C++继承 多态 文件操作 职工管理系统 提高编程阶段 模板 STL初识 string容器 vector容器 deque容器
类和对象-继承-基本语法
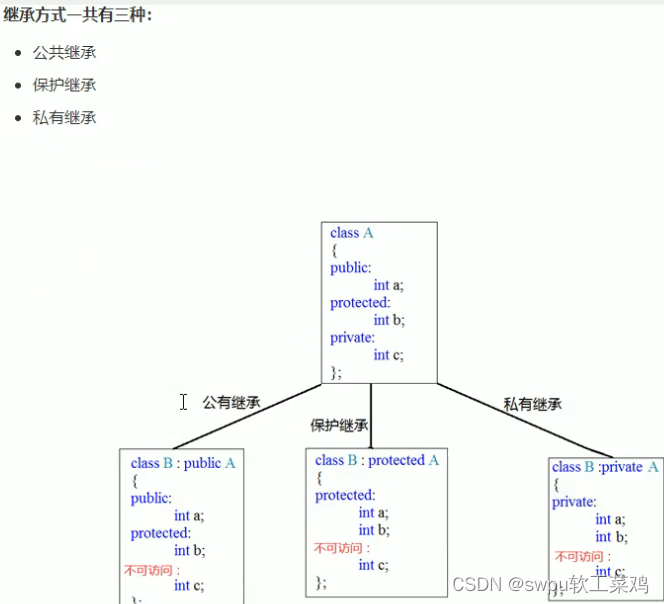
类和对象-继承-继承方式
![]()
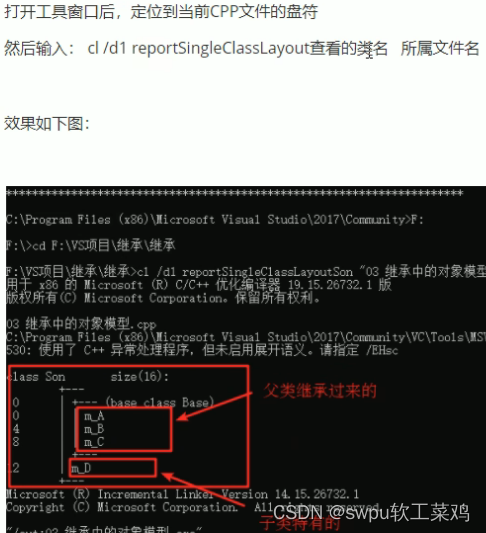
类和对象-继承-继承中的对象模型
父类中非静态成员属性都会被继承![]()
![]()
类和对象-继承-构造和析构顺序
![]()
![]()
类和对象-继承-同名成员处理
![]()
![]()
![]()
类和对象-继承-同名静态成员处理
![]()
![]()
类和对象-继承-继承语法
![]()
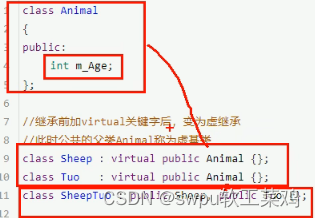
类和对象-继承-菱形继承问题以及解决方法
![]()
![]()
![]()
类和对象-多态-多态的基本语法
![]()
![]()
类和对象-多态-多态的原理剖析
类和对象-多态-案例1-计算器类![]()
![]()
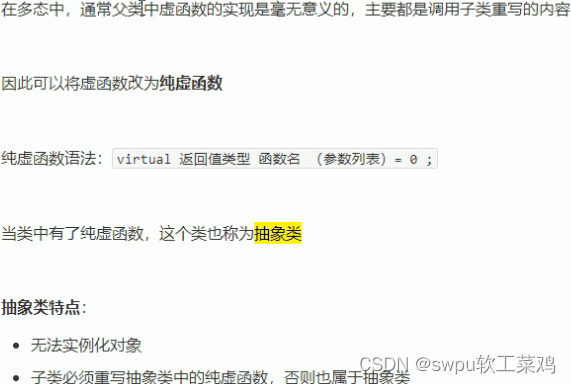
类和对象-多态-纯虚函数和抽象类
![]()
类和对象-多态-案例2-制作饮品
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class AbstactDrinking {
public:
//煮水
virtual void Boil() = 0;
//冲泡
virtual void Brew() = 0;
//倒入
virtual void PourInCup() = 0;
//加作料
virtual void PutSomething() = 0;
//制作饮品
void makeDrink() {
Boil();
Brew();
PourInCup();
PutSomething();
}
};
//制作咖啡
class Coffee :public AbstactDrinking {
public:
//煮水
virtual void Boil() {
cout << "煮农夫山泉" << endl;
}
//冲泡
virtual void Brew() {
cout << "冲泡咖啡" << endl;
}
//倒入
virtual void PourInCup() {
cout << "倒入杯中" << endl;
}
//加作料
virtual void PutSomething() {
cout << "加入咖啡作料" << endl;
}
//制作饮品
void makeDrink() {
Boil();
Brew();
PourInCup();
PutSomething();
};
};
//制作茶水
class Tea :public AbstactDrinking {
public:
//煮水
virtual void Boil() {
cout << "煮百岁山" << endl;
}
//冲泡
virtual void Brew() {
cout << "冲泡茶水" << endl;
}
//倒入
virtual void PourInCup() {
cout << "倒入杯中" << endl;
}
//加作料
virtual void PutSomething() {
cout << "加入茶作料" << endl;
}
//制作饮品
void makeDrink() {
Boil();
Brew();
PourInCup();
PutSomething();
};
};
void dowork(AbstactDrinking* abs) {
abs->makeDrink();
delete abs;
}
void test01() {
dowork(new Coffee);
cout << "-------------------" << endl;
dowork(new Tea);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}类和对象-多态-虚析构和纯虚析构
![]()
![]()
![]()
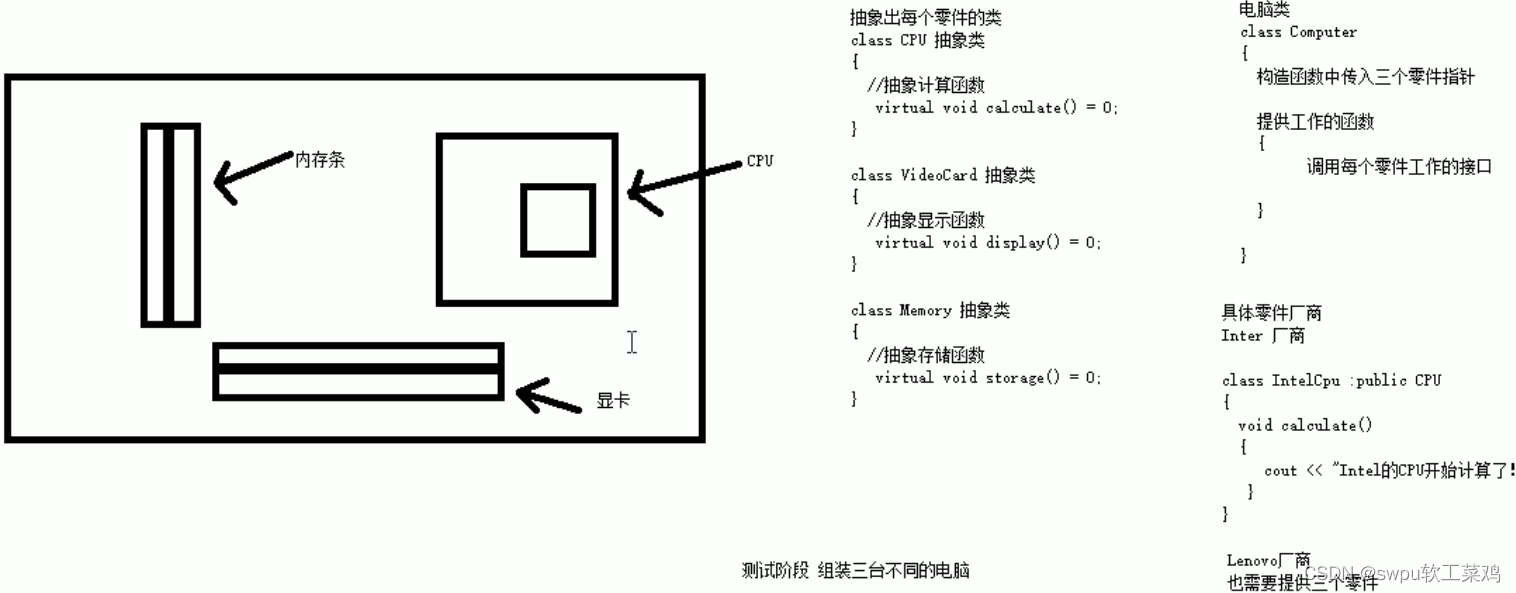
类和对象-多态-案例3-电脑组装具体案例
![]()
![]()
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CPU {
public:
//抽象计算函数
virtual void calculate() = 0;
};
class VideoCard {//显卡
public:
//抽象显示函数
virtual void display() = 0;
};
class Memory { //内存条
public:
//抽象存储函数
virtual void storage() = 0;
};
class Computer {
public:
//抽象存储函数
Computer(CPU * cpu, VideoCard* vc, Memory* mem) {
m_cpu=cpu;
m_vc = vc;
m_mem = mem;
}
void work() { //提供工作的函数
m_cpu ->calculate();
m_vc ->display();
m_mem ->storage();
}
~Computer() {
//析构函数 释放零件
if (m_cpu != NULL) {
delete m_cpu;
m_cpu = NULL;
}
if (m_vc != NULL) {
delete m_vc;
m_vc = NULL;
}
if (m_mem != NULL) {
delete m_mem;
m_mem = NULL;
}
}
private:
CPU* m_cpu;
VideoCard* m_vc;
Memory * m_mem;
};
//具体厂商
class IntelCPU :public CPU {
public:
virtual void calculate() {
cout << "Intel的cpu开始计算了" << endl;
}
};
class IntelVideoCard :public VideoCard {
public:
virtual void display() {
cout << "Intel的VideoCard开始显示了" << endl;
};
};
class IntelMemory :public Memory {
public:
virtual void storage() {
cout << "Intel的Memory开始存储了" << endl;
}
};
//Lenovo
class LenovoCPU :public CPU {
public:
virtual void calculate() {
cout << "Lenovo的cpu开始计算了" << endl;
}
};
class LenovoVideoCard :public VideoCard {
public:
virtual void display() {
cout << "Lenovo的VideoCard开始显示了" << endl;
};
};
class LenovoMemory :public Memory {
public:
virtual void storage() {
cout << "Lenovo的Memory开始存储了" << endl;
}
};
void test01() {
//第一台电脑
CPU* intelCPU = new IntelCPU;
VideoCard* intelCard = new IntelVideoCard;
Memory* intelMem = new IntelMemory;
//创建第一台电脑
Computer* computer1 = new Computer(intelCPU, intelCard, intelMem);
computer1->work();
delete computer1;
cout << "-------------------" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
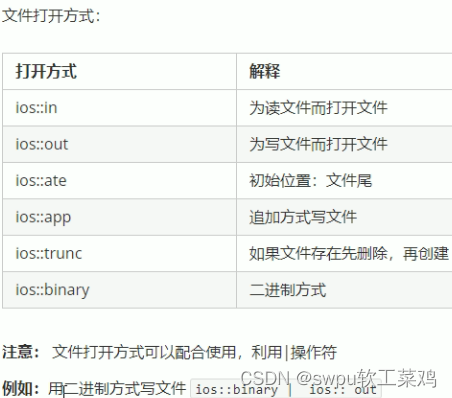
}文件操作-文本文件-写文件
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
文件操作-文本文件-读文件
![]()
![]()
//4.读数据
//第一种
char buf[1024]={ 0 };
while(ifs>>bud){
cout<<buf<<endl;
}
//第二种
char buf[1024]={ 0 };
while(ifs.getline(buf,sizeof(buf) ){
cout<<buf<<endl;
}
//第三种
#include<string>
string buf;
while(getline(ifs,buf) ){
cout<<buf<<endl;
}
//第四种 不太推荐 把文件中的字符全读出来
char c;
while((c = ifs.get() ) != EOF) {//没读到文件尾 就一直读
cout<<c;
}
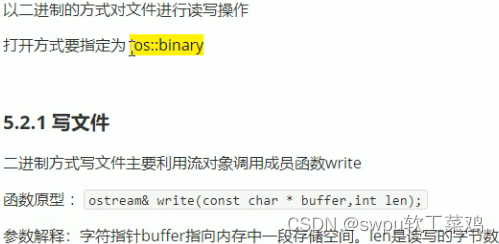
文件操作-二进制文件-写文件
![]()
![]()
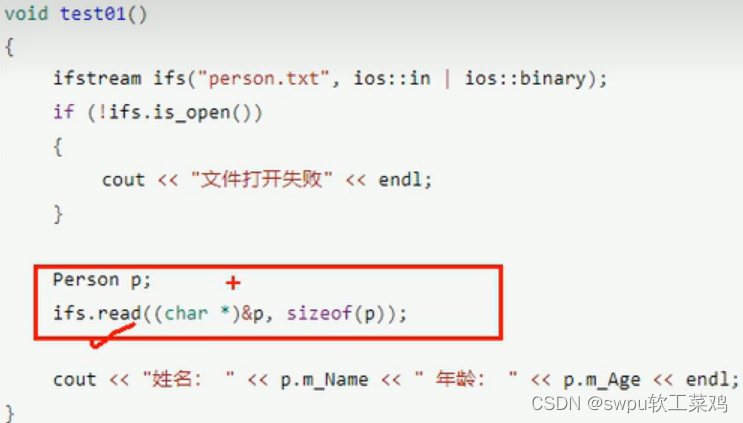
文件操作-二进制文件-读文件
![]()
![]()
P50 职工管理系统
![]()
本阶段主要针对
C++泛型编程和STL技术做详细讲解,探讨c++更深层的使用
模板-模板的概念
(模板就是建立通用的模具,大大提高复用性)![]()
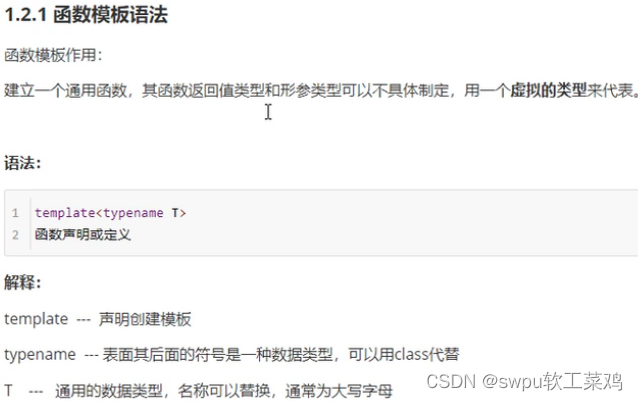
模板-函数模板基本语法
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
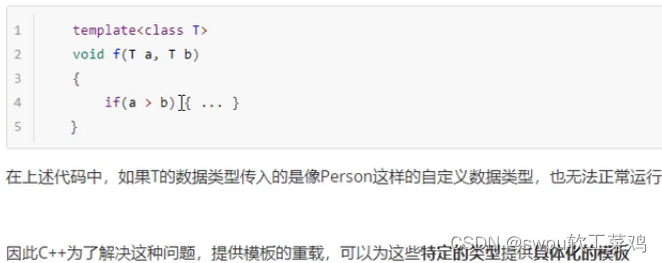
模板-函数模板注意事项
![]()
![]()
模板-函数模板案例-数组排序
模板-普通函数与函数模板区别![]()
![]()
模板-普通函数与函数模板调用规则
![]()
![]()
![]() 模板-模板的局限性
模板-模板的局限性
![]()
![]()
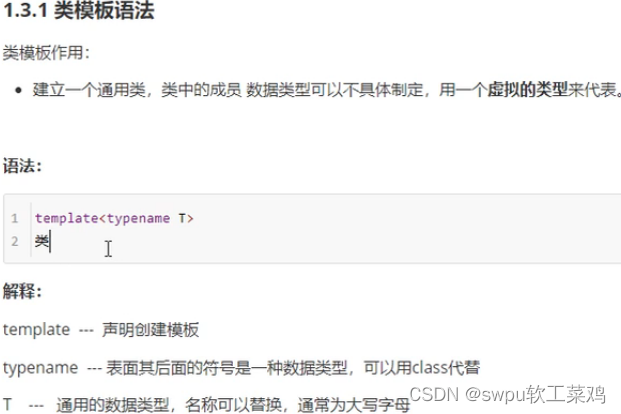
模板-类模板基本语法
![]()
模板-类模板与函数模板区别
![]()
![]()
模板-类模板中成员函数创建时机
![]()
模板-类模板对象做函数参数
![]()
![]()
![]()
模板-类模板与继承
如果父类是类模板,子类继承的时候需要指定父类中T的数据类型
![]()
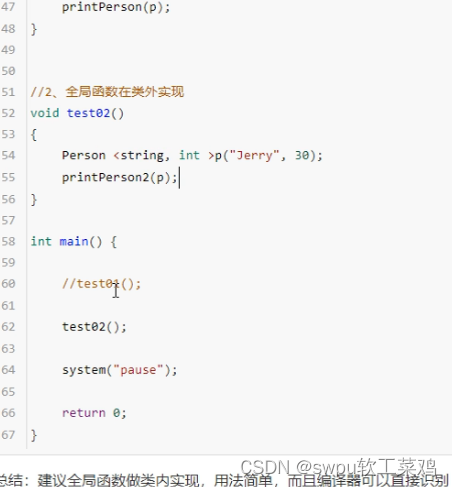
模板-类模板成员函数类外实现
学习目标:掌握类模板中的成员函数类外实现
![]()
模板-类模板分文件编写
![]()
![]()
模板-类模板与友元
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
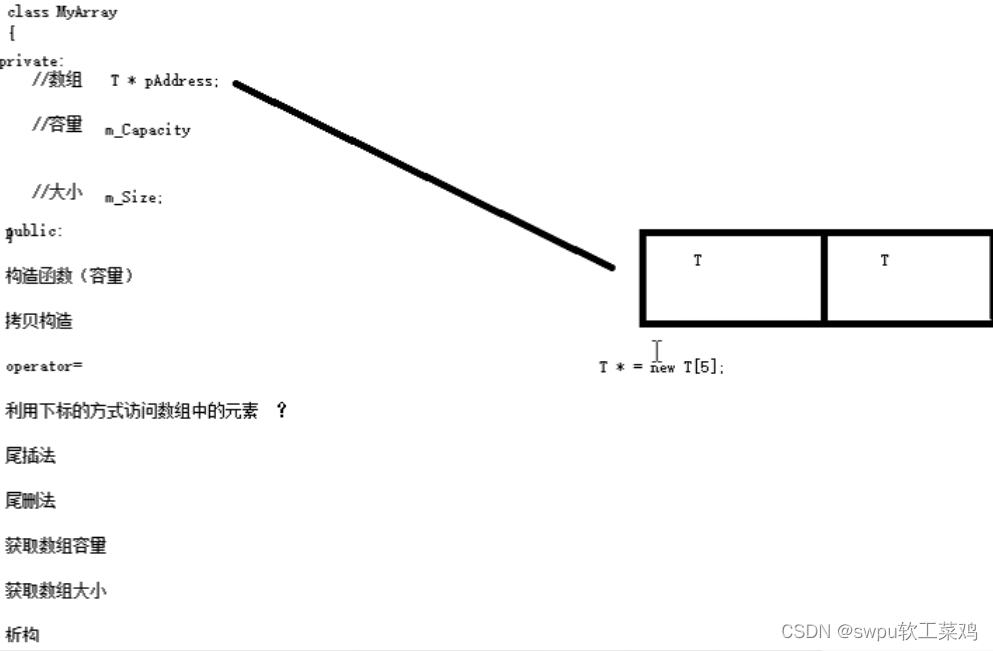
模板-类模板案例-数组类封装的需求分析
![]()
![]()
模板-类模板案例-数组类封装(上) 模板-类模板案例-数组类封装(下)
//自己通用的数组类 .hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class MyArray {
public:
//有参构造 参数 容量
MyArray(int capacity)
{
//cout << "Mtarray有参构造调用" << endl;
this->m_Capacity = capacity;
this->m_Size = 0;
this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity];
}
//拷贝构造 防止浅拷贝
MyArray(const MyArray& arr) {
//cout << "Mtarray拷贝构造调用" << endl;
this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;
this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;
//this->pAddress = arr.pAddress; 浅拷贝指针直接赋值 导致堆区数据重复放置
//深拷贝
this->pAddress=new T[arr.m_Capacity];
//将arr中的数据都拷贝过来
for (int i = 0; i < this->m_Size; i++)
{
this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];
}
}
//operator= 放止浅拷贝问题
MyArray& operator=(const MyArray& arr)
{
//cout << "Mtarray 的 operator调用" << endl;
//先判断原来堆区是否有数据, 如果有先释放
if (this->pAddress != NULL)
{
delete[] this->pAddress;
this->pAddress= NULL;
this->m_Capacity = 0;
this->m_Size = 0;
}
//深拷贝
this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;
this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;
this->pAddress = new T[arr.m_Capacity];
//将arr中的数据都拷贝过来
for (int i = 0; i < this->m_Size; i++)
{
this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];
}
}
//尾插法
void Push_Back(const T & val) {
if (this->m_Capacity == this->m_Size)//判满
{
return ;
}
this->pAddress[this->m_Size] = val; //在数组末尾插入数据
this->m_Size++;//更新数组大小
}
//尾删法
void Pop_Back(MyArray& arr) {
//让用户访问不到最后一个元素,即为尾删,逻辑删除
if (this->m_Size==0)//判空
{
return;
}
this->m_Size--;//更新数组大小
}
//通过下标的方式访问数组中的元素 arr[0]
T& operator[](int index)
{
return this->pAddress[index];
}
//返回数组容量
int getCap()
{
return this->m_Capacity;
}
//返回数组大小
int getSize()
{
return this->m_Size;
}
//析构函数
~MyArray()
{
if (this->pAddress != NULL) {
// cout << "Mtarray析构调用" << endl;
delete[] this->pAddress;
this->pAddress=NULL;
}
}
private:
T* pAddress; //指针指向堆区开辟的真实数组
int m_Capacity;//数组容量
int m_Size; //数组大小
};
//----------------------------------
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "MyArray.hpp"
#include <string>
void printIntArray(MyArray <int>& arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.getSize(); i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
}
void test01()
{
MyArray <int>arr1(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
arr1.Push_Back(i);//尾插法插入数组
}
cout << "arr1的打印输出:" << endl;
printIntArray(arr1);
cout << "arr1的容量:" <<arr1.getCap()<< endl;
cout << "arr1的大小:" <<arr1.getSize()<< endl;
MyArray<int> arr2(arr1);
arr2.Pop_Back(arr2);
cout << "arr2的容量:" << arr2.getCap() << endl;
cout << "arr2的大小:" << arr2.getSize() << endl;
printIntArray(arr2);
}
//测试自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person() {};
Person(string name, int age) {
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void printPersonArray(MyArray <Person>& arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.getSize(); i++)
{
cout <<"姓名: "<< arr[i].m_Name<<"年龄: "<<arr[i].m_Age << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
MyArray<Person> arr(10);
Person p1 ("孙悟空", 999);
Person p2 ("韩信",30 );
Person p3 ("妲己", 20);
Person p4 ("赵云", 25);
Person p5 ("安其拉", 27);
//将数据插入到数组
arr.Push_Back(p1);
arr.Push_Back(p2);
arr.Push_Back(p3);
arr.Push_Back(p4);
arr.Push_Back(p5);
printPersonArray(arr);
cout << "arr的容量:" << arr.getCap() << endl;
cout << "arr的大小:" << arr.getSize() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
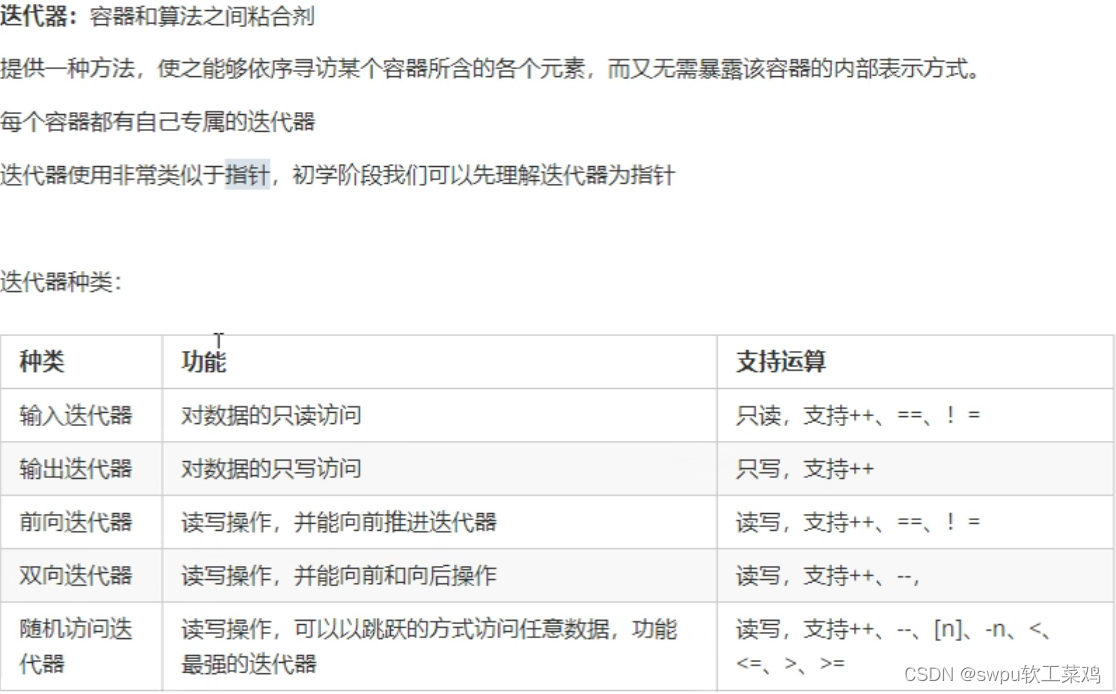
}STL初识-STL的基本概念
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
常用容器中 迭代器种类为双向迭代器和随机访问迭代器
STL初识-Vector存放内置数据类型
![]()
![]()
![]()
STL初识-Vector存放自定义数据类型
STL初识-容器嵌套容器
string容器-构造函数
![]()
![]()
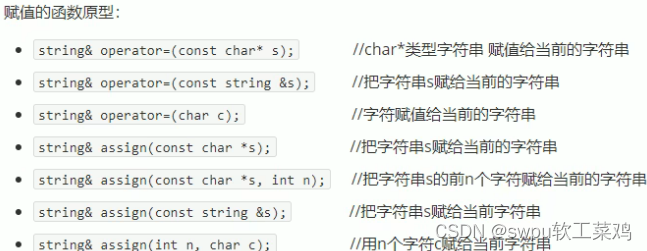
string容器-赋值操作
![]()
string容器-字符串拼接
![]()
string容器-字符串查找和替换
![]()
string容器-字符串比较
![]()
string容器-字符存取![]()
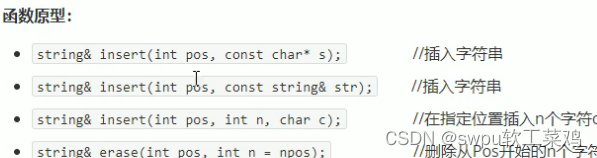
string容器-字符串插入和删除![]()
string容器-子串获取 (pos,npos); 包左不包右
![]()
vector容器-构造函数 (单端数组) 最常用的容器之一
![]()
![]()
![]()
vector容器-赋值操作
![]()
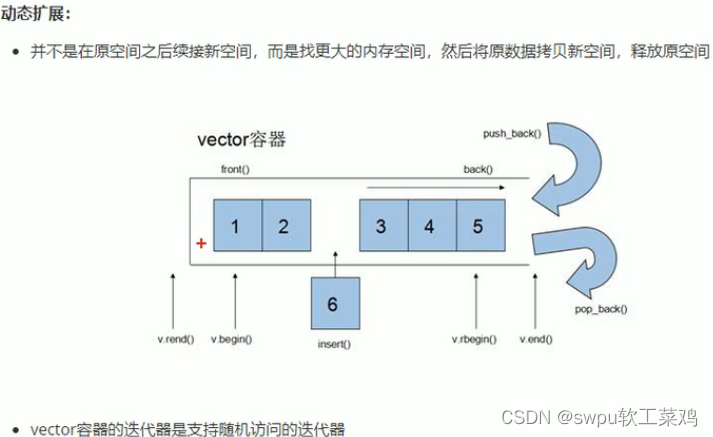
vector容器-容量和大小
![]()
vector容器-插入和删除![]()
![]()
vector容器-数据存取
![]()
vector容器-互换容器
![]()
![]()
vector容器-预留空间
![]()
![]()
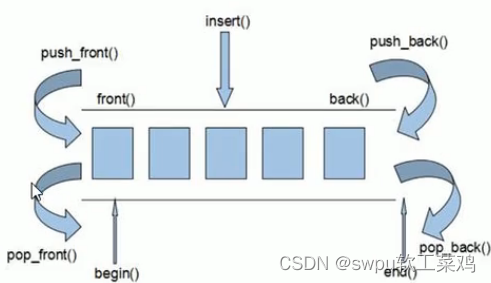
deque容器-构造函数 双端数组 访问慢 删改快 迭代器也支持随机访问
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
deque容器-赋值操作
![]()
deque容器-大小操作
![]()
deque容器-插入和删除
![]()
deque容器-数据存取
![]()
deque容器-排序操作
![]()
STL 案例1-评委打分
![]()
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
class Person {//选手类
public:
Person(string name, int score) {
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Score = score;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Score;
};
void createPerson(vector<Person>& v)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
string name = "选手";
name += nameSeed[i];
int score = 0;
Person p(name, score);
//将创建的person对象 放入到容器中
v.push_back(p);
}
}
void setScore(vector<Person>& v) {
for (vector<Person> ::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//将评委的分数 放入到 deque容器
deque <int> d;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int score =rand() %41 +60 ;//60~100的随机打分
d.push_back(score);
}
//cout << "选手: " << it->m_Name << "打分: " << endl;
//for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)
//{
//cout<< *dit<<" ";
//}cout<< endl;
//平均分 取最高最低
sort(d.begin(), d.end());
d.pop_back();
d.pop_front();
//取平均数
int sum = 0;
for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)
{
sum += *dit;
}
int avg = sum / d.size();
//将平均分赋值
it->m_Score = avg;
}
}
void showScore(vector<Person>& p) {
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = p.begin(); it != p.end(); it++) {
cout << "选手: " << it->m_Name << "平均分: " <<it->m_Score<< endl;
}
}
int main()
{
//随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1.创建5名选手
vector<Person> v;
createPerson(v);
//for (vector<Person> ::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
//{
// cout << "姓名: " << (*it).m_Name << "分数: " << (*it).m_Score << endl;
//}
//2.给5名选手打分
setScore(v);
//3.显示最后得分
showScore(v);
system("pause");
return 0;
}本文来自博客园,作者:软工菜鸡,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/SElearner/p/17676720.html








































































 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号