异常与多线程
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Exception:
Exception:
![]()
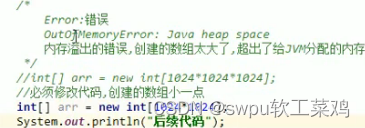
![]() Error:
Error:![]() 异常产生过程解析
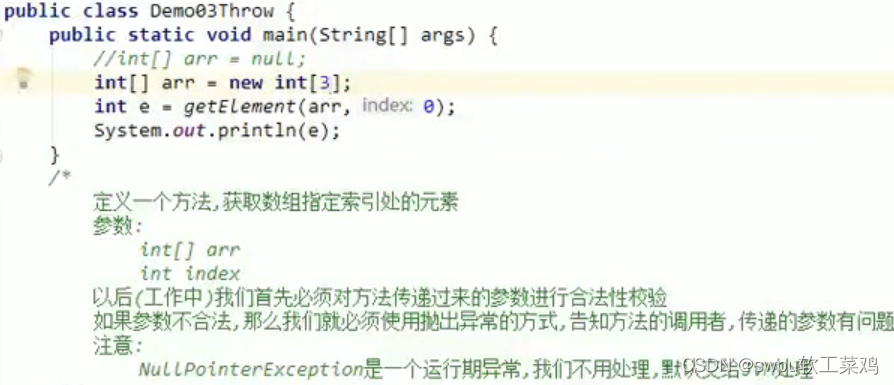
异常产生过程解析![]() 异常的处理 throw
异常的处理 throw![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 声明异常:throws
声明异常:throws
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 2.4捕获异常 try...catch 快捷键:Ctrl+Alt+t
2.4捕获异常 try...catch 快捷键:Ctrl+Alt+t
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 处理异常的方法
处理异常的方法
![]()
![]() finally代码块:
finally代码块:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=0;
String input ="";
while(true)
{
System.out.println("请输入一个整数: ");
input =sc.next();
try {
num=Integer.parseInt(input);//这里有可能抛出异常
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("你输入的不是一个整数");
}
}
System.out.println("你输入的值是: "+num);
}
}
异常注意事项:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import java.util.Scanner;
public class exception {
static String[] usernames = {"张三", "李四", "王五"};
public static void main(String[] args) throws RegisterException {
//使用Scanner获取用户输入的注册的用户名(前端,页面)
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您注册的用户名: ");
String username = sc.next();
checkUsername(username);
}
//定义一个方法,对用户输入的注册用户名进行决断
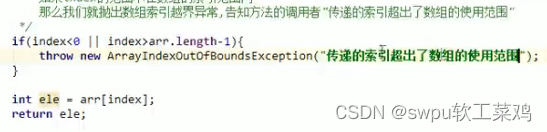
public static void checkUsername(String username) throws RegisterException {
for (int i = 0; i < usernames.length; i++) {
if (username.equals(usernames[i])) {
//用户名已经存在,抛出registerException异常
throw new RegisterException("亲,该用户名已经被注册");
}
}
System.out.println("恭喜您!注册成功");
}
}
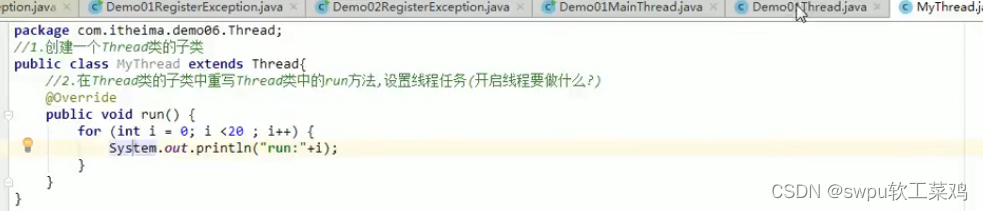
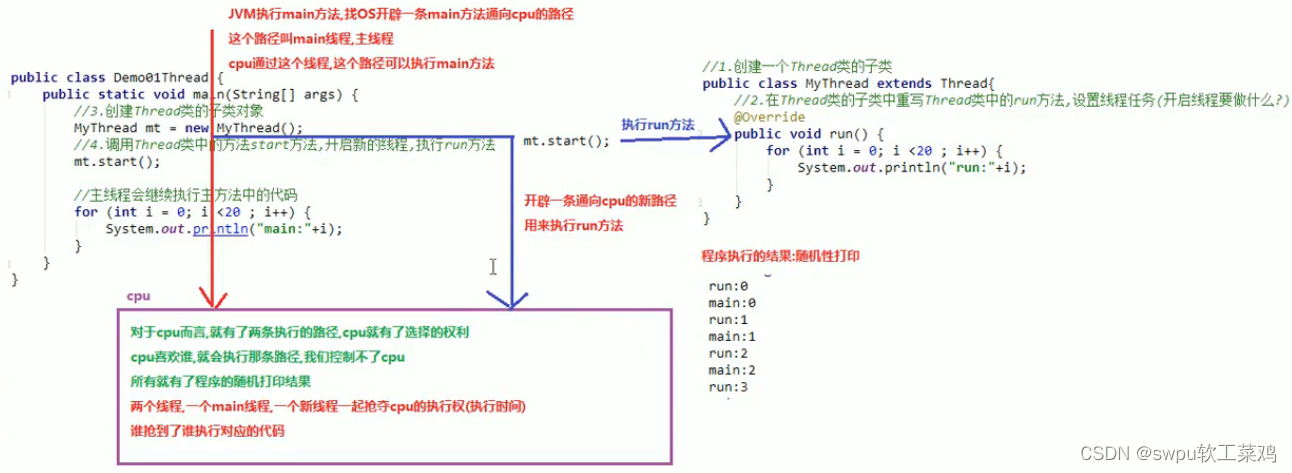
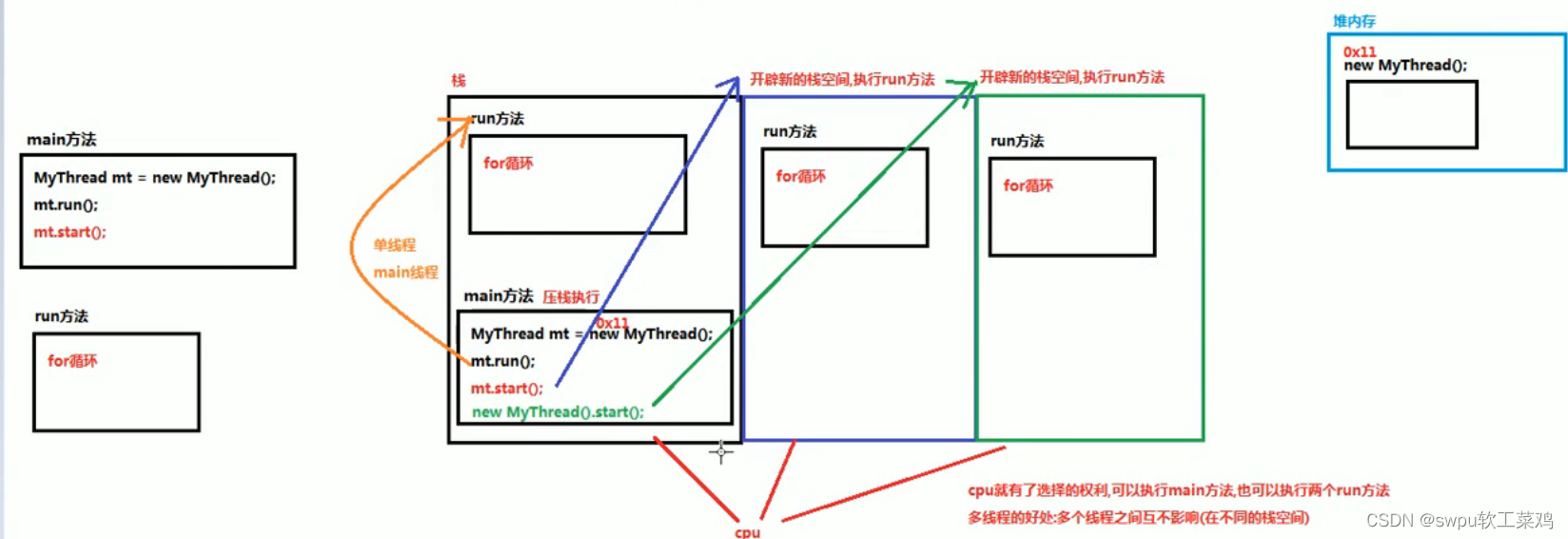
多线程 ! ![]() 线程与进程
线程与进程![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
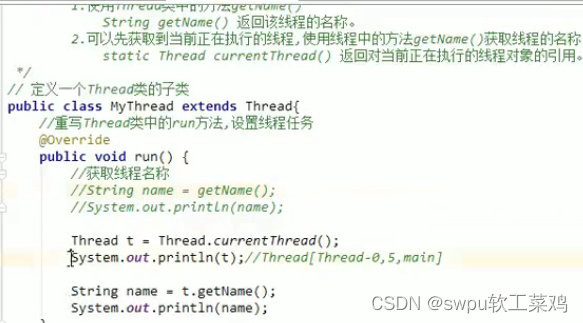
Thread类:
![]()
获取当前线程的名称: 设置线程的名称(了解):
![]()
![]()
sleep(本身有异常)
![]()
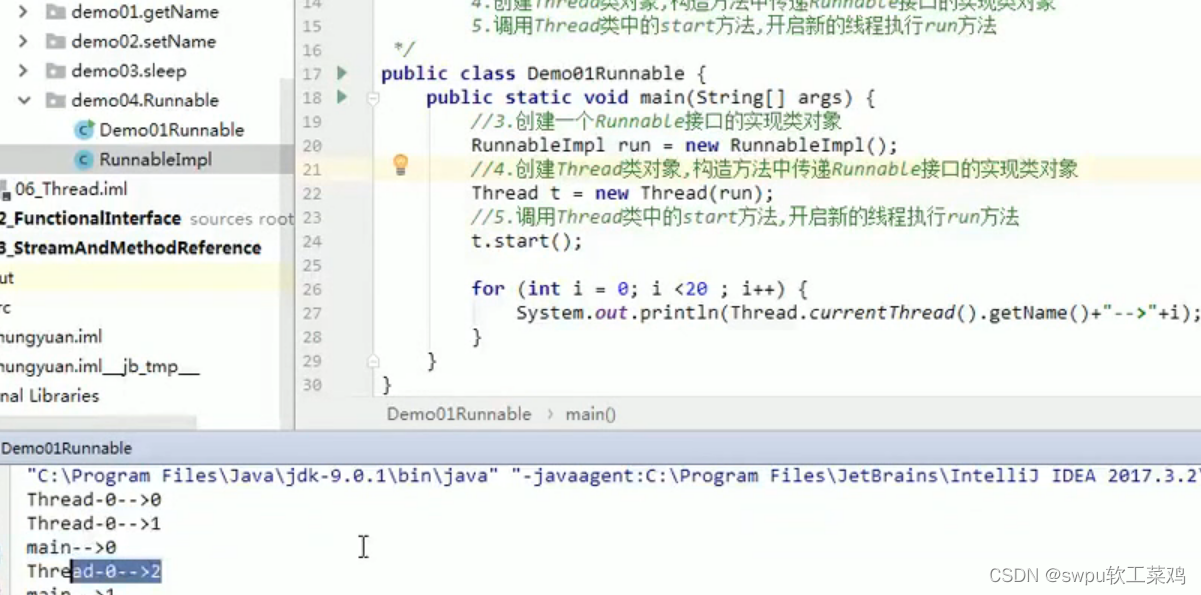
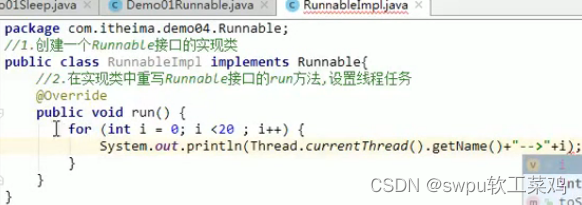
创建多线程程序的第二种方式:实现Runnable接口![]()
![]()
![]()
1.4Thread和Runnable的区别
![]()
![]()
1.5匿名内部类方式实现线程的创建
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
public static void main(String[] args) {
t1 t1 = new t1();
t2 t2 = new t2();
Thread T1 = new Thread(t1);
Thread T2 = new Thread(t2);
T1.start();
T2.start();
}
}
class t1 implements Runnable {
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello " + (++count));
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (count == 10)
break;
}
}
}
class t2 implements Runnable {
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hi " + (++count));
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (count == 5)
break;
}
}
}线程常用方法


yield(根据 内核态 资源是否紧张 决定的)在 资源紧张的时候 礼让成功的概率更大
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T t = new T();
Thread Thread1 = new Thread(t);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Hi" + i);
if (i == 5) {
Thread1.start();
Thread1.join();
}
}
System.out.println("主线程结束");
}
}
class T implements Runnable {
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello " + (++count));
try {
sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (count == 10) {
//System.out.println("子线程结束");
break;
}
}
}
}
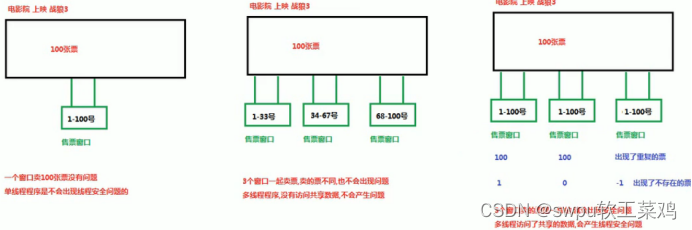
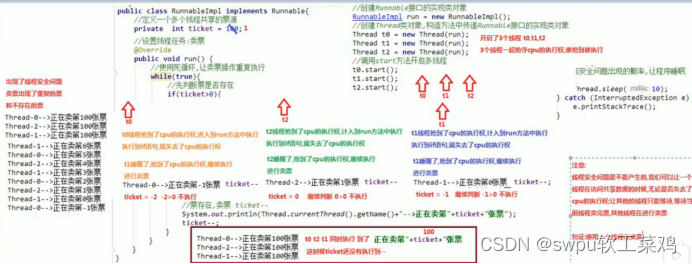
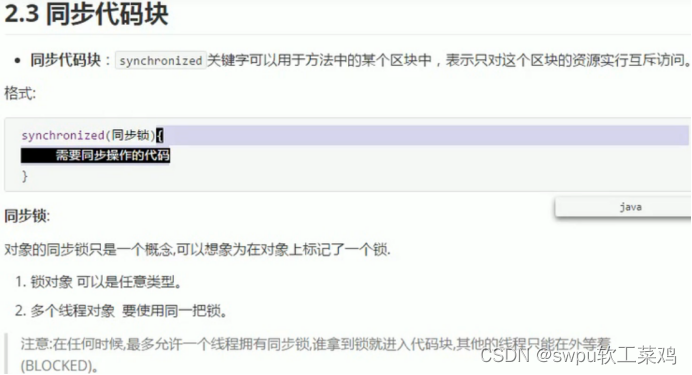
第二章 线程安全 (多线程访问共享数据)
![]()
![]()
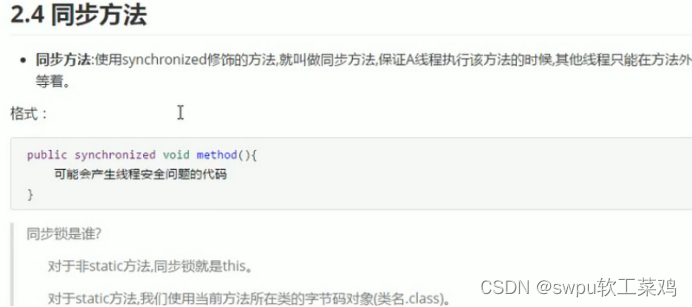
2.2解决线程安全问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws exception {
ThreadA a = new ThreadA();
Thread t1 = new Thread(a);
Thread t2 = new Thread(a);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
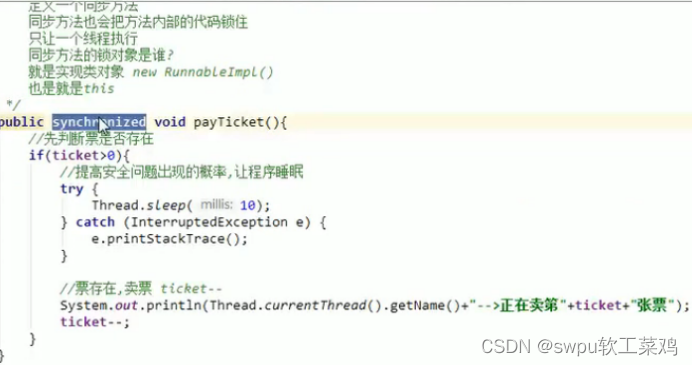
class ThreadA extends Thread {
private boolean flag = true;
private int amount = 10000;
public synchronized void get() {
if (amount <= 1000) {
System.out.println("余额不足1000元");
flag = false;
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取钱,余额:"
+ (amount -= 1000));
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
get();
}
}
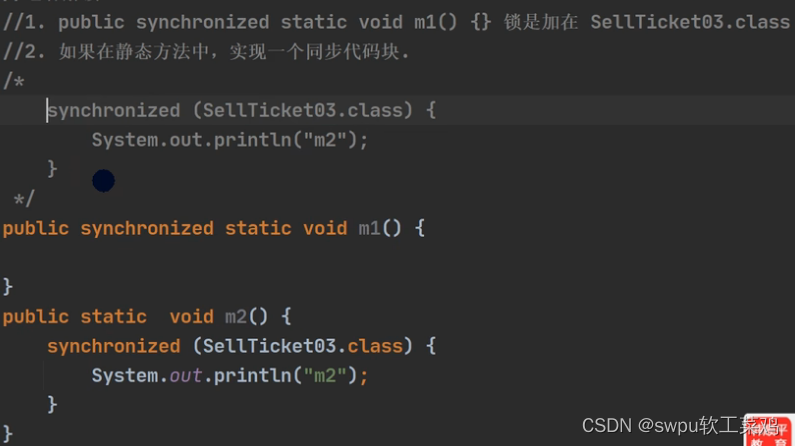
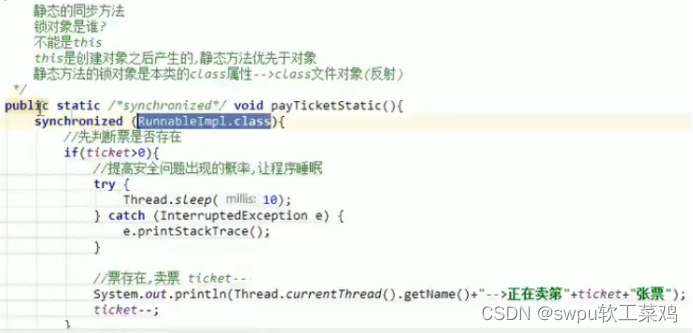
}为啥synchronized建议用Runnable而不是继承Thread???
![]()
![]()
线程的死锁
![]()
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟 死锁现象
deadLock A = new deadLock(true);
A.start();
deadLock B = new deadLock(false);
B.start();
}
}
class deadLock extends Thread {
static Object o1 = new Object();//多线程使用static 共享一个对象
static Object o2 = new Object();
boolean flag;
public deadLock(boolean flag) {//构造器
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//下面业务逻辑的分析:
//1. if(flag)=T, 线程A就会得到o1对象锁,然后尝试获取o2对象锁
//2.如果线程A得不到o2对象锁,就会Blocked阻塞
//3. if(flag)=F, 线程B就会得到o2对象锁,然后尝试获取o1对象锁
//4.如果线程B得不到o1对象锁,就会Blocked
//5.此业务 极有可能 阻塞 死锁
if (flag) {
synchronized (o1) {//对象互斥锁,下面就是同步代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进入1");
synchronized (o2) {//获得l1对象的监事权
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"进入2");
}
}
} else {
synchronized (o2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"进入3");
synchronized (o1) {//获得l3对象的监事权
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"进入4");
}
}
}
}
}import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T t = new T();
new Thread(t).start();
new Thread(t).start();
new Thread(t).start();
}
}
//使用synchronized实现线程同步
class T implements Runnable {
private int count = 50;
private boolean loop = true;
public synchronized void sell() {//同步方法 同一时刻 只有一个线程执行
if (count <= 0) {
System.out.println("售票结束...");
loop=false;
return;
}
try {
sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("窗口" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"售出一张票,剩余" + (--count) + "张票");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (loop) {
sell();
}
}
}
线程终止
![]()
//启动一个线程t,要求在main线程中 停止线程t
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T t = new T();
t.start();
//希望main线程去控制t1的终止,必须可以修改loop
//t退出 run 方法,聪儿终止t线程->通知方式
//主线程休眠5秒,再通知 t1线程退出
System.out.println("主线程休眠");
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
t.setLoop(false);
}
}
class T extends Thread {
private static int count = 0;
//设置 控制变量
private boolean loop = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (loop) {
try {
sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程运行===" + (++count));
}
}
public void setLoop(boolean b) {
this.loop = b;
}
}用户线程和 守护线程 在主方法里setDaemon(true);
![]()
![]()
![]()
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadA A = new ThreadA();
ThreadB B = new ThreadB(A);
A.start();
B.start();
}
}
class ThreadA extends Thread {
boolean flag = true;
public void setflag(boolean flag) {//构造器
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
System.out.println((int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1));
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class ThreadB extends Thread {
private Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
private ThreadA a;
public ThreadB(ThreadA a) {
this.a = a;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入你的指令");
char n = sc.next().toUpperCase().charAt(0);
if (n == 'Q') {
a.setflag(false);
System.out.println("B线程退出");
break;
}
}
}
}2.5Lock锁
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
线程状态 Waiting(无限等待):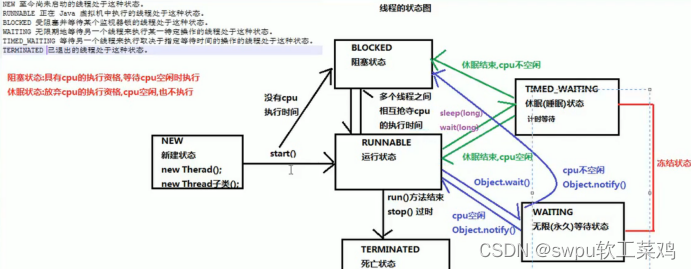



public class WaitAndNotify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建锁对象,保证唯一
Object obj = new Object();
//创建一个顾客线程(消费者)
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
//保证等待和唤醒的线程只能有一个执行,需要使用同步技术
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("告知老板要的包子种类和数量");
//调用wait方法,放弃cpu的执行,进入到WAITING状态(无限等待)
try {
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//唤醒之后执行的代码
System.out.println("包子已经做好了,开吃");
}
}
}.start();
//创建一个老板线程(生产者)
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
//花了5秒做包子
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//保证等待和唤醒的线程只能有一个执行,需要使用同步技术
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("老板5秒之后做好包子,告知顾客");
//调用wait方法,放弃cpu的执行,进入到WAITING状态(无限等待)
obj.notify();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
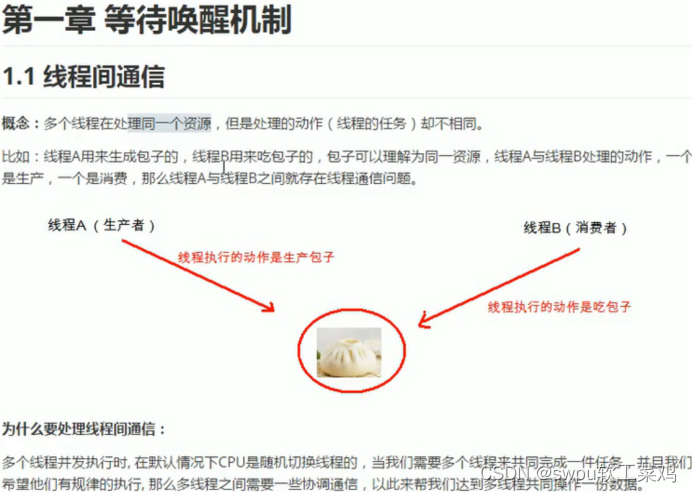
线程间通信
![]()
![]()
等待唤醒机制
![]()
![]()
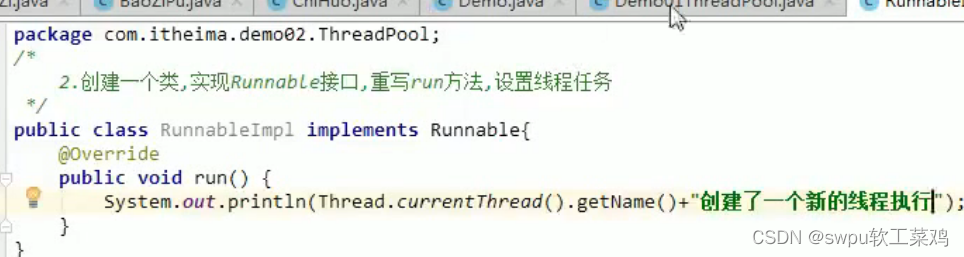
![]() 线程池
线程池
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
本文来自博客园,作者:软工菜鸡,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/SElearner/p/17676722.html


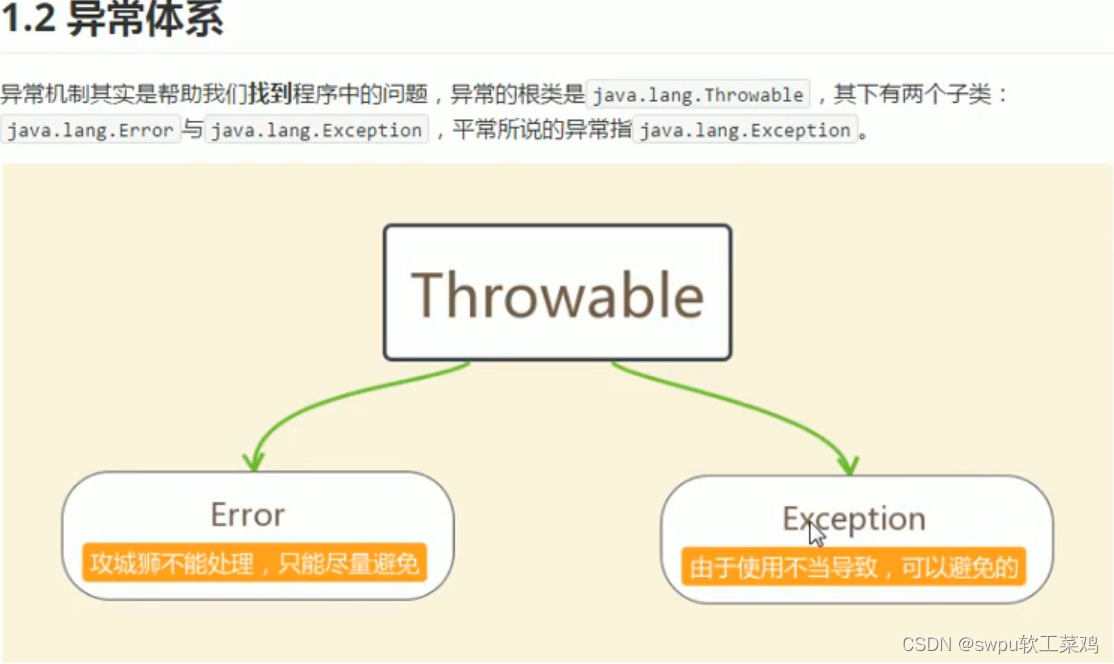



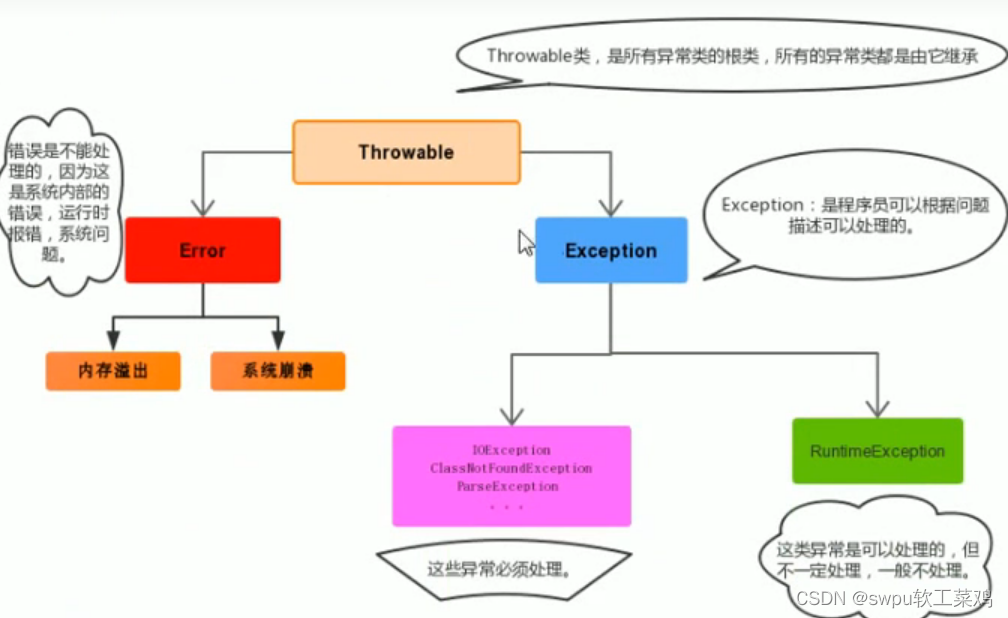
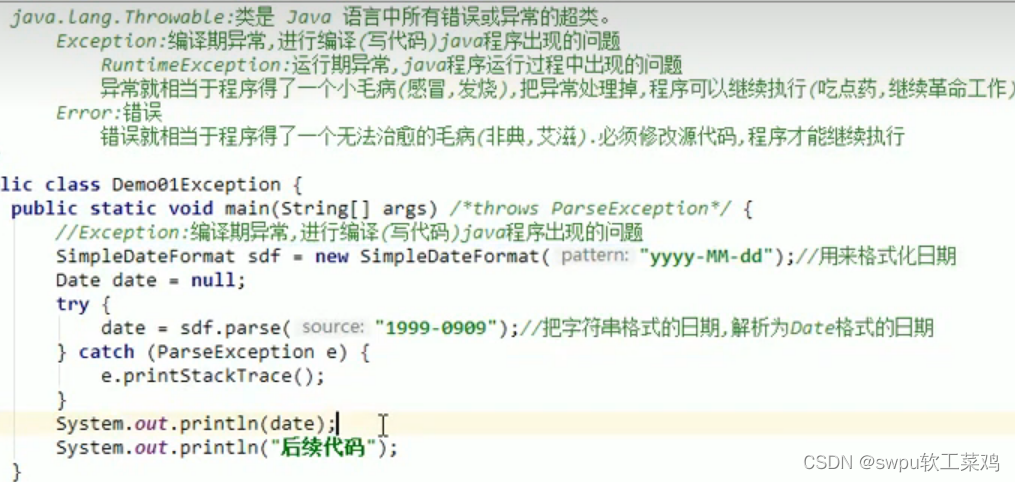
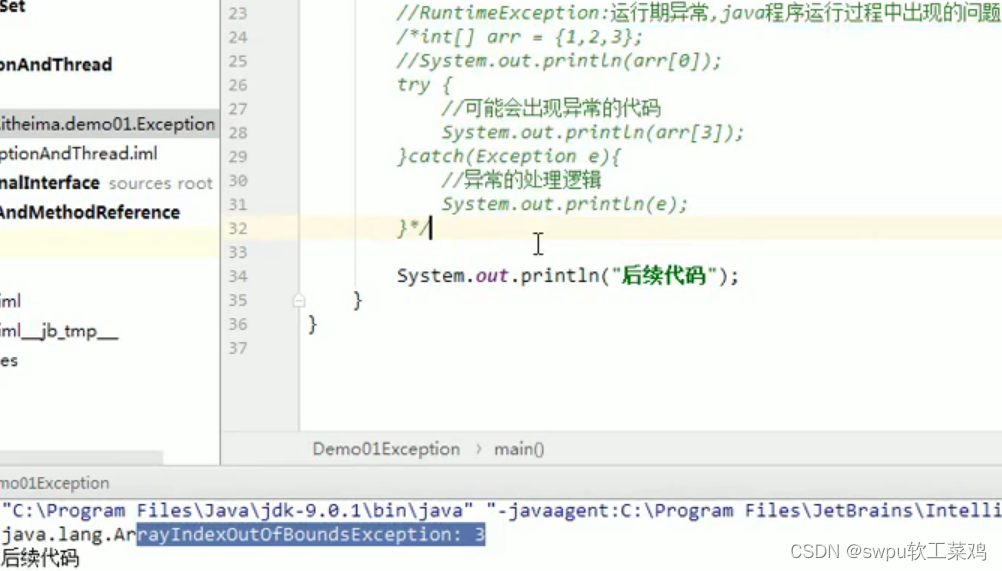
 异常产生过程解析
异常产生过程解析


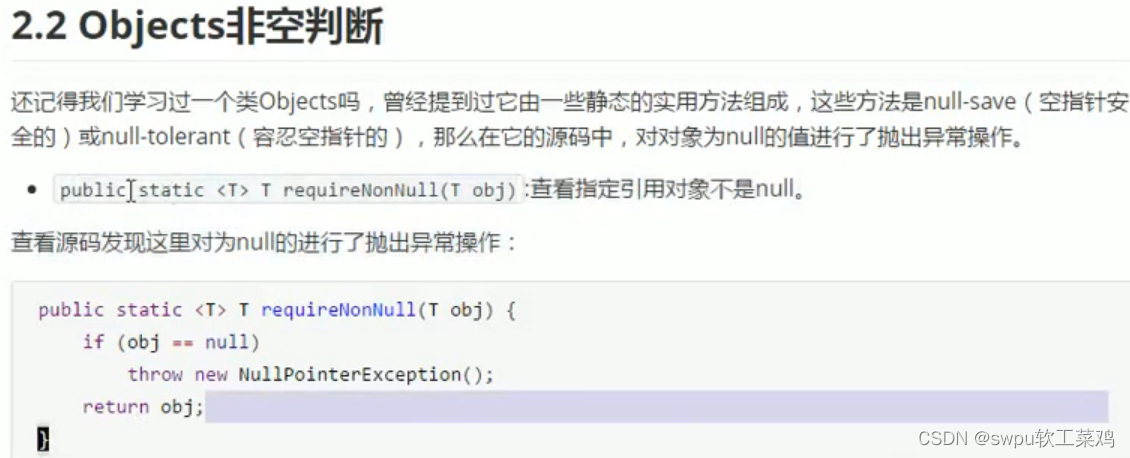
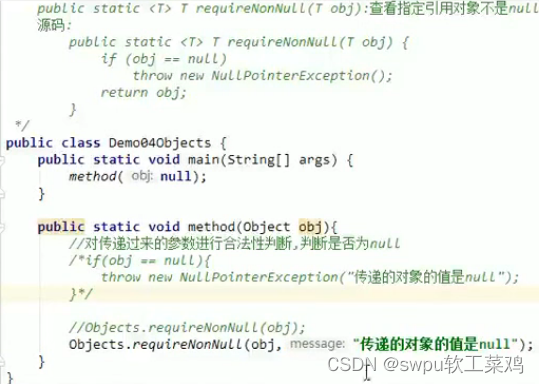 声明异常:throws
声明异常:throws


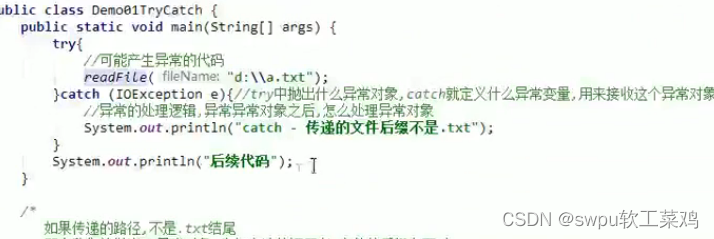
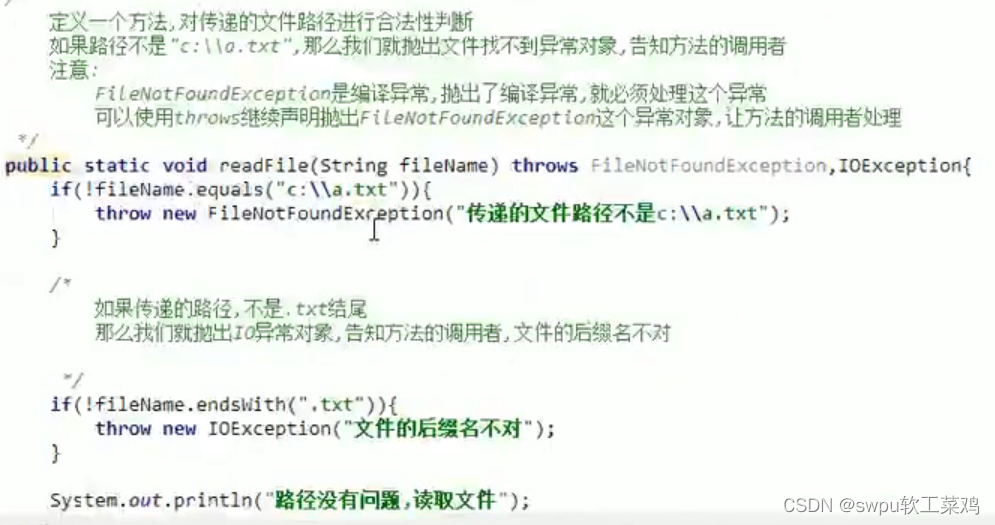 2.4捕获异常
2.4捕获异常 

 处理异常的方法
处理异常的方法
 finally代码块:
finally代码块:







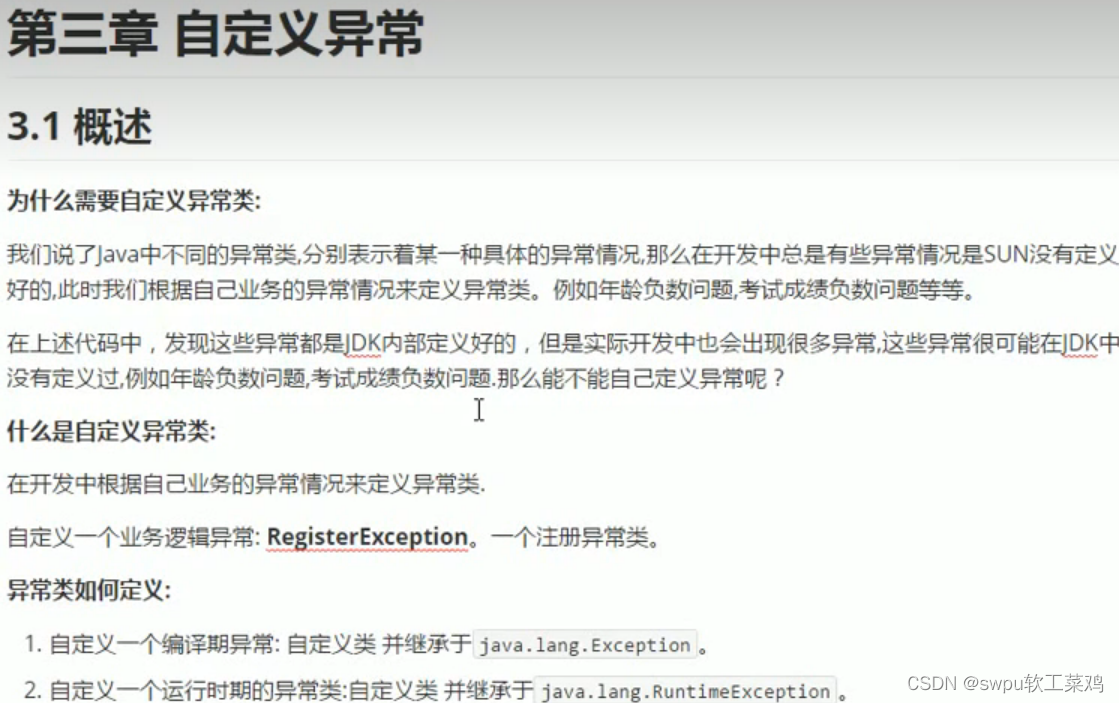


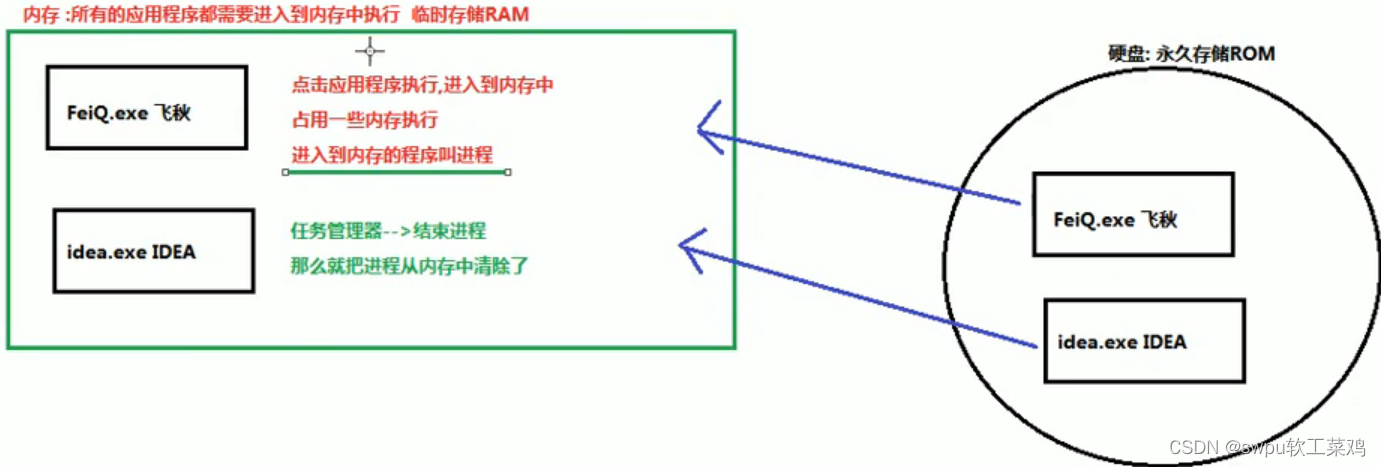
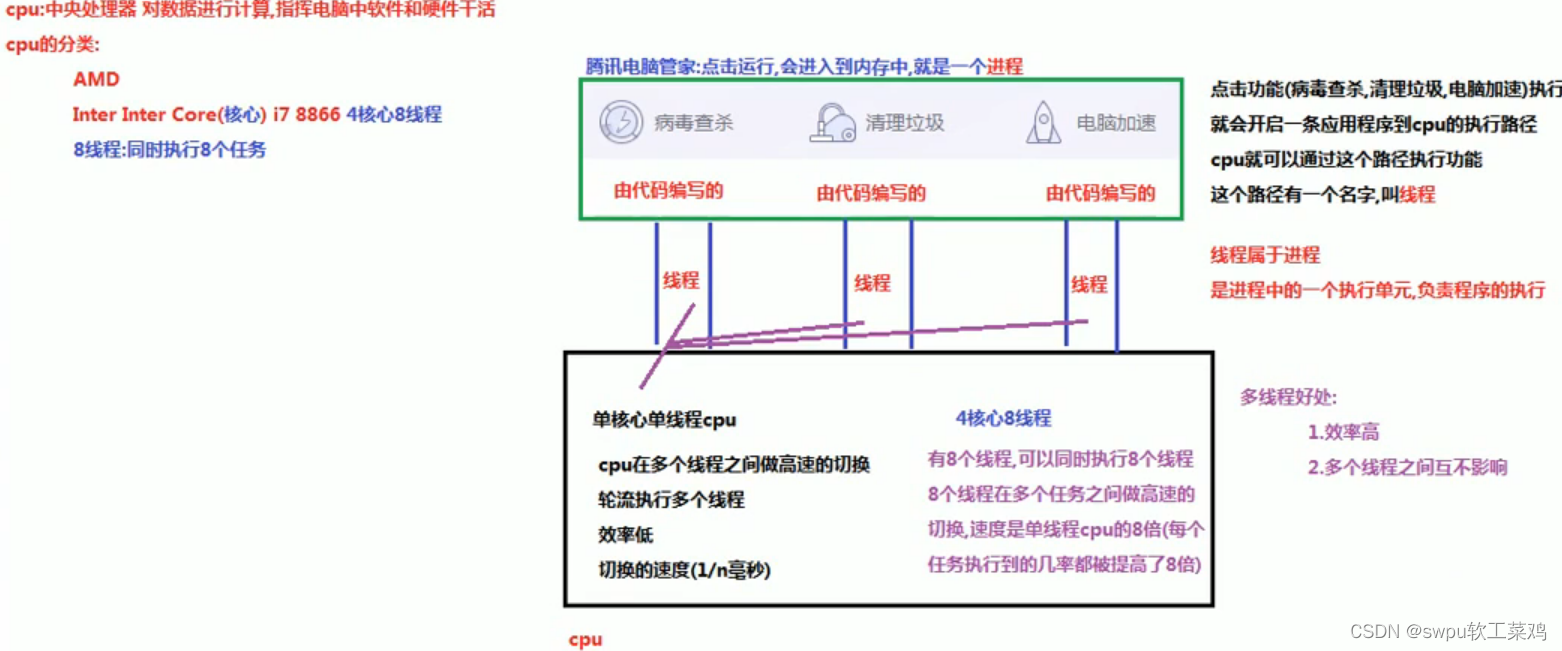
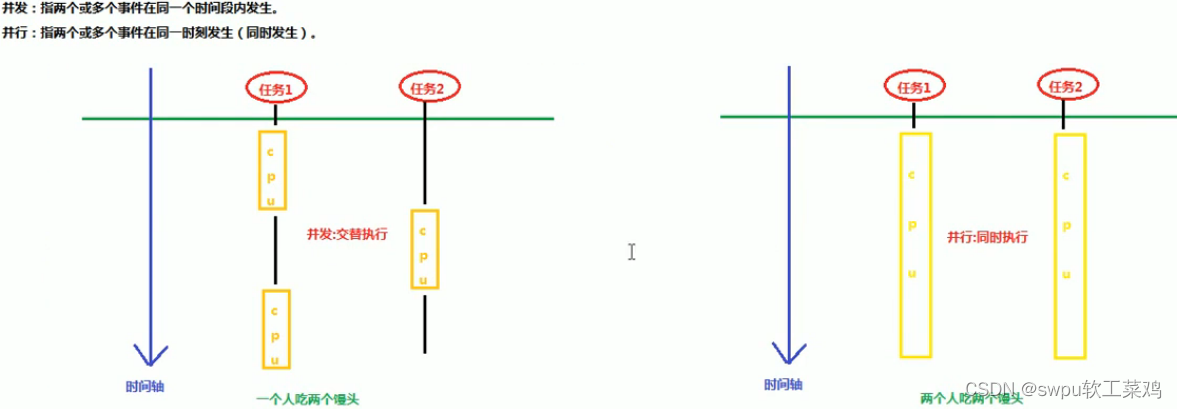 线程与进程
线程与进程




























 线程池
线程池





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号