12 IO流(九)——装饰流 BufferedInputStream/OutputStream
我们按功能可以将IO流分为节点流与处理流
节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
处理流(装饰流):不直接连接到数据源或目的地,是其他流(必须包含节点流)进行封装。目的主要是简化操作和提高性能。
Buffered流的引入
当我们使用节点流来传输数据时,节点流单次传输的数据太少,会频繁读写硬盘,这使得整体速度不高,就像蚂蚁搬家。
这时我们引入处理流Buffered流,就好像找来一辆卡车来搬家,单次运输的数据多了,访问硬盘的次数少了,速度得到提升。
copy文件示例
不引入Buffered流copy一个600m的文件,计算它所花费的时间,此节点流的缓冲区大小为1024B
import java.io.*;
public class IOTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//文件源
String src = "1.rar";
String dest = "1_cp.rar";
//计算copy花费的时间
long l1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
copy(src,dest);
long l2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long time = l2-l1;
System.out.println(time);
}
public static void copy(String srcPath,String destPath){
//选择流
//操作
try(InputStream is = new FileInputStream(srcPath);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(destPath)){
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = is.read(flush))!=-1){//读入
os.write(flush,0,len);//写出
}
os.flush();//刷新
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出时间(cmd中):
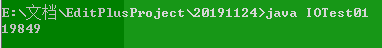
输出时间(Eclipse中):
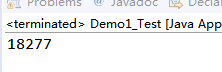
引入Buffered流 重点
引用Buffered流包装的方法一
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
输出流同理
引用Buffered流包装的方法二
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
输出流同理
其它
Buffered流无需放在最外层,只需要保证它在节点流外层即可。
包装后的copy的时间花费
copy 600MB文件,缓冲区为byte[1024]情况下:
在Eclipse中
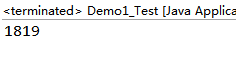
甚至在Eclipse中多运行几次后时间也变长了:

这是为什么???
在cmd中
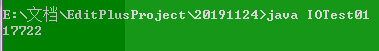
为何差别这么大????
提出问题
设想不引用Buffered流,直接修改字节流的缓冲池大小,看能不能提高速度(600MB的文件):
当缓冲池大小为byte[1024*1000]花费的时间为:

当缓冲池大小为byte[1024*100]花费的时间为:
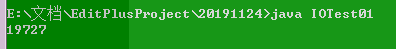
当缓冲池大小为byte[1024*50]花费的时间为:
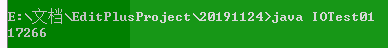
当缓冲池大小为byte[1024*20]花费的时间为:
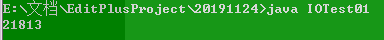
当缓冲池大小为byte[1024*8]花费的时间为:
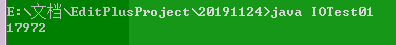
可见缓冲区大小与花费时间不成规律,这究竟是怎么回事呢?
完整代码
import java.io.*;
public class IOTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//文件源
String src = "1.rar";
String dest = "1_cp.rar";
//计算copy花费的时间
long l1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
copy(src,dest);
long l2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long time = l2-l1;
System.out.println(time);
}
public static void copy(String srcPath,String destPath){
//选择流
//操作
try(InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath))){
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = is.read(flush))!=-1){//读入
os.write(flush,0,len);//写出
}
os.flush();//刷新
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

