拆箱、装箱、为什么需要包装类型
一、有基本数据类型,为什么还要包装类型
1、基本数据类型不具有对象性质
如集合中只能接收Object类型,无法直接存储基本数据类型
2、基本数据类型不能存null,包装类型可以
3、包装类数据缓存
在自动装箱的时候调用valueOf方法。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); }
这里IntegerCache.low为-128,IntegeCache.high为127,IntegerCache.cache为数组存储的就是-128到127的Integer对象。在-128~127区间的数会被缓存,当类加载的时候就创建这256个数对应的对象,并放到名为cache的数组中,调用valueOf()方法时会先判断该数是否在-128~127的区间,如果在则直接获取数组中该对象的引用,如果不在则创建该对象。
例如:
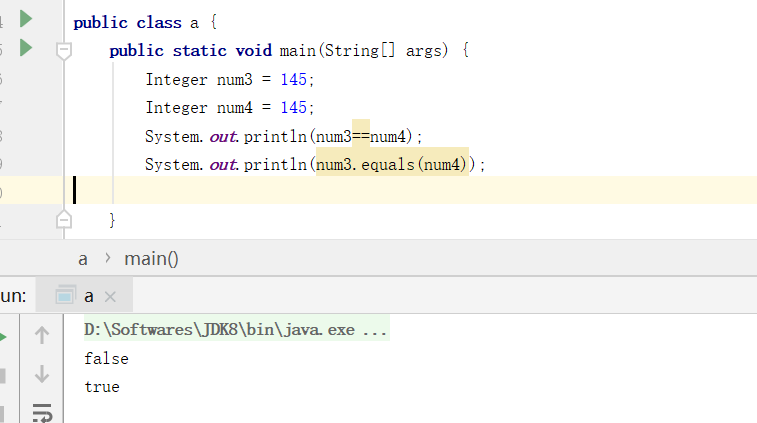
Integer num3 = 145,因为145不在这个范围区间,所以会在堆中生成对象num3和num4分别指向两个不同地址的对象,所以===返回false。
各包装类缓存的取值范围:
· Boolean:使用静态 final 定义;
· Byte:缓存区 -128~127
· Short:缓存区 -128~127;
· Character:缓存区 0~127;
· Long:缓存区 -128~127;
· Integer:缓存区 -128~127。
Float 和 Double 不会有缓存。
二、装箱、拆箱
装箱:自动将基本数据类型转换为包装器类型
拆箱:自动将包装器类型转换为基本数据类型
当 "=="运算符的两个操作数都是 包装器类型的引用,则是比较指向的是否是同一个对象,而如果其中有一个操作数是表达式(即包含算术运算)则比较的是数值(即会触发自动拆箱的过程)。另外,对于包装器类型,equals方法并不会进行类型转换。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer a = 1; Integer b = 2; Integer c = 3; Integer d = 3; Integer e = 321; Integer f = 321; Long g = 3L; Long h = 2L; System.out.println(c==d); System.out.println(e==f); System.out.println(c==(a+b)); System.out.println(c.equals(a+b)); System.out.println(g==(a+b)); System.out.println(g.equals(a+b)); System.out.println(g.equals(a+h)); } }
true false true true true false true



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号