Mybatis基础
1.1 什么是Mybatis

-
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架(完成持久化工作的代码块)
-
它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射
-
MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。
-
MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
-
MyBatis本是apache的一个
-
2013年11月迁移到
1.2 为什么要用Mybatis
-
传统JDBC复杂,需要框架简化。
-
简单易学,灵活
-
解除sql与程序代码的耦合:通过提供DAO层,将业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离,使系统的设计更清晰,更易维护,更易单元测试。sql和代码的分离,提高了可维护性。
-
提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系映射。
-
提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组建维护。
-
提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
2、测试程序
2.1 搭建环境
链接MySQL本地数据库,新建一个数据库;
新建项目
1.新建maven项目
2.删除src目录
3.导入maven依赖
<dependencies>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.2 创建一个模块
-
编写mytais核心配置文件
-
编写mybatis工具类
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static{
try {
//使用mybatis第一步:获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//既然有了 SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们可以从中获得 SqlSession 的实例。
//SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法。你可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句。
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
2.3 编写代码
-
实体类
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
-
Dao接口
public interface UserDao {
List<User> getUserList();
}
-
接口实现类(从JDBC的UserDaoImpl转换为一个Mapper配置文件)
2.4 测试
2.4.1 Junit测试
public class UserDaoTest {
2.4.2 遇到的问题
1、配件文件没有注册
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Type interface com.dao.UserDao is not known to the MapperRegistry.
resources下的配置文件加入注册段
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
2、绑定接口错误
org.apache.ibatis.builder.BuilderException: Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: java.io.IOException: Could not find resource com/dao/UserMapper.xml
在pom.xml配置文件中加入以下配置代码
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
3、时区问题
Error querying database. Cause: java.sql.SQLException: The server time zone value '�й���ʱ��' is unrecognized or represents more than one time zone. You must configure either the server or JDBC driver (via the 'serverTimezone' configuration property) to use a more specific time zone value if you want to utilize time zone support.
idea右侧的Database中找到高级设置Advance里面的serverTimezone将时区设置为上海
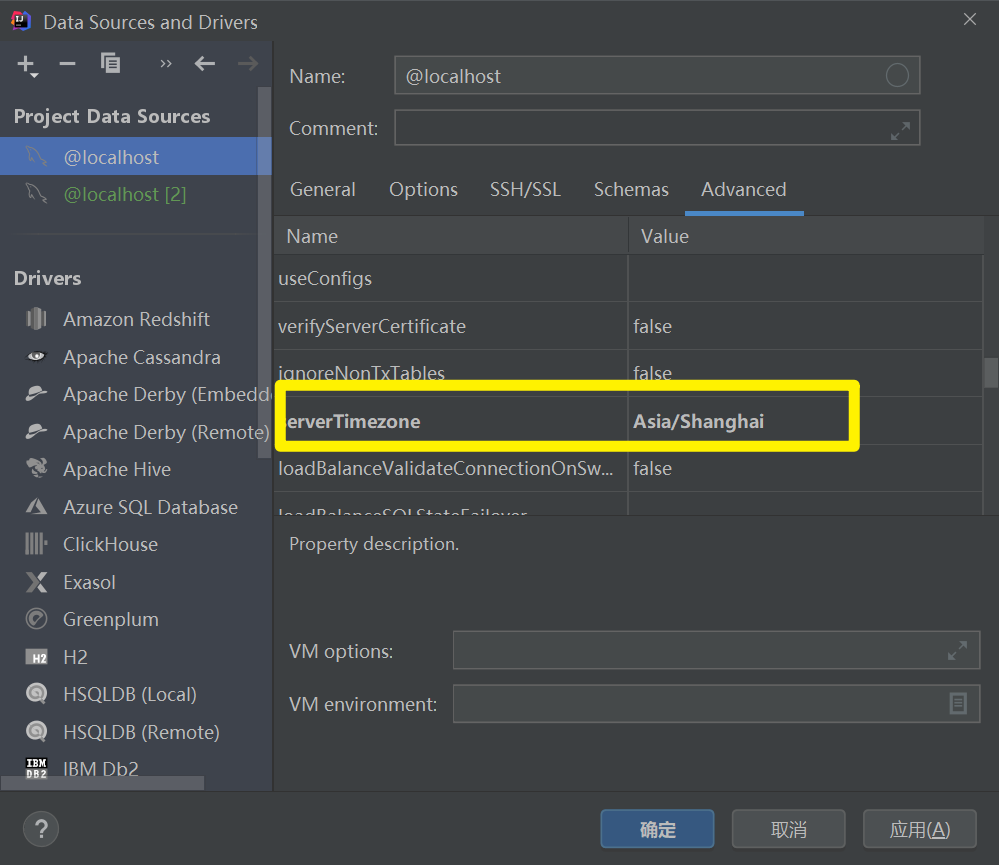
并在resources配置文件中在url设置中加入serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&
2.5模糊查询
1.java代码执行的时候,传递通配符 % %
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserList("%李%");
2.在sql中拼接使用通配符
select * from user where name like "%"#{value}"%"
3、配置解析
1. 环境配置(environment)
Mybatis可以配置成适应多种环境,不过配置多个环境每个SqlSessionFactory实例只能选择一种环境。
Mybatis默认的事务管理器就是JDBC,连接池POOLED
2. 属性(properties)
通过properties属性来实现应用配置文件
这些属性都是可外部配置且可动态替换的,既可以在典型的java属性文件中配置或通过properties元素的子元素传递。
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username=root
password= 123456
在核心配置文件中引入
<properties resource="db.properties">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
</properties>
可以直接引入外部文件,也可以在其中增加一些属性配置,当都存在时优先选择外部文件中的属性。
3. 类别别名(type aliases)
可以指定一个包名,Mybatis会自动搜索这个包下的类,默认类别名为类的类名
修改该类别名需要在该类上增加注解@Alias("别名")
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
也可以指定类型一个类并设置他的别名
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.pojo.User" alias="User"/>
</typeAliases>
4.映射器(Mapper)
使用配置文件注册Mapper文件方式推荐,
其余两种方式需要接口和配置文件同名并且位于同一包中才能生效。
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
<!-- <mapper class = "com.mapper.UserMapper"/>-->
<!-- <package name="com.mapper"/>-->
</mappers>
4、resultMap
在UserMapper.xml文件中重写接口方法,修改resultType为resultMap创建映射,并在resultMap标签中设置映射关系
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<!-- <result column="id" property="id"/>-->
<!-- <result column="name" property="name"/>-->
<result column="pwd" property="password"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from `user` where id = #{id}
</select>
5、日志
数据库操作出现异常时需要排错使用日志。
比较重要的两个
LOG4J(deprecated since 3.5.9) |
SDOUT_LOGGING |(标准日志输出)
5.1 日志工厂
在设置中配置标准日志工厂
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
获取控制台中输出的日志信息
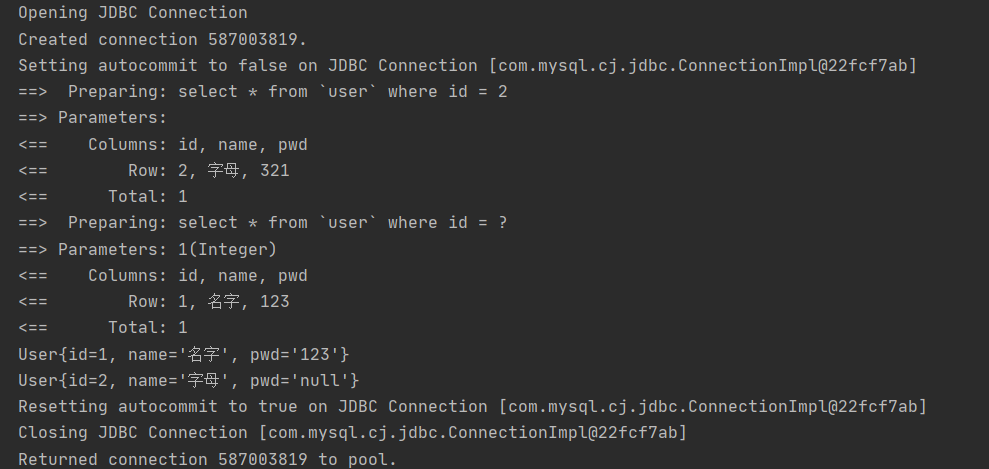
5.2 Log4j
什么是log4j
-
Log4j是Apache的一个开源项目,通过使用Log4j,我们可以控制日志信息输送的目的地是控制台、文件、GUI组件;
-
可控制每一条日志的输出;
-
可定义每一条日志信息的级别,更加细致的控制日志的生成过程;
-
可通过配置文件来灵活配置,不需要修改代码。
1.导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
2.log4j.properties
#将等级为DEBUG的日志信息输出到console和file这两个目的地,console和file的定义在下面的代码
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file
#控制台输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n
#文件输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/kuang.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n
#日志输出级别
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
3.设置中配置为log4j日志
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>
6、一对多查询
创建两个数据库表有多对一关系
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`tid` INT(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fktid` (`tid`),
CONSTRAINT `fktid` FOREIGN KEY (`tid`) REFERENCES `teacher` (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
在项目包pojo中分别创建学生和教室对应的类
在接口中定义查询方法并在配置文件中实现
方式一:查询嵌套查询
多对一查询
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from student;
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<!--复杂的属性需要单独处理
对象:association
集合:collection-->
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher" column="tid" select="getTeacher"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from teacher where id = #{id}
</select>
方式二:结果嵌套查询
利用修改resulMap将学生类传入教师查询中(教师-->学生)一对多查询
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tid
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号