spring AOP 编程演示
Spring中AOP代理由Spring的IOC容器负责生成、管理,其依赖关系也由IOC容器负责管理。因此,AOP代理可以直接使用容器中的其它bean实例作为目标,这种关系可由IOC容器的依赖注入提供。Spring创建代理的规则为:
1、默认使用Java动态代理来创建AOP代理,这样就可以为任何接口实例创建代理了
2、当需要代理的类不是代理接口的时候,Spring会切换为使用CGLIB代理,也可强制使用CGLIB
AOP编程概念
Aop, aspect object programming 面向切面编程
功能: 让关注点代码与业务代码分离!
关注点,
重复代码就叫做关注点;
切面,
关注点形成的类,就叫切面(类)!
面向切面编程,就是指 对很多功能都有的重复的代码抽取,再在运行的时候网业务方法上动态植入“切面类代码”。
切入点,
执行目标对象方法,动态植入切面代码。
可以通过切入点表达式,指定拦截哪些类的哪些方法; 给指定的类在运行的时候植入切面类代码。

需求:实现数字的四则运算,并进行日志打印。
实现将打印日志这些重复代码与核心代码进行分离。
代码演示
方式一:基于注解的实现
一、开启注解扫描与AOP注解 (spring 配置文件)

二、定义核心代码的接口并进行实现

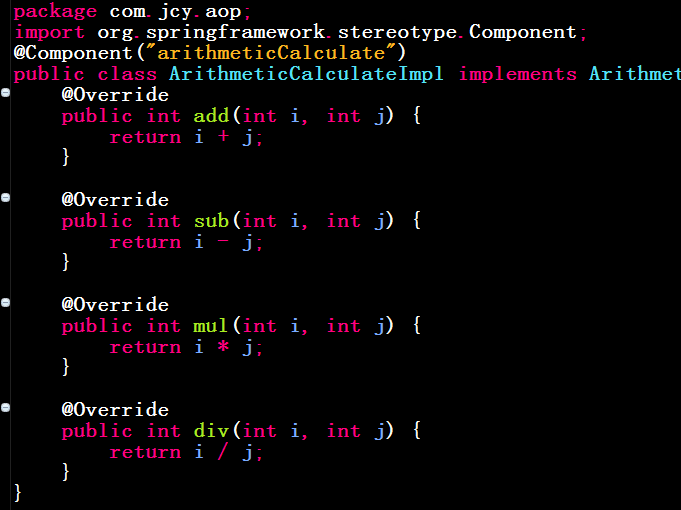
三、定义切面类
package com.jcy.aop;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.mysql.fabric.xmlrpc.base.Array;
@Order(2) //设置优先级(值越小越高的优先级)
@Aspect //指定为切面类
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
/**
* 定义一个方法, 用于声明切入点表达式. 一般地, 该方法中再不需要添入其他的代码.
* 使用 @Pointcut 来声明切入点表达式.
* 后面的其他通知直接使用方法名来引用当前的切入点表达式.
* 在其他类中使用 包名.类名.方法 com.jcy.aop.LoggingAspect.describePointcut()
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.jcy.aop.ArithmeticCalculateImpl.*(..))")
public void describePointcut(){}
/**
* 方法使用前的前置通知
*
* @param joinPoint
*/
@Before("describePointcut()")
public void beforeLogging(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> l = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的开始,参数有" + l);
}
/**
* 不看方法执行结果,方法执行后也会执行
* 后置通知
* @param joinPoint
*/
@After("execution(public int com.jcy.aop.ArithmeticCalculateImpl.*(int, int))")
public void afterLogging(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的结束。");
}
/**
* 方法执行成功后,执行
* 结果返回通知
* @param joinPoint
* @param result
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int com.jcy.aop.ArithmeticCalculateImpl.*(int, int))", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningLogging(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的结果:" + result);
}
/**
* 方法执行异常时,执行 异常通知
* @param joinPoint
* @param e
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public int com.jcy.aop.ArithmeticCalculateImpl.*(int, int))", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowingExceptionLogging(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(methodName + " 执行失败,方法的异常结果:" + e);
}
// /**
// * 环绕通知
// * 类似代理
// * 包含以上的所有通知
// * @return 返回的结果就是当前目标方法的返回结果
// */
// @Around("execution(public int com.jcy.aop.ArithmeticCalculateImpl.*(int, int))")
// public Object aroundLogging(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
//
// String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//
// Object result = null;
// //前置通知
// System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的开始,参数有" +Arrays.asList( proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()));
// try {
//
// //执行当前目标方法
// result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//
// //结果返回通知
// System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的结果:" + result);
//
// } catch (Throwable e) {
// // 异常通知
// System.out.println(methodName + " 执行失败,方法的异常结果:" + e);
// }
//
// //后置通知
// System.out.println(methodName + " 方法的结束。");
//
//
// return result;
//
// }
}
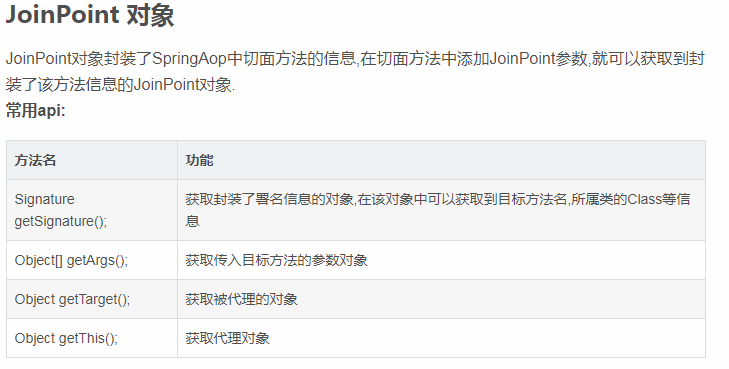
ProceedingJoinPoint 对象
ProceedingJoinPoint继承JoinPoint子接口,它新增了两个用于执行连接点方法的方法:
java.lang.Object proceed() throws java.lang.Throwable:通过反射执行目标对象的连接点处的方法;
java.lang.Object proceed(java.lang.Object[] args) throws java.lang.Throwable:通过反射执行目标对象连接点处的方法,不过使用新的入参替换原来的入参。
四、运行测试
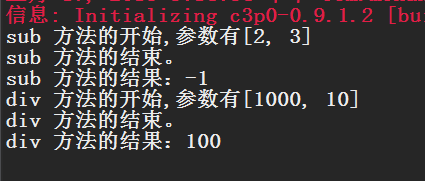
测试结果:
五、验证 @Order(2) 注解的优先级:
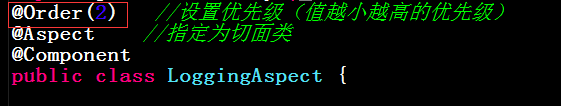
再定义一个切面类(对传入参数进行验证是否合法)如下:
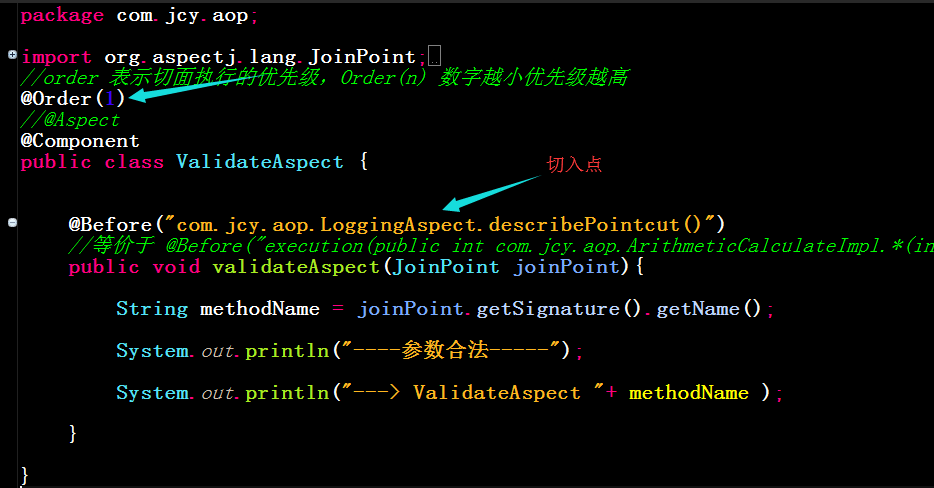
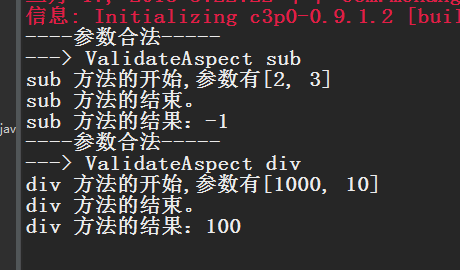
再次就行运行测试:
方式二:基于 xml 配置实现 AOP
spring xml 配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置 bean -->
<bean id="arithmeticCalculate" class="com.jcy.aop.xml.ArithmeticCalculateImpl">
</bean>
<!-- 配置切面的 bean 类 -->
<bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.jcy.aop.xml.LoggingAspect"></bean>
<bean id="validateAspect" class="com.jcy.aop.xml.ValidateAspect"></bean>
<!-- 配置 AOP -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切点表达式 execution(* com.jcy.aop.xml.ArithmeticCalculate.*(int,int)) -->
<aop:pointcut
expression="execution(* com.jcy.aop.xml.ArithmeticCalculate.*(*,*))"
id="pointcut" />
<!-- 配置切面及通知 -->
<aop:aspect ref="loggingAspect" order="2">
<aop:before method="beforeLogging" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningLogging"
pointcut-ref="pointcut" returning="result" />
<aop:after method="afterLogging" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingExceptionLogging"
pointcut-ref="pointcut" throwing="e" />
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="validateAspect" order="1">
<aop:before method="beforeValidateAspect" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
定义切点表达式的方式:
<!-- 定义一个切入点表达式: 拦截哪些方法 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.*.*(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【拦截所有public方法】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * *(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【拦截所有save开头的方法 】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* save*(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【拦截指定类的指定方法, 拦截时候一定要定位到方法】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【拦截指定类的所有方法】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.UserDao.*(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【拦截指定包,以及其自包下所有类的所有方法】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn..*.*(..))" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【多个表达式】 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.UserDao.save()) || execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>-->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.UserDao.save()) or execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 下面2个且关系的,没有意义 -->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.UserDao.save()) && execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>-->
<!--<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.UserDao.save()) and execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>-->
<!-- 【取非值】 -->
<!--
<aop:pointcut expression="!execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>
<aop:pointcut expression=" not execution(* cn.itcast.g_pointcut.OrderDao.save())" id="pt"/>
-->
自己用JDK动态代理的方式实现上述的切面编程。代码如下:
package com.jcy.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArithmeticCalculateLoggingProxy {
//要代理的对象
private ArithmeticCalculate target;
public ArithmeticCalculateLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculate target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
//返回代理对象
public ArithmeticCalculate getLoggingProxy(){
ArithmeticCalculate proxy = null;
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class [] interfaces = new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculate.class};
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* proxy: 代理对象。 一般不使用该对象
* method: 正在被调用的方法
* args: 调用方法传入的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
//打印日志
System.out.println("[before] The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args));
//调用目标方法
Object result = null;
try {
//前置通知
result = method.invoke(target, args);
//返回通知, 可以访问到方法的返回值
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//异常通知, 可以访问到方法出现的异常
}
//后置通知. 因为方法可以能会出异常, 所以访问不到方法的返回值
//打印日志
System.out.println("[after] The method ends with " + result);
return result;
}
};
/**
* loader: 代理对象使用的类加载器。
* interfaces: 指定代理对象的类型. 即代理代理对象中可以有哪些方法.
* h: 当具体调用代理对象的方法时, 应该如何进行响应, 实际上就是调用 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 方法
*/
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculate) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}



