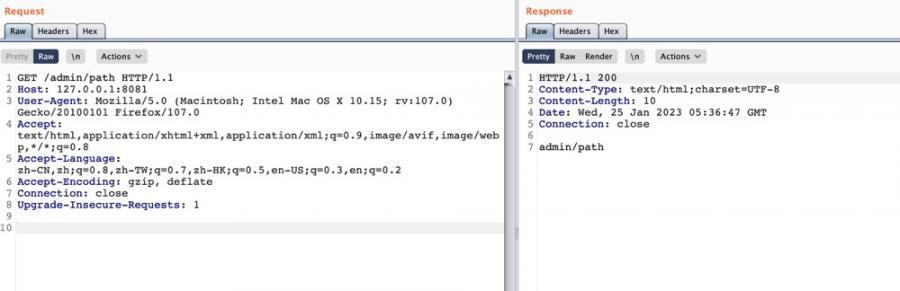
@GetMapping("/admin/{*path}")
public String adminBypass(@PathVariable String path) {
System.out.println(path);
return "admin"+path;
}
变量path获取的内容为/path:
同时, {*spring} 是可以匹配剩余所有path的,类似 /** ,只是功能更强,可以获取到这部分动态匹配到的内容。
同样是上面的例子,可以看到 {*spring} 成功获取了对应的内容:
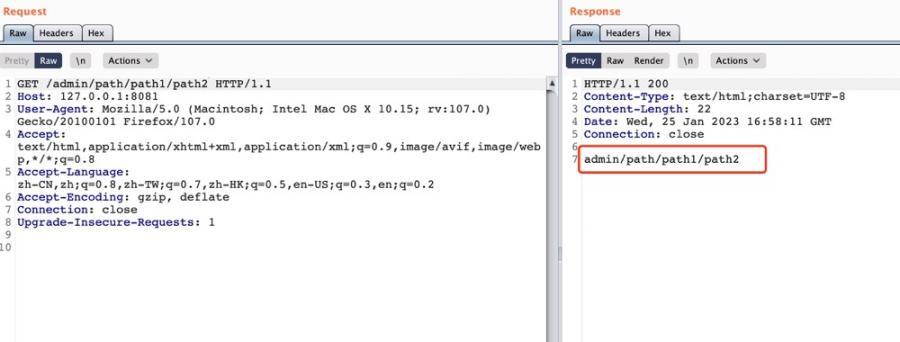
2.1.3 两者的区别
首先,PathPattern新增{*spring}语法支持,功能更加的强大
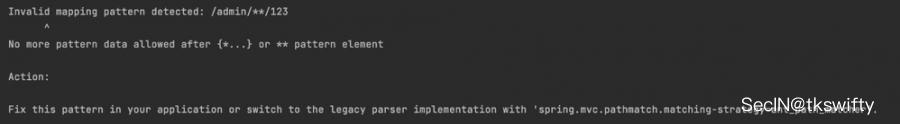
PS:这里做一个额外的测试,在设置spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy = ant_path_matcher基础上,尝试注册{*spring} ,可以看到抛出了异常,并建议使用PathPattern模式。

除此以外,相比AntPathMatcher,还有以下区别:
- PathPattern通配符只能定义在尾部,而AntPathMatcher可以在中间:
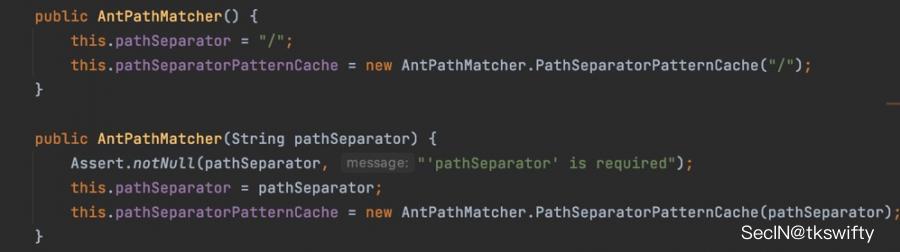
- AntPathMatcher默认使用
/作为分隔符。也可以根据实际情况自行指定分隔符(例如windows是\,Linux是/,包名是.),这点从其构造器可以看出:
因为PathPattern的构造器不是public的,只能通过PathPatternParser创建其实例,这里构造方法初始化了pathOptions变量:

查看Options.HTTP_PATH,可以看到跟AntPathMatcher一样,默认使用/作为分隔符:
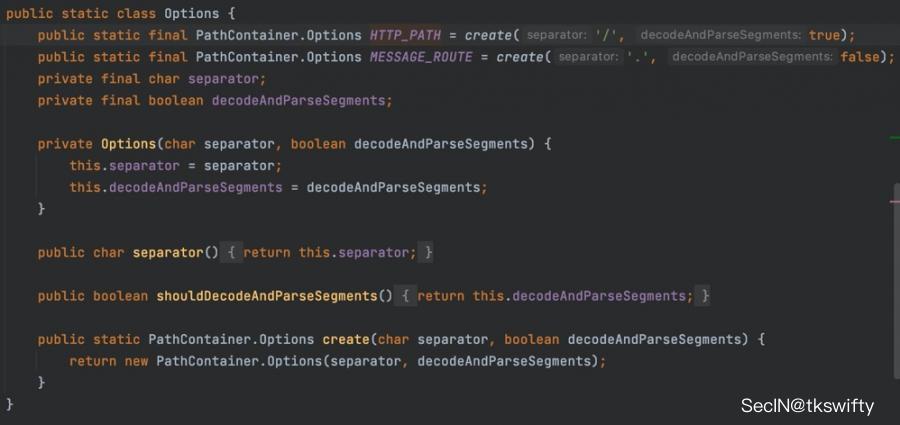
但是 PathPattern只支持两种分隔符(/和.) 。
三、复现过程
在Shiro中,ShiroFilter 是整个 Shiro 的入口点,用于拦截需要安全控制的请求进行处理。使用filterChainDefinitions(filterChainDefinitions是Shiro连接约束配置,通过对应的参数定义权限相关的filter Chain,验证顺序是自上而下,从左往右)声明url和filter对应的权限控制关系。
常见的filterChainDefinitions参数如下:
| 参数 | 对应的Filter | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| 身份验证相关 | ||
| authc | org.apache.shiro.web.filter. authc.FormAuthentication Filter | 表示需要认证通过后才可以访问 |
| logout | org.apache.shiro.web.filter. authc.LogoutFilter | 表示退出成功后重定向的地址 |
| anon | org.apache.shiro.web.filter. authc.AnonymousFilter | 表示可以非登陆状态下匿名使用,一般静态资源和登陆接口会用到比较多 |
| 授权相关 | <br/> | <br/> |
| roles | org.apache.shiro.web.filter. authz.RolesAuthorizationF ilter | 表示必须拥有相关角色才可以访问 |
| perms | org.apache.shiro.web.filter. authz.PermissionsAuthoriz ationFilter | 表示必须拥有相关权限 |
这里使用注解的方式,通过Shiro的Filter工厂,设置对应的过滤条件和跳转条件:
@Bean
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterConfiguration shiroFilterConfiguration = new ShiroFilterConfiguration();
shiroFilterConfiguration.setStaticSecurityManagerEnabled(true);
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
bean.setShiroFilterConfiguration(shiroFilterConfiguration);
bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager());
bean.setLoginUrl("/login");
bean.setSuccessUrl("/index");
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauthorizedurl");
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("/doLogin", "anon");
map.put("/admin/*", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return bean;
}
相关的路由Controller:
@GetMapping("/admin/page")
public String admin() {
return "admin page";
}
@GetMapping("/admin/{*path}")
public String adminBypass(@PathVariable String path) {
System.out.println(path);
return "admin Bypass page";
}
根据上面filterChainDefinitions的配置,当访问/admin/下的目录时,如果没有认证通过,会重定向到login页面:
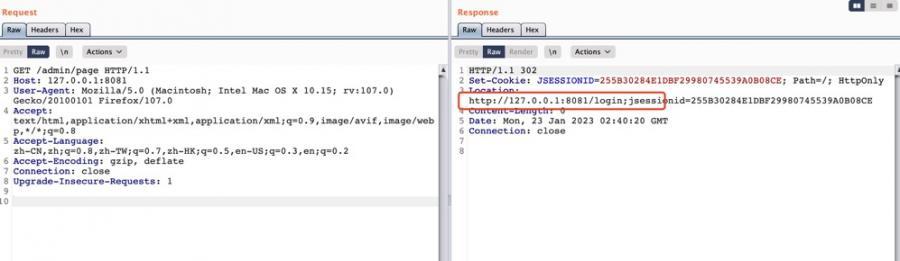
根据前面的分析,同样的,路由/admin/{*path}正常情况下也覆盖了:
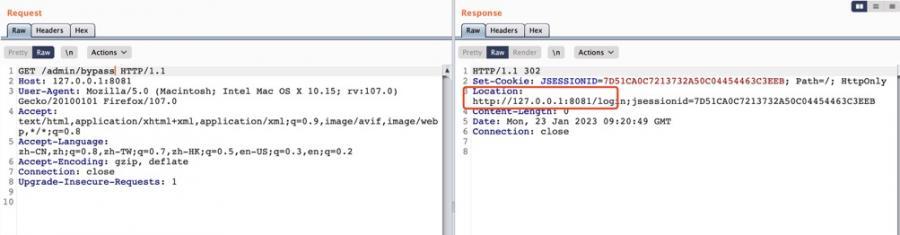
根据前面的分析,实际上, {*spring} 是可以匹配剩余所有path的,类似 /** ,只是功能更强,可以获取到这部分动态匹配到的内容。
结合这一点,因为1.11.0 及之前版本的 Shiro 只兼容 Spring 的ant-style路径匹配模式(pattern matching),而/admin/*只能匹配他的下级目录,结合两种模式的区别在特定场景下可以绕过了对应的权限控制:
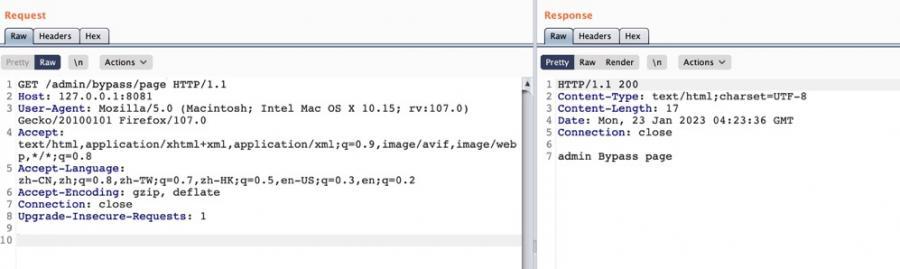
除此之外,应该还有其他的绕过场景,欢迎师傅们讨论。
对比下shiro1.11.0跟1.10.1的改动,可以发现主要是通过Spring动态的读取文件留下的扩展接口来将路径匹配模式修改为 AntPathMatcher :
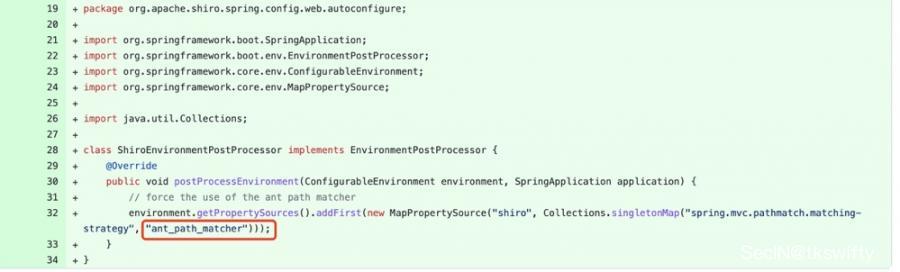
这里简单的做下测试,将shiro版本修改成1.11.0:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.11.0</version>
</dependency>
同样的尝试访问/admin/{*path}接口,此时返回500异常:
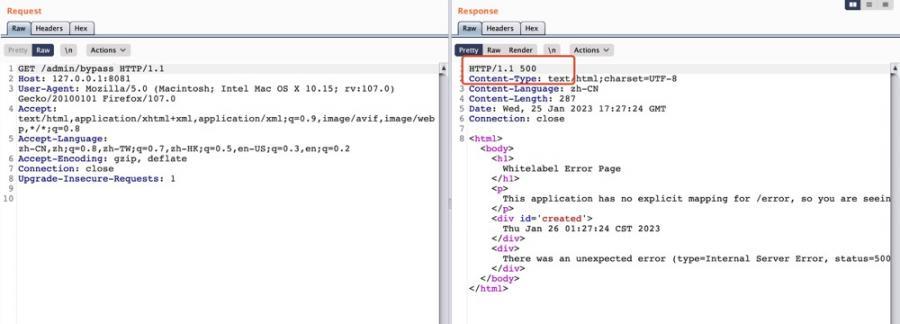
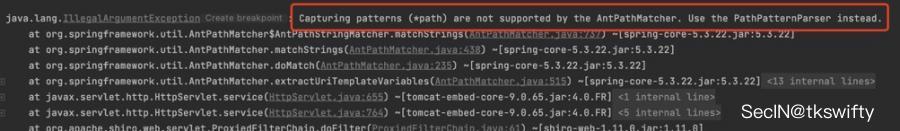
查看对应的Exception日志,可以看到提示AntPathMatcher不支持{*path}这种方式,说明已经切换路径匹配模式为 AntPathMatcher 了:
四、修复建议
- 升级到 1.11.0 或更高版本
- 开发者可通过修改 Spring boot 的路径匹配模式为 AntPathMatcher 缓解此漏洞:
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy = ant_path_matcher

 Apache Shiro 是一个可执行身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理的 Java 安全框架。
Apache Shiro 是一个可执行身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理的 Java 安全框架。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号