Java 把一个文本文档的内容复制到另一个文本文档
src.txt放在工程目录下,dest.txt可创建,也可不创建。一旦运行程序,如果dest.txt不存在,将自行创建这个文本文档,再将src.txt中的内容复制到dest.txt
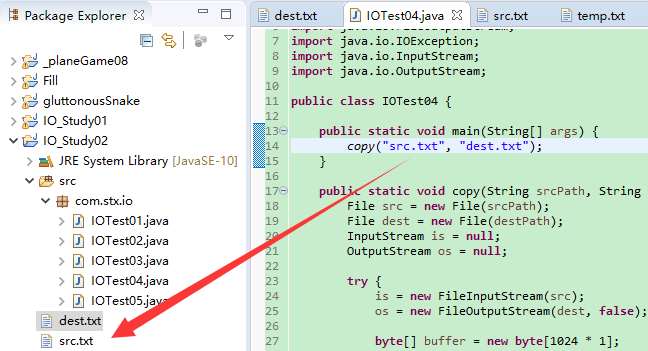
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStream; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 9 public class IOTest04 { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 copy("src.txt", "dest.txt"); 13 } 14 15 public static void copy(String srcPath, String destPath) { 16 File src = new File(srcPath); 17 File dest = new File(destPath); 18 InputStream is = null; 19 OutputStream os = null; 20 21 try { 22 is = new FileInputStream(src); 23 os = new FileOutputStream(dest, false); 24 25 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1]; // 1k bytes 26 int length = -1; 27 while ((length = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { 28 os.write(buffer, 0, length); 29 os.flush(); 30 } 31 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 try { 37 if (os != null) { 38 os.close(); 39 System.out.println("OutputStream Closed."); 40 } 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 try { 45 if (is != null) { 46 is.close(); 47 System.out.println("InputStream Closed."); 48 } 49 } catch (IOException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
读取文本文档A中的内容,先进行“加密”,将加密的内容写入到另一个文本文档B;完成加密和写入之后,再将文本文档B中(已加密)的内容复制、并覆盖文本文档A中原本的内容,删除文本文档B。
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStream; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 9 public class Encrypt { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 encrypt("src.txt", 1); 13 } 14 15 public static void encrypt(String srcPath, int password) { 16 File src = new File(srcPath); 17 File dest = new File(src.getParent(), ("temp" + src.getName())); 18 InputStream is = null; 19 OutputStream os = null; 20 21 try { 22 is = new FileInputStream(src); 23 os = new FileOutputStream(dest); 24 25 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1]; // 1k bytes 26 int length = -1; 27 while ((length = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { 28 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 29 buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] + password); 30 } 31 os.write(buffer, 0, length); 32 os.flush(); 33 } 34 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } catch (IOException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } finally { 39 try { 40 if (os != null) { 41 os.close(); 42 } 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 try { 47 if (is != null) { 48 is.close(); 49 } 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 } 54 55 try { 56 is = new FileInputStream(dest); 57 os = new FileOutputStream(src); 58 59 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1]; // 1k bytes 60 int length = -1; 61 while ((length = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { 62 os.write(buffer, 0, length); 63 os.flush(); 64 } 65 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } catch (IOException e) { 68 e.printStackTrace(); 69 } finally { 70 try { 71 if (os != null) { 72 os.close(); 73 } 74 } catch (IOException e) { 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 try { 78 if (is != null) { 79 is.close(); 80 } 81 } catch (IOException e) { 82 e.printStackTrace(); 83 } 84 } 85 86 dest.delete(); 87 } 88 }
文本文档A中的内容:

对每一个字符执行+1(实际就是将字符所对应的编码进行+1)的操作,之后变成:
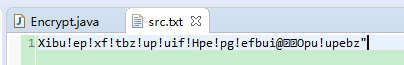
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
分解一
16 File src = new File(srcPath); 17 File dest = new File(src.getParent(), ("temp" + src.getName()));
getParent() - 返回此抽象路径名父目录的路径名字符串;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null。
getName() - 返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称。
绝对路径名的定义与系统有关。在 UNIX 系统上,如果路径名的前缀是 "/",那么该路径名是绝对路径名。在 Microsoft Windows 系统上,如果路径名的前缀是后跟 "\\" 的盘符,或者是 "\\\\",那么该路径名是绝对路径名。
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class IO_Test01 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 File src = null; 7 File dest = null; 8 9 // Relative path 10 src = new File("src.txt"); 11 dest = new File(src.getParent(), ("temp" + src.getName())); 12 13 System.out.println("Is absolute path: " + src.isAbsolute()); 14 System.out.println("src's parent: " + src.getParent()); 15 System.out.println("src's name: " + src.getName()); 16 17 System.out.println("dest's parent: " + dest.getParent()); 18 System.out.println("dest's name: " + dest.getName()); 19 System.out.println("--------"); 20 21 // Absolute path 22 src = new File("E:/Java/workspace/IO_Study02/src.txt"); 23 dest = new File(src.getParent(), ("temp" + src.getName())); 24 25 System.out.println("Is absolute path: " + src.isAbsolute()); 26 System.out.println("src's parent: " + src.getParent()); 27 System.out.println("src's name: " + src.getName()); 28 29 System.out.println("dest's parent: " + dest.getParent()); 30 System.out.println("dest's name: " + dest.getName()); 31 } 32 }
输出结果:
Is absolute path: false src's parent: null src's name: src.txt dest's parent: null dest's name: tempsrc.txt -------- Is absolute path: true src's parent: E:\Java\workspace\IO_Study02 src's name: src.txt dest's parent: E:\Java\workspace\IO_Study02 dest's name: tempsrc.txt
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
分解二
25 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1]; // 1k bytes 26 int length = -1; 27 while ((length = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { 28 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 29 buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] + password); 30 } 31 os.write(buffer, 0, length); 32 os.flush(); 33 }
其中的28~30行很好理解,这里不解释。
关键在于方法read(byte[] b)、write(byte[] b, int off, int len)。
public int read(byte[] b) - 从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。在某些输入可用之前,此方法将阻塞。返回:读入缓冲区的字节总数,如果因为已经到达文件末尾而没有更多的数据,则返回 -1。
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 7 public class IO_Test01 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 File src = new File("E:/Java/workspace/IO_Study02/src.txt"); 11 InputStream is = null; 12 13 try { 14 is = new FileInputStream(src); 15 16 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1]; // 1k bytes 17 int length = -1; 18 int times = 0; 19 while ((length = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { 20 ++times; 21 System.out.println("length: " + length); 22 System.out.println("times: " + times); 23 } 24 System.out.println("length: " + length); 25 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } finally { 30 try { 31 if (is != null) { 32 is.close(); 33 } 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 }
输出结果:
length: 47 times: 1 length: -1
length = 47,代表从src.txt中读取到的字节数,也就是有read()返回的。
times = 1,表示while()循环只执行了一次。
length = -1,是while()执行第二次判断,因为src.txt中的内容已经读取完毕了,所以read()返回-1。
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) - 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此文件输出流。参数:b - 数据。 off - 数据中的起始偏移量。 len - 要写入的字节数。
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
分解三
功力不够深厚,理解不了,写不出!!!
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
分解X
86 dest.delete();
public boolean delete() - 删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录。如果此路径名表示一个目录,则该目录必须为空才能删除。返回: 当且仅当成功删除文件或目录时,返回 true;否则返回 false
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
总结:待完善、纠错。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号