OC之分类相关
一、分类
1.1 分类结构体
struct category_t { const char *name; classref_t cls; WrappedPtr<method_list_t, PtrauthStrip> instanceMethods; WrappedPtr<method_list_t, PtrauthStrip> classMethods; struct protocol_list_t *protocols; struct property_list_t *instanceProperties; // Fields below this point are not always present on disk. struct property_list_t *_classProperties; method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta) { if (isMeta) return classMethods; else return instanceMethods; } property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi); protocol_list_t *protocolsForMeta(bool isMeta) { if (isMeta) return nullptr; else return protocols; } };
从中我们可以总结出:
1.分类中有实例方法和类方法列表 2.分类没有成员变量列表(ivars),所以我们不能给分类添加成员变量 3.额外补充:分类不会为新增的属性添加set/get方法,除非使用关联对象(在第三部分具体说明)
1.2 分类的加载时机
分类通过 attachCategories 添加:

调用attachCategories方法的objc中的所有方法如下所示:一个是load_images,一个是realizeClassWithoutSwift
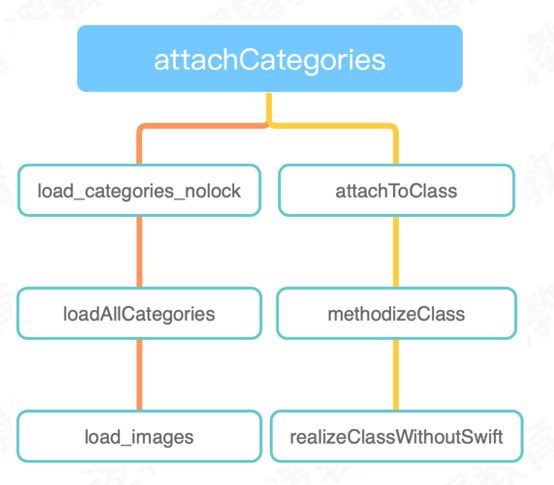
无论是懒加载还是非懒加载,最后都会通过realizeClassWithoutSwift去加载类,并对类的rw、rwe进行操作(上篇博客)。因为本类和分类组合起来有四种情况,并会对rw中方存放的元素产生不同的影响,因此我们总结如下:
1.分类的加载会在本类的加载之后,分类的方法会粘贴在本类之前 2.当本类和分类存在同名时,会优先访问分类 3.当多个分类存在同名方法时,则先编译的后调用 4.只有在非懒加载和非懒加载分类的情况下,ro负责保存本类,rwe负责保存分类和本类,其他情况下ro保存本类和分类,没有rwe 5.在runtimeAPI对类进行修改的时候才会产生rwe
1.类为非懒加载、分类为非懒加载 编译时ro里面只有类的数据没有分类的数据,分类的数据在运行是被加载到rwe里面 2.类为非懒加载、分类为懒加载 编译时类和分类的数据都被加载ro里面了。 3.类为懒加载类、分类为非懒加载类 编译时类和分类的数据都被加载ro里面了 4.类为懒加载类、分类懒加载类 在类第一次接收到消息时加载数据,类和分类的数据都被加载在ro里面。
三、关联对象
3.1 关联对象的实现:objc源码中找到关联对象api的实现部分如下:
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy) { _object_set_associative_reference(object, key, value, policy); } void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object) { if (object && object->hasAssociatedObjects()) { _object_remove_assocations(object, /*deallocating*/false); } }
我们重点关注_object_set_associative_reference方法:
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, const void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) { // This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code // probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly. // rdar://problem/44094390 if (!object && !value) return; //isa有一位信息为禁止关联对象,如果设置了,直接报错 if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects()) _objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object)); //包装对象,转换类型 DisguisedPtr<objc_object> disguised{(objc_object *)object}; //包装值和属性信息 ObjcAssociation association{policy, value}; // retain the new value (if any) outside the lock. //设置属性信息 association.acquireValue(); bool isFirstAssociation = false; { //调用构造函数,构造函数内加锁操作 AssociationsManager manager; //获取全局的HasMap AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get()); //如果值不为空 if (value) { //去关联对象表中找对象对应的二级表,如果没有内部会重新生成一个 auto refs_result = associations.try_emplace(disguised, ObjectAssociationMap{}); //如果没有找到 if (refs_result.second) { /* it's the first association we make */ //说明是第一次设置关联对象,把是否关联对象设置为YES isFirstAssociation = true; } /* establish or replace the association */ auto &refs = refs_result.first->second; //在二级表中找key对应的内容, auto result = refs.try_emplace(key, std::move(association)); //如果已经有内容了,没有内容上面根据association已经插入了值,所以啥也不用干 if (!result.second) { //替换掉 association.swap(result.first->second); } //如果value为空 } else { //通过object找对应的二级表 auto refs_it = associations.find(disguised); // 如果有 if (refs_it != associations.end()) { auto &refs = refs_it->second; //通过key再在二级表里面找对应的内容 auto it = refs.find(key); //如果有 if (it != refs.end()) { //删除掉 association.swap(it->second); refs.erase(it); if (refs.size() == 0) { associations.erase(refs_it); } } } } } // Call setHasAssociatedObjects outside the lock, since this // will call the object's _noteAssociatedObjects method if it // has one, and this may trigger +initialize which might do // arbitrary stuff, including setting more associated objects. if (isFirstAssociation) object->setHasAssociatedObjects(); // release the old value (outside of the lock). association.releaseHeldValue(); }
// Inserts key,value pair into the map if the key isn't already in the map. // The value is constructed in-place if the key is not in the map, otherwise // it is not moved. template <typename... Ts> std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace(KeyT &&Key, Ts &&... Args) { BucketT *TheBucket; //如果已经存在了 if (LookupBucketFor(Key, TheBucket)) return std::make_pair( makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true), false); // Already in map. // Otherwise, insert the new element. //不存在就插入一个新的对象 TheBucket = InsertIntoBucket(TheBucket, std::move(Key), std::forward<Ts>(Args)...); return std::make_pair( makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true), true); }
再看看get_associtiond的源码:
id _object_get_associative_reference(id object, const void *key) { ObjcAssociation association{}; { //加锁 AssociationsManager manager; //全局的表 AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get()); //通过object找对应的二级表 AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find((objc_object *)object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap &refs = i->second; //在二级表内通过key在找对应的值 ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs.find(key); if (j != refs.end()) { association = j->second; association.retainReturnedValue(); } } } //取值并返回然后放到自动释放池中 return association.autoreleaseReturnedValue(); }
由此,我们可以总结出关联对象的结构图:
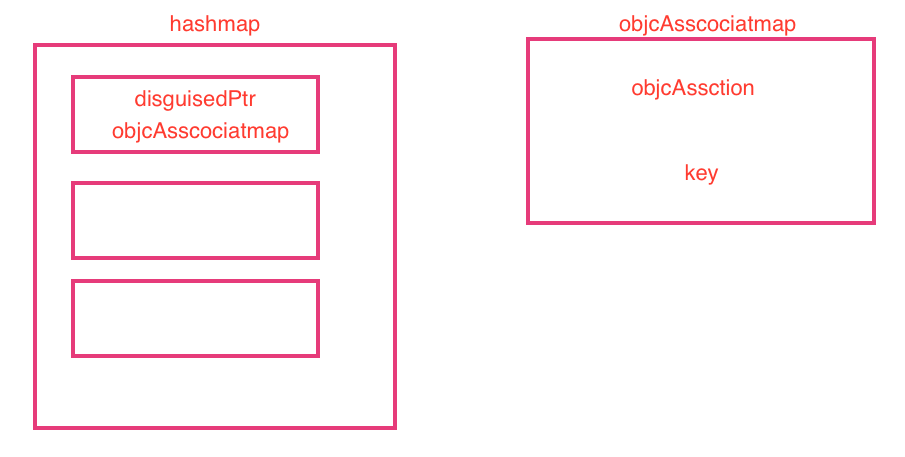
3.2关联对象的设值流程:
1.创建一个AssociationManager管理类 2.获取唯一的全局静态哈希Map 3.判断是否插入的关联值是否存在,如果存在走4,如果不存在则走插入空流程 4.创建一个空的ObjectAssociationMap去取查询的键值对(key是我们调用API传递进来的MyNameKey;value是ObjcAssociation对象(关联策略和关联属性的值)) 5.如果发现没有这个key就插入一个空的BucketT进去并返回 6.标记对象存在关联对象 7.用当前修饰策略和值组成一个ObjcAssociation替换原来BucketT中的空 8.标记一下ObjcAssociationMap的第一次为false
3.3关联对象插入关联值为空流程:
1.根据DisguisePtr找到AssociationsHashMap中的iterator迭代查询器 2,清理迭代器 3,其实如果是插入空,相当于清除
3.4关联对象取值流程:
1.创建一个AssociationsManager管理类 2.获取唯一的全局静态哈希Map 3.根据DisuisedPtr找到AssocationHashMap中的iterator迭代查询器 4.如果这个迭代查询器不是end(),说明存在key-value 5.返回value
3.5 具体实现:
//关联对象的形式为属性添加set/get方法 static const char *LGNameKey = "LGNameKey"; //关联策略 五种 //set -(void)setName:(NSString *)name { objc_setAssociatedObject(self, LGNameKey, name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); } //get -(NSString *)name { return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, LGNameKey); }
四、分类(category)和类扩展(extension)的区别
1.分类原则上只能增加方法(也可以通过rutime关联对象实现添加属性)。 2.类扩展不仅可以增加方法,还可以增加实例变量(或者属性)。(私有) 3.类扩展是在编译阶段被添加到类中,而分类是在运行时添加到类中。 4.类扩展不能像分类那样拥有独立的实现部分(@implementation部分),也就是说,类扩展所声明的方法必须依托对应类的实现部分来实现。 5.定义在 .m 文件中的类扩展方法为私有的,定义在 .h 文件(头文件)中的类扩展方法为公有的。类扩展是在 .m 文件中声明私有方法的非常好的方式。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号