- 构造函数的基本应用
-
1 package cn.sasa.demo1;
2
3 public class Computer {
4
5 //构造函数,可以在创建对象时,为一些变量给定初始值
6 //如果不写构造函数,编译时默认会添加一个空参的构造函数
7 //public Computer() {}
8
9 //如果写了构造函数,那么编译时不会再添加空参的构造函数
10 //在new对象时,因为没有空参的构造函数,所以在new的时候,必须调用有参的构造函数
11 public Computer(String name) {
12 this.name = name;
13 }
14
15 //构造函数可以重载
16 public Computer(String name, double price) {
17 this.name = name;
18 this.price = price;
19 }
20
21 //构造函数可以为成员变量赋值,但只有在new的时候执行一次,之后不会再执行
22 //所以还需要get和set方法,使这之后还可以修改变量值。
23 private String name;
24 public String getName() {
25 return this.name;
26 }
27 public void setName(String name) {
28 this.name = name;
29 }
30
31 private double price;
32 public double getPrice() {
33 return this.price;
34 }
35 public void setPrice(double price) {
36 this.price = price;
37 }
38
39 }
1 package cn.sasa.demo1;
2
3 public class Test {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 //因为没有空参的构造函数,所以必须调用有参的构造函数。
6 //new的"()",就是在调用构造函数
7 Computer com = new Computer("华硕");
8 System.out.println(com.getName() + "======" + com.getPrice());
9 com.setName("联想");
10 System.out.println(com.getName());
11
12 Computer com1 = new Computer("宏基" , 5000);
13 System.out.println(com1.getName() + "======" + com1.getPrice());
14 }
15 }
- this()和super()
- this()调用的是本类的构造函数,super()调用的是父类的构造函数
- this()和super()在同一个构造方法中必须只有其中一个,并且放在第一行
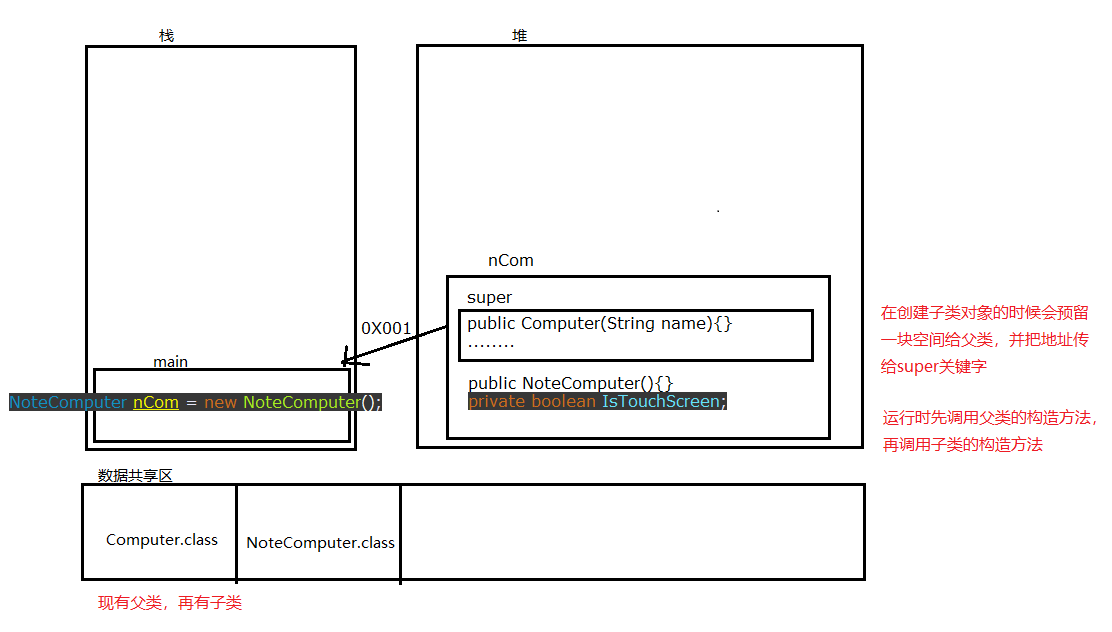
1 package cn.sasa.demo1;
2
3 public class NoteComputer extends Computer{
4 public NoteComputer() {
5 //子类继承父类,在构造函数的第一行默认添加了super()
6 //但是父类重写了构造方法,没有空参的构造方法,就会报错
7 //解决方法是用super()调用父类的其中一个构造方法
8 super("");
9 }
10
11 public NoteComputer(boolean isTouch) {
12 //this()调用的是本类的构造方法
13 this();
14 this.IsTouchScreen = isTouch;
15 }
16
17 private boolean IsTouchScreen;
18
19 public boolean getIsTouchScreen() {
20 return this.IsTouchScreen;
21 }
22
23 public void setIsTouchScreen(boolean isTouch) {
24 this.IsTouchScreen = isTouch;
25 }
26 }






