List集合 Set接口 Map集合 Debug调试 JDK9新特性
目录
List集合数据拷贝方式_list 拷贝_理想在路上的博客-CSDN博客
1.有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的(存储 123,取出123)2.有索引,包含了一些带索引的方法 3.允许存储重复的元素list 常用方法
LinkedHashSet(有序)集合 继承HashSet集合 他俩方法都一样编辑
TreeeSet 直接用collection 方法就行不重复 无索引 可排序编辑编辑aaa list)方法:编辑sort(List list,Comparator) 方法:编辑编辑
Debug调试程序:编辑 JDK9新特性:编辑斗地主 (有序版本)编辑
如何优雅地给List集合添加元素_火锅好好吃的博客-CSDN博客_list添加数据
该代码有直接new的时候添加元素的方法;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
if (numRows < 1) return new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(){{add(1);}});
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
Integer[] arr = new Integer[i + 1];
arr[0] = arr[i] = 1;
for (int x = 1; x < i; x++)
arr[x] = ans.get(i - 1).get(x) + ans.get(i - 1).get(x - 1);
ans.add(Arrays.asList(arr));
}
return ans;
}
}List集合数据拷贝方式_list 拷贝_理想在路上的博客-CSDN博客
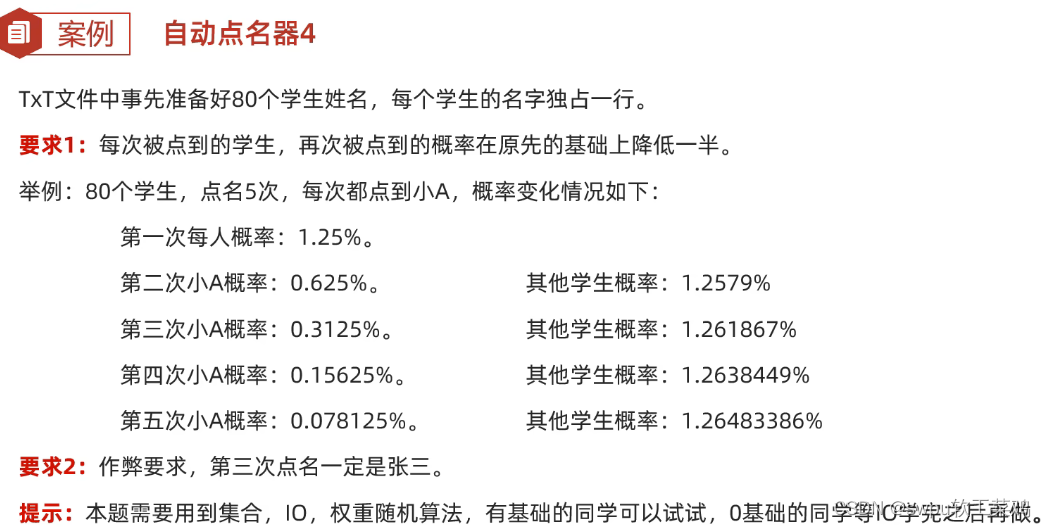
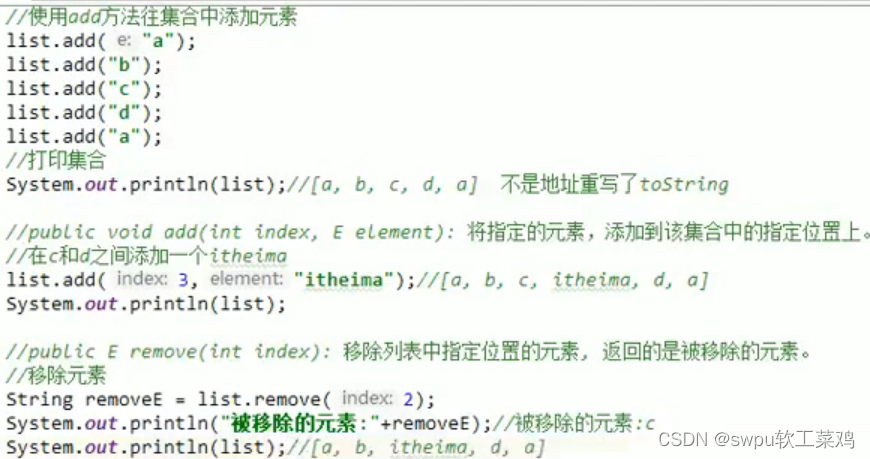
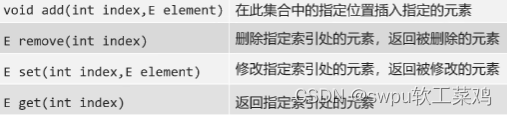
List接口的特点:
1.有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的(存储 123,取出123)
2.有索引,包含了一些带索引的方法 3.允许存储重复的元素
list 常用方法:
![]()
![]()
![]() list.indexOf(Object O)和list.lastIndexOf(Object O)的用法_攻城日记的博客-CSDN博客_list.indexof
list.indexOf(Object O)和list.lastIndexOf(Object O)的用法_攻城日记的博客-CSDN博客_list.indexof![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
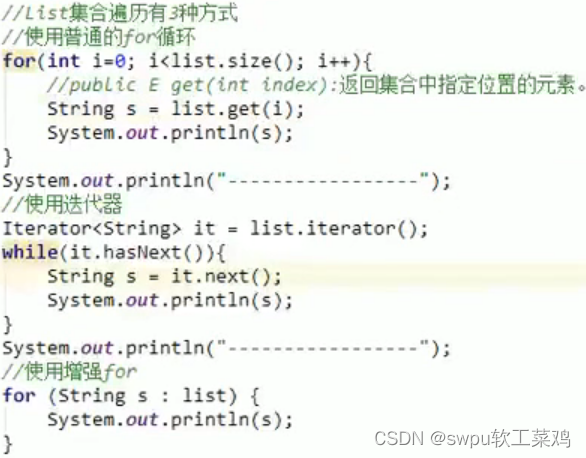
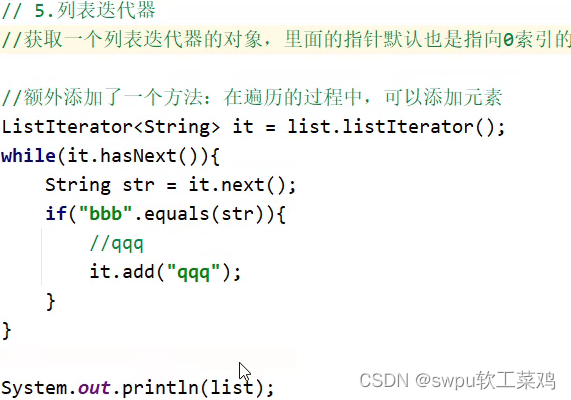
列表迭代器![]()
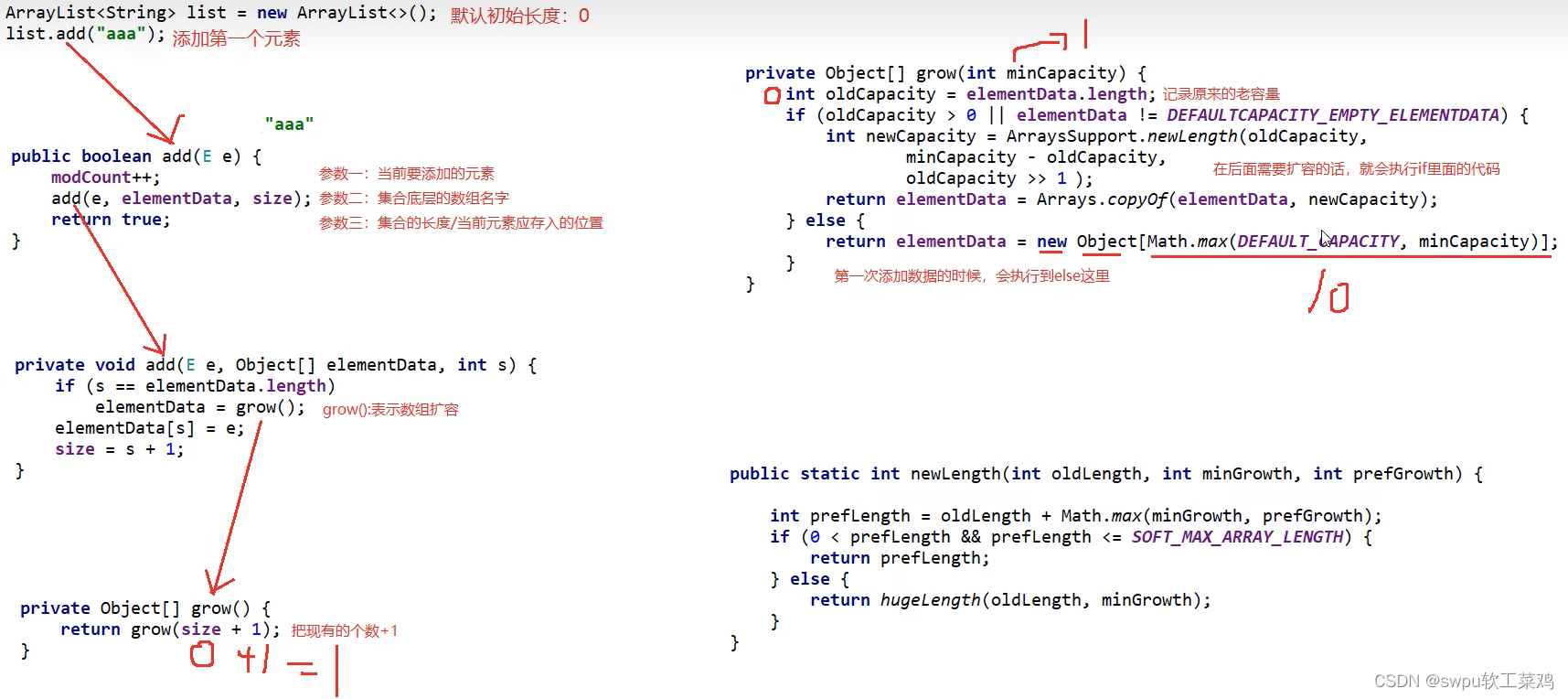
List接口的第一个实现类:ArrayList集合 增删慢,查找快
![]()
![]()
![]()
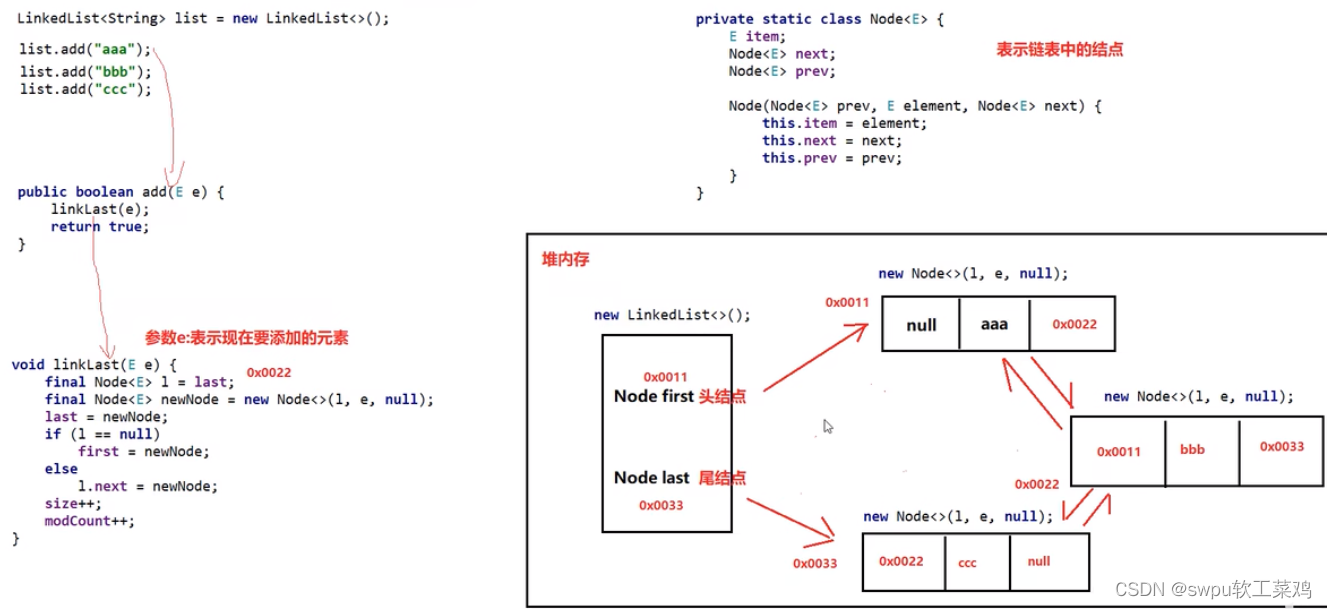
List接口的第二个实现类:LinkedList集合 是一个双链表
特点:增删快,查找慢,操作首尾快;里边包含大量操作首尾的方法
![]()
![]()
Vector集合 是ArrayList集合的 父类. 已经被市场淘汰 被ArrayList集合替代
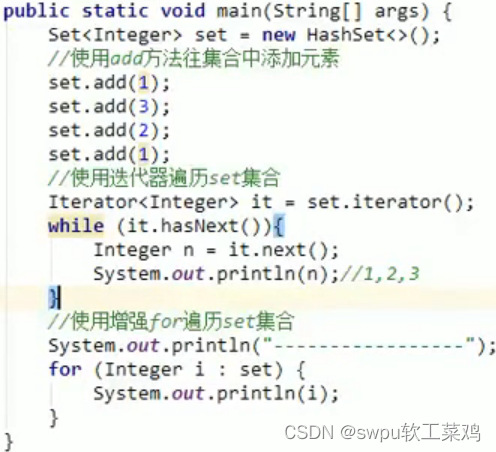
Set接口的特点:
无序,不重复,无索引(跟Collection的API基本一致 所以我们不用学了)
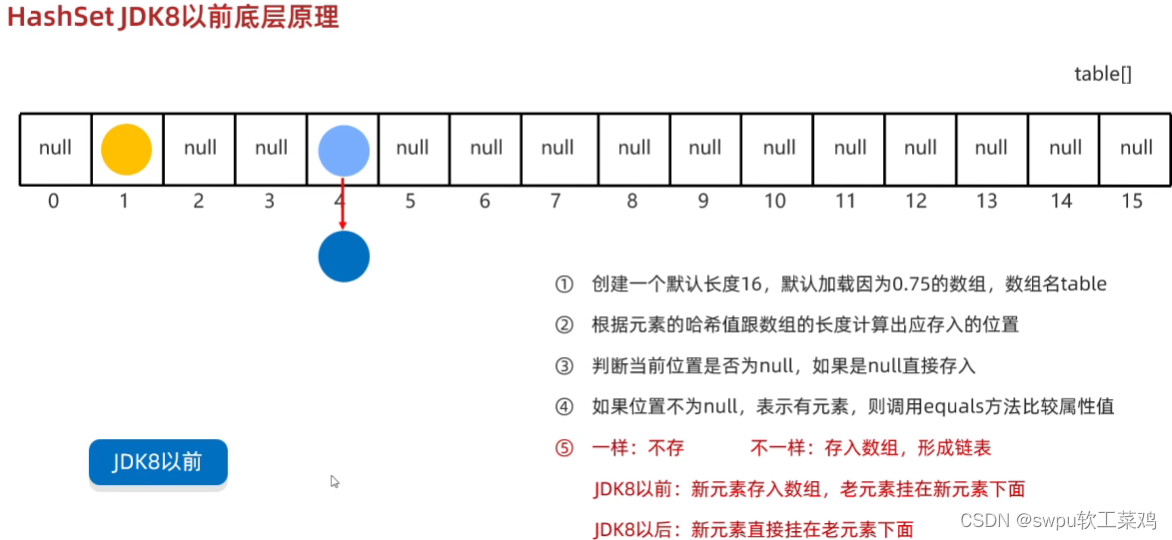
Set接口的第一个实现类: HashSet集合 特点:
1.不允许存储重复的元素
2.没有元素,没有带索引的方法,也不能使用普通的for循环遍历
3.是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致
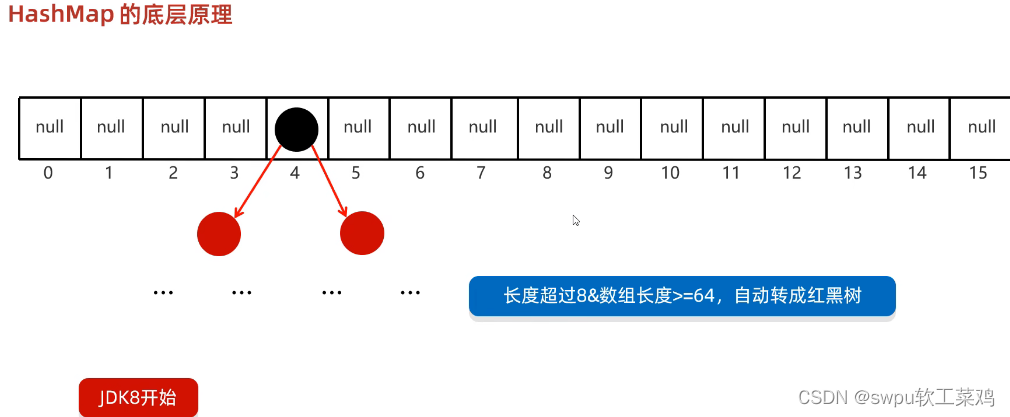
4.底层是一个哈希表结构(查询的速度非常快)
加载因:16*0.75=12,当数组元素到达12 会自动扩容到自己两倍
JDK8以后:当链表长度>8并且数组长度>=64时 链表自动转换为红黑树
HashSet为什么存取顺序不一样 遍历是从数组[0]开始 遇到链表或树会先遍历 所以存取顺序不一致
HashSet为什么没有索引 同一个索引处 可能挂有链表或树 所以无法规定索引
HashSet利用什么机制保证去重 HashCode()得到哈希值;equals()比较对象属性值
LinkedHashSet(有序)集合 继承HashSet集合 他俩方法都一样
![]()
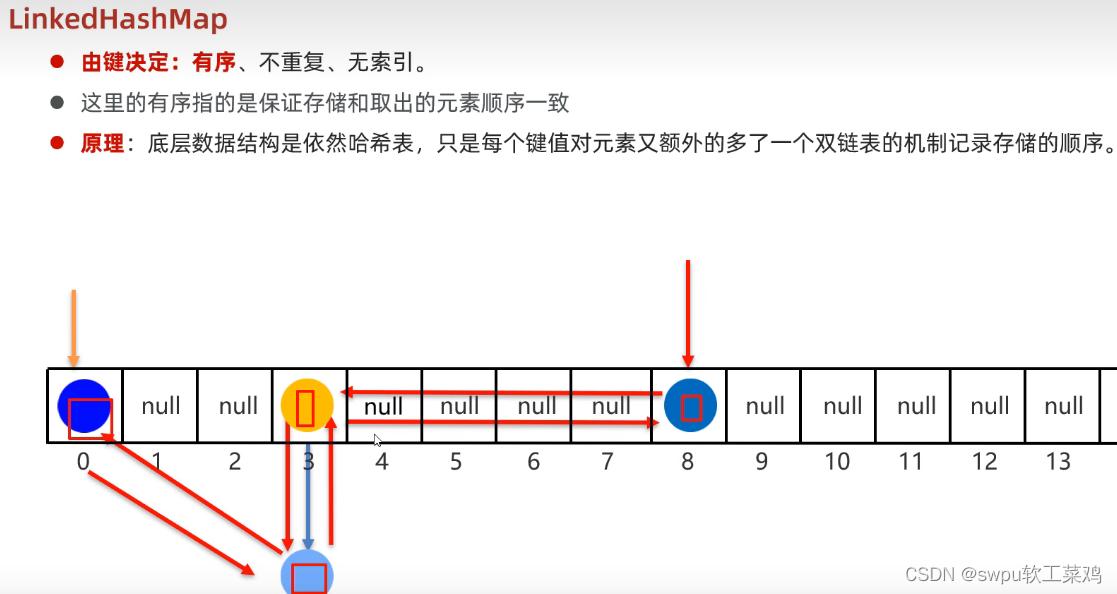
特点:底层是一个哈希表(数组+链表/红黑树)+双链表(记录存储顺序 )
多一条双链表用来记录元素存储顺序,保证元素有序 因为HashSet效率更高
因为HashSet效率更高
TreeeSet 直接用collection 方法就行
不重复 无索引 可排序
![]()
![]()
aaa<ab<aba<cd<qwer;
![]()
![]()
单列集合使用场景:
![]()
可变参数
![]()
![]()
![]()
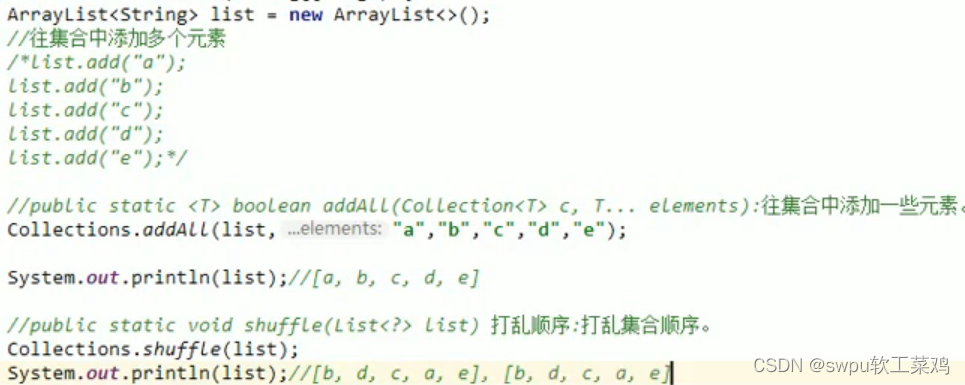
Collections集合工具类的方法:![]()
![]()
![]()
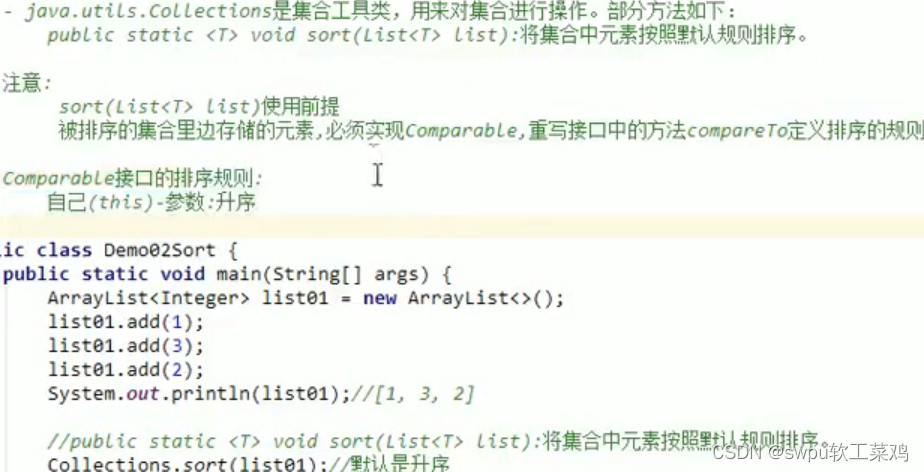
sort(List<T> list)方法:
![]()
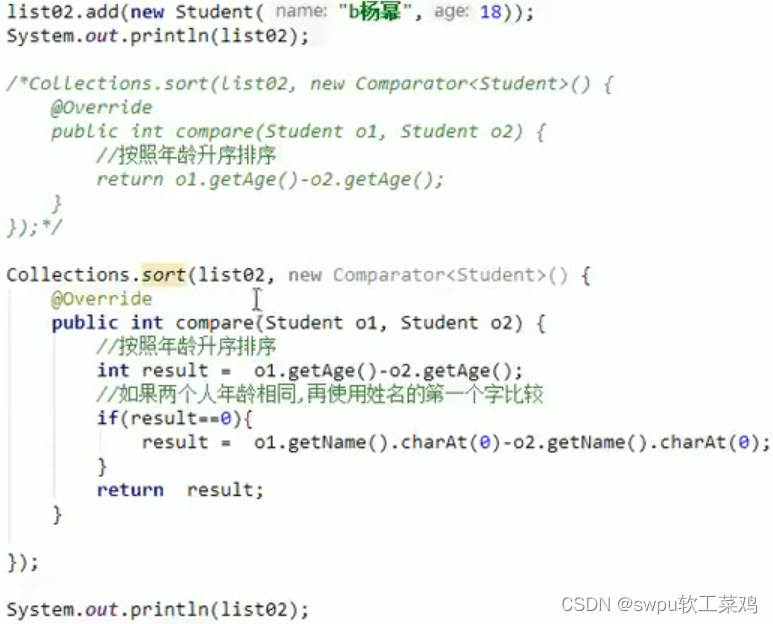
sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T>) 方法:![]()
![]()
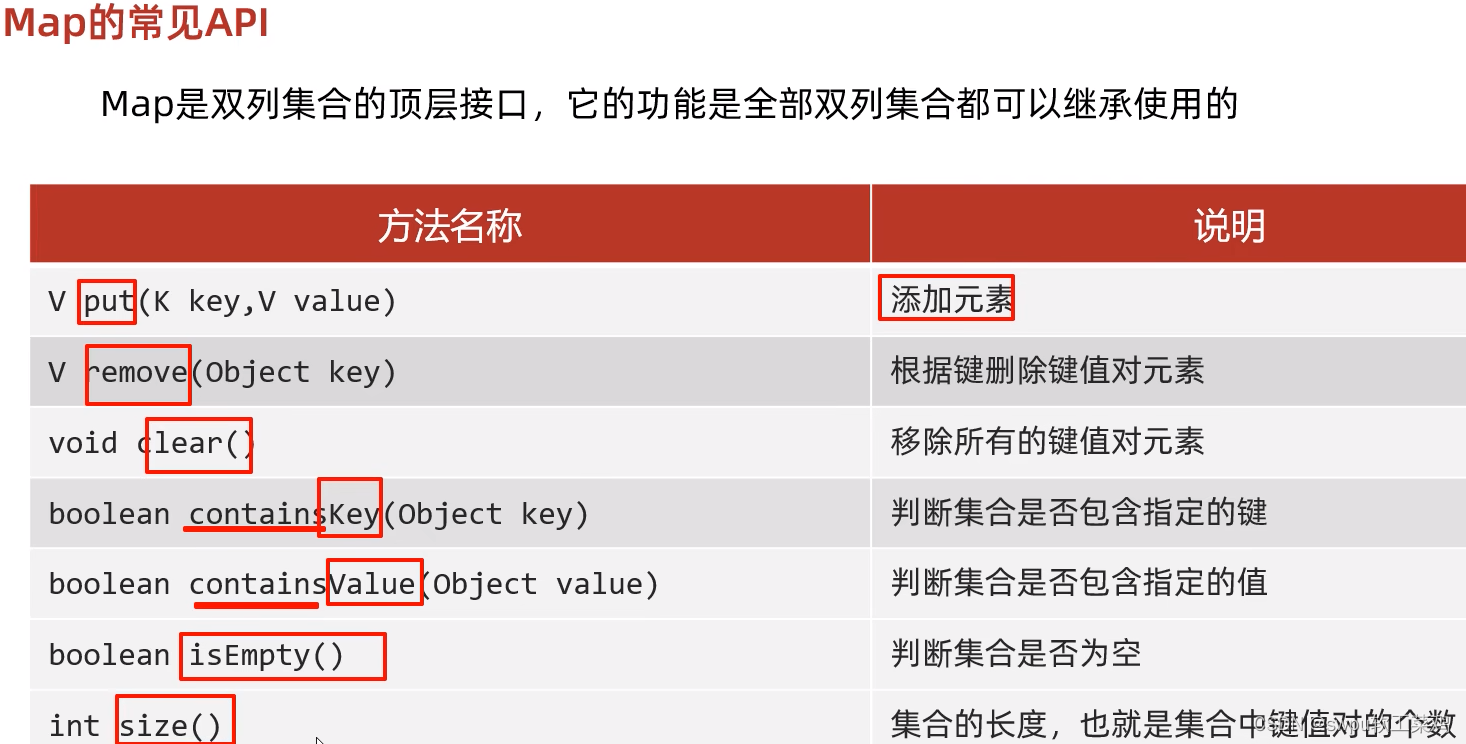
Map集合 特点:
1.Map集合是一个双列集合,一个元素包含两个值(一个key,一个value)
2.Map集合中的元素,key和value的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同
3.Map集合中的元素,key是不允许重复的,value可以重复
4.Map集合中的元素,key和value一一对应![]()
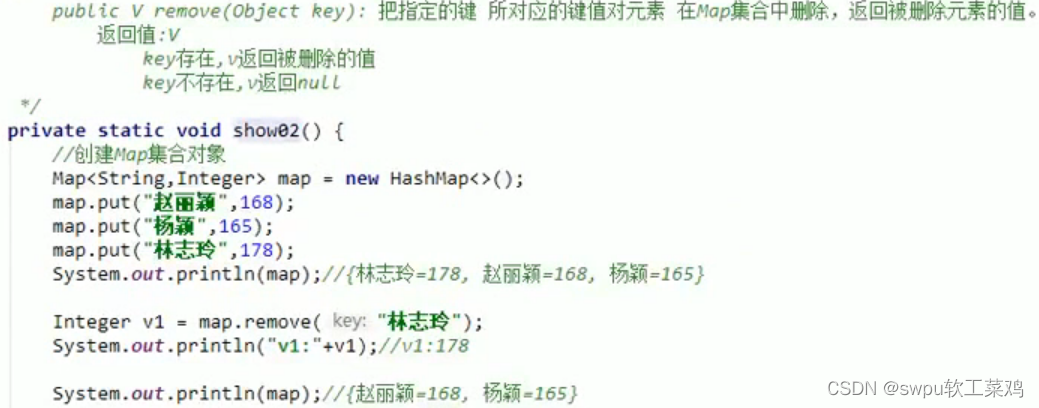
public V get(Object key) 返回散列映射中使用key做键的“键/值”对中 的值![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
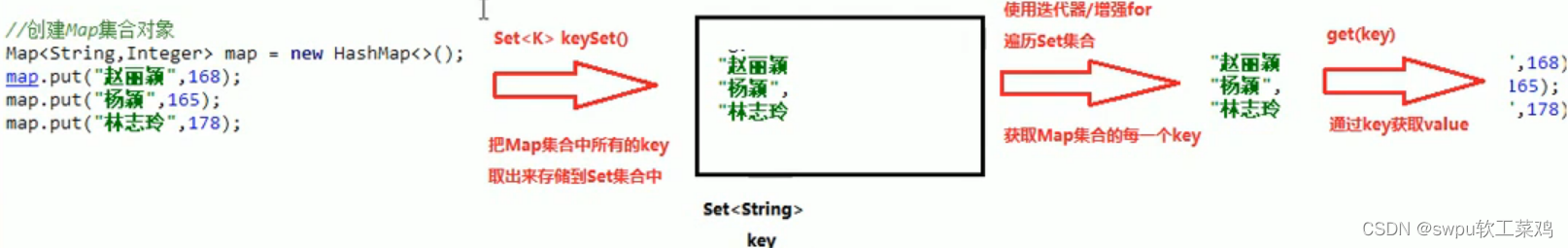
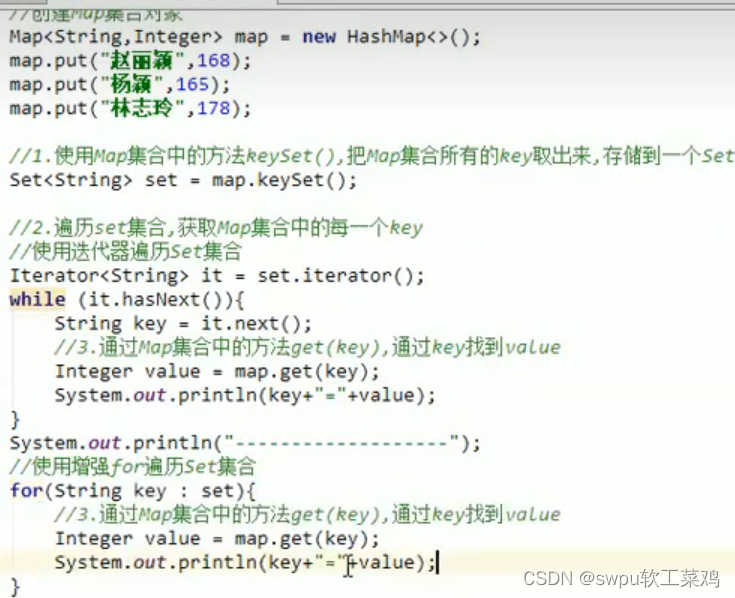
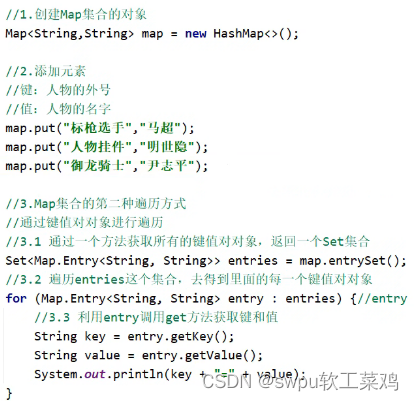
Map集合遍历 (1)键找值方法:![]()
![]()
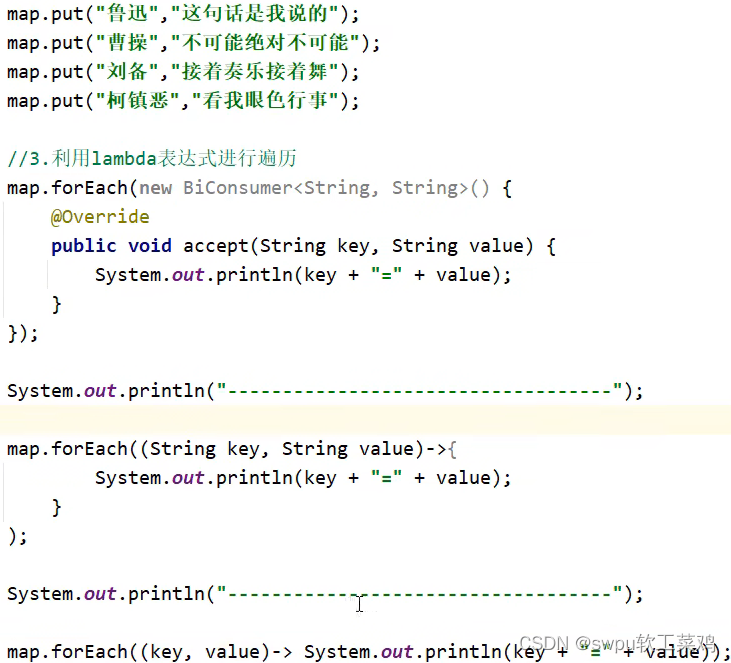
![]() Map 遍历 (2)键值对:
Map 遍历 (2)键值对:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
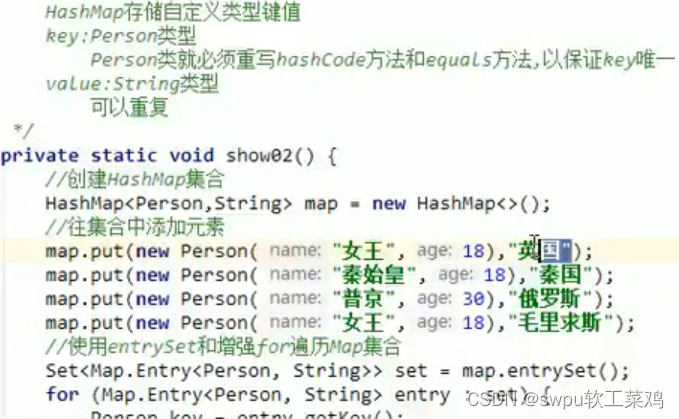
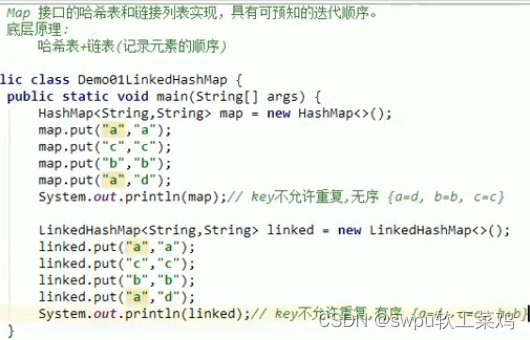
HashMap
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() LinkedHashMap集合 (有序,不重复,无索引集合) 双链表
LinkedHashMap集合 (有序,不重复,无索引集合) 双链表![]()
![]()
TreeMap
![]()
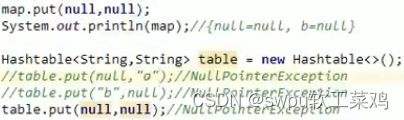
Map集合的另外一个接口: Hashtable集合 之前学的所有集合都可以存null 这个不行
![]()
![]()
![]()
Map集合底层原理(面试经常考) 感觉看不懂底层源码 等强了再看这五个吧
![]()
![]()
 学完IO来玩吧
学完IO来玩吧
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串");
String str = sc.next();
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//遍历字符串 加强for
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
//使用获取到的字符,去map集合判断key是否存在
if (map.containsKey(c)) {
//key存在
Integer value = map.get(c);
value++;
map.put(c, value);
} else {//key不存在
map.put(c, 1);
}
}
//遍历map 输出结果
for (Character key : map.keySet()) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
}
Debug调试程序:![]() JDK9新特性:
JDK9新特性:![]()
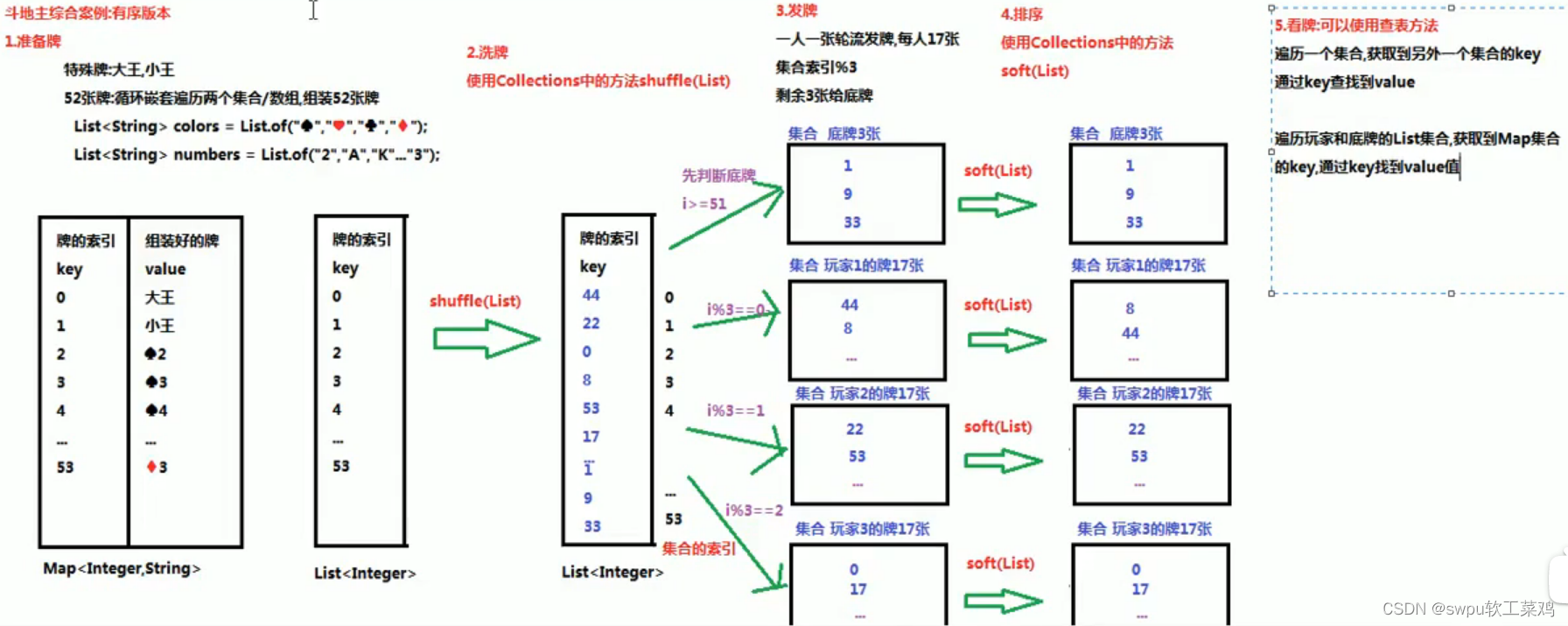
斗地主 (有序版本)
![]()
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class dizhu02jihe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.准备牌 创建map集合 存储牌索引和装好的牌
HashMap<Integer, String> poker = new HashMap<>();
//创建list集合 存储牌索引
ArrayList<Integer> pokerIndex = new ArrayList<>();
//定义两个数组,一个数组存储花色 一个存储牌序号
List<String> colors = List.of("♠", "♥", "♣", "♦");
List<String> numbers = List.of("2", "A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3");
//把大小王存储到poker中
int index = 0;
poker.put(index, "大王");
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
poker.put(index, "小王");
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
//循环嵌套遍历两个数组,组装52张牌
for (String number : numbers) {
for (String color : colors) {
//System.out.println(color + number);
//把组装好了的牌存储到poker集合中
poker.put(index, (color + number));
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
}
}
//2.洗牌
//使用集合的工具类Collections中的方法
//static void shuffle(List<?> list) 使用默认随机源对指定列表进行置换
Collections.shuffle(pokerIndex);
//3.发牌
//定义三个集合存储 玩家的牌的索引,一个集合存储三张底牌
ArrayList<Integer> player01 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> player02 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> player03 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> diPai = new ArrayList<>();
//使用poker集合的索引%3 给3个玩家轮流发牌
//注意: 先判断底牌(i>=51) 否则三张底牌发没了
for (int i = 0; i < pokerIndex.size(); i++) {
Integer in = pokerIndex.get(i); //获取每一张牌
if (i >= 51) diPai.add(in); //最后三张给底牌
else if (i % 3 == 0) player01.add(in);
else if (i % 3 == 1) player02.add(in);
else if (i % 3 == 2) player03.add(in);
}
//4.给牌排序Collections.sort(List)默认是 升序排序
Collections.sort(player01);
Collections.sort(player02);
Collections.sort(player03);
Collections.sort(diPai);
//5.看牌
lookPoker("刘德华", poker, player01);
lookPoker("周润发", poker, player02);
lookPoker("周星驰", poker, player03);
lookPoker("底牌", poker, diPai);
}
//定义一个看牌方法,提高代码复用性
//查表法: 便利玩家或者底牌集合,获取牌的索引
// 使用牌的索引,去Map集合中,找到对应的牌
public static void lookPoker(String name, HashMap<Integer, String> poker, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
//输出玩家名称
System.out.print(name + ": ");
for (Integer key : list) {
//使用牌的索引,去Map集合中,找到对应的牌
String value = poker.get(key);
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();//打印完每个玩家 再换行
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:软工菜鸡,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/SElearner/p/17676723.html

























 Map 遍历 (2)
Map 遍历 (2)








 JDK9新特性:
JDK9新特性:

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号