ACWing算法基础课(1) 快排 归并 二分 高精度
y总说 java不能用Scanner读入,要用Buffer.read();快十倍二十倍;
y总19年5月的视频,牛13!
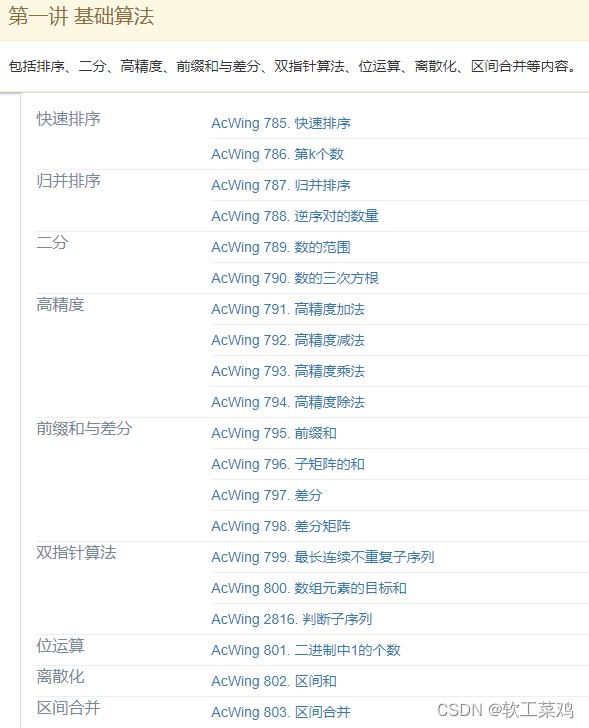
第一讲 基础算法
包括排序、二分、高精度、前缀和与差分、双指针算法、位运算、离散化、区间合并等内容。
快速排序
一定要先移动end(就是把大数移到右边),后移动start;
否则 先找小数,会出现end start重合位置大于基准数,在交换位置就左边不全是小数了!
处理大数据最快的排序算法之一
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
/*
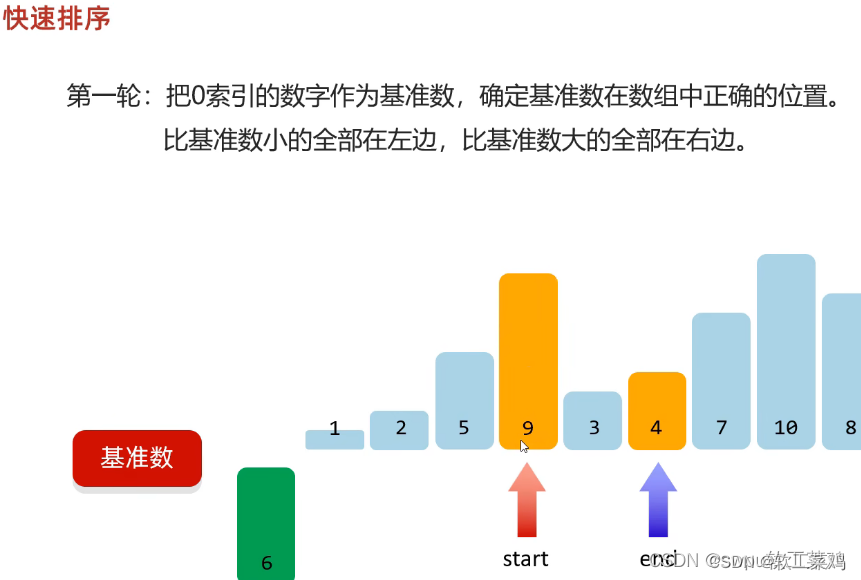
快速排序:
第一轮:以0索引的数字为基准数,确定基准数在数组中正确的位置。
比基准数小的全部在左边,比基准数大的全部在右边。
后面以此类推。
*/
int[] arr = {1,1, 6, 2, 7, 9, 3, 4, 5, 1,10, 8};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//课堂练习:
//我们可以利用相同的办法去测试一下,选择排序,冒泡排序以及插入排序运行的效率
//得到一个结论:快速排序真的非常快。
}
/*
* 参数一:我们要排序的数组
* 参数二:要排序数组的起始索引
* 参数三:要排序数组的结束索引
* */
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
//定义两个变量记录要查找的范围
int start = i;
int end = j;
if(start > end){
//递归的出口
return;
}
//记录基准数
int baseNumber = arr[i];
//利用循环找到要交换的数字
while(start != end){
//利用end,从后往前开始找,找比基准数小的数字
//int[] arr = {1, 6, 2, 7, 9, 3, 4, 5, 10, 8};
while(true){
if(end <= start || arr[end] < baseNumber){
break;
}
end--;
}
System.out.println(end);
//利用start,从前往后找,找比基准数大的数字
while(true){
if(end <= start || arr[start] > baseNumber){
break;
}
start++;
}
//把end和start指向的元素进行交换
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
}
//当start和end指向了同一个元素的时候,那么上面的循环就会结束
//表示已经找到了基准数在数组中应存入的位置
//基准数归位
//就是拿着这个范围中的第一个数字,跟start指向的元素进行交换
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[start];
arr[start] = temp;
//确定6左边的范围,重复刚刚所做的事情
quickSort(arr,i,start - 1);
//确定6右边的范围,重复刚刚所做的事情
quickSort(arr,start + 1,j);
}
}三部排序
AcWing 785. 快速排序(模板)
快速排序属于分治算法,快速排序的算法步骤,用分治的思想
确定分界点,数组内任意一个值(这里建议取中点,即(l+r)/2);
调整区间,让x左边的数都小于x,右边的数都大于x;
递归处理左右两个区间,直到细分到不能细分
对于第二步的调整区间,具体就是弄两个指针,分别指向数组的左右边界;不断的向中间遍历,将遍历过程中左边比x大的数和右边比x小的数交换;直到i,j相遇。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] q = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){q[i] = sc.nextInt();}
quickSort(q, 0, n-1);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){System.out.print(q[i] + " ");}
}
public static void quickSort(int[] q, int l, int r){
if(l >= r) return;//边界l==r也可以
//先把基准 定在数组 中间 ,两侧指针的位置决定后面的边界写法
int x = q[l + r >> 1], i = l - 1, j = r + 1;
while(i < j){
do{i++;} while( q[i] < x );//>x的时候停
do{j--;} while( q[j] > x) ;//<x的时候停
if(i < j){//两个指针都停了还没相遇的话就交换
int t = q[i];
q[i] = q[j];
q[j] = t;
}
}
quickSort(q, l, j);
quickSort(q, j + 1, r);
}
}AcWing 786. 第k个数
太简单了就是输出arr[k-1];不写了
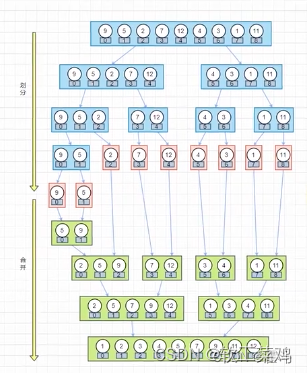
归并排序
具体思想:弄个临时数组,将有序的两个数组通过两个指针将数从小到大放入临时数组,然后再将临时数组里面已经排好序的数放回本数组那段位置。

先递归再合一
AcWing 787. 归并排序(模版)
import java.util.*;
class Main{
static int N=100010;//题目里给的数据不超过100000
static int[] a=new int[N];
static void merge_sort(int l,int r){
if(l>=r) return;
int mid=l+r>>1;//分成两半,
merge_sort(l,mid);
merge_sort(mid+1,r);
//合二为一
int[] h=new int[r-l+1];//结果数组
int idx=0,i=l,j=mid+1;//idx是结果数组的起始,双指针指向两半数组的起始
while(i<=mid&&j<=r){
//前面的指针值 和 后面的指针值 比较; 哪个小放哪个
if(a[i]<=a[j]) h[idx++]=a[i++];//=的时候取前面数组的值,保证位置的稳定性
else h[idx++]=a[j++];
}
while(i<=mid) h[idx++]=a[i++];//May i指针没走完,就把后面的补到结果数组
while(j<=r) h[idx++]=a[j++];//May j指针没走完,就把后面的补到结果数组
for(int k=l;k<idx;k++){
a[k]=h[k];//结果 区域数组赋值给 原数组+l,结果输出原数组
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = s.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){a[i] = s.nextInt();}
merge_sort(0,n-1);
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){System.out.print(a[i] + " ");}
}
//import java.io.*; //感觉快读挺危险的
// public static void main(String[]args)throws IOException{
// BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// int n=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
// String[]arr=in.readLine().split(" ");
// for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=Integer.parseInt(arr[i]);
// merge_sort(0,n-1);
// for(int i=0;i<n;i++) System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
// }
}AcWing 788. 逆序对的数量
最后返回一个Long res当右边a[j]>左边a[i]时,要res+=(mid-i+1);
二分查找
给定某个区间,在区间上定义了某种性质(check函数),使得整个区间一分为二,一个区间满足性质,另一个不满足,二分可以寻找性质的边界
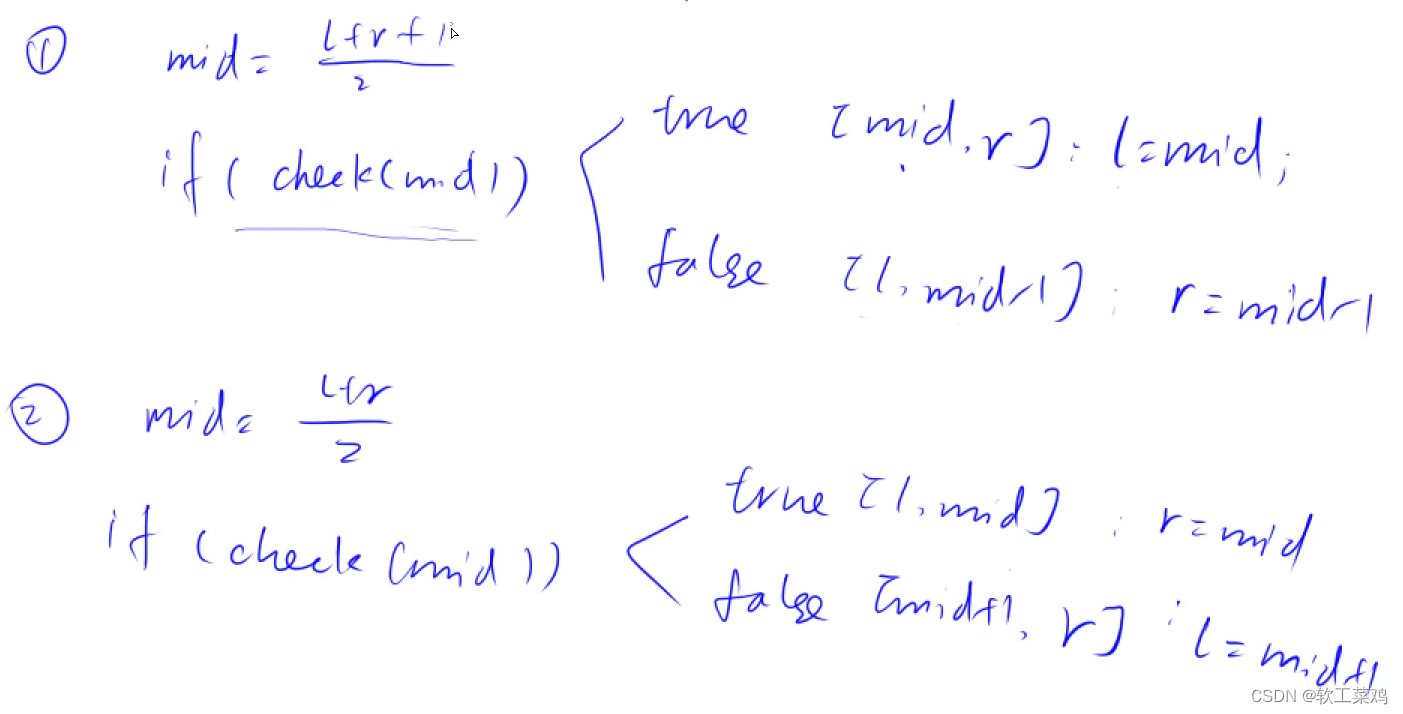
为什么要+1?
C++和Java除法向下取整,假设L=r-1;(L+r)/2=L;check(mid),假设为true,mid==L;死循环
什么情况用哪个模版?
先写check函数,根据check函数判断,答案区间如何划分,是l=mid(设mid的时候要+1)还是r=mid(不+1);
AcWing 789. 数的范围(整数二分模版)

import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args ){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in );
int n=sc.nextInt();
int q=sc.nextInt();
int[] a=new int [n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=sc.nextInt();
while(q-->0){
int x=sc.nextInt(),l=0,r=n-1;
while(l<r){
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(a[mid]>=x) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
if(a[l]!=x){
System.out.println("-1 -1");
}else{
System.out.print(l+" ");
l=0;r=n-1;
while(l<r){
int mid= (l+r+1)>>1;
if(a[mid]<=x) l=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
System.out.println(l);
}
}
}
}2187. 完成旅途的最少时间
class Solution {
public long minimumTime(int[] time, int totalTrips) {
Arrays.sort(time);
long left = 0;
// 记录当前最大完成旅途的时间
long right = 1L* time[0] * totalTrips ;
// 在最小时间和最大时间之间搜索符合条件的时间
while (left < right ){
long mid = right + left >>1;
// 记录当前完成旅途的车
long trips = 0;
// 遍历每个车次需要完成的时间
for(int t : time){
if(mid < t){
break;
}
// 记录当前时间能完成的趟数
trips += mid / t;
}
// 如果当前完成的车次已经到达了完成的次数则缩小范围 搜索前面时间范围
if(trips >= totalTrips){
right = mid;
} else {
// 反之搜索后面时间范围
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}AcWing 790. 数的三次方根
(前提是 数据有序) 说明:元素必须是有序的,从小到大,或者从大到小都是可以的。
public static int binarySearc(int[] arr,int number){
int min=0;
int max=arr.length-1;
while(true){
if(min>max){
return -1;
}
int mid=(max+min)/2;
if(arr[mid]==number)
return mid;
else if(arr[mid]>number)
max=mid-1;
else if(arr[mid]<number)
min=mid+1;
}
}35. 搜索插入位置
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if(nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}268. 丢失的数字 太简单了
34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
这道题目比Acw789 加了数据比如说[],0;[1] 1;
class Solution {//y总模板解法
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums.length==0)
return new int[]{-1,-1};
int l=0,r=nums.length-1,mid=l+r>>1;
while(l<r){
mid=l+r+c>>1;
if(nums[mid]>=target) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
int[] res=new int[2];
if(nums[l]!=target)
return new int[]{-1,-1};
else{
res[0]=l;
l=0;r=nums.length-1;
while(l<r){
mid=l+r+1+c>>1;
if(nums[mid]<=target) l=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
res[1]=l;
return res;
}
}
}
class Solution {//不能解决数组内 负数 问题
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums.length==0)
return new int[]{-1,-1};
int[] arr=new int[nums[nums.length-1]+1];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
arr[i]=0;
}
int c=-1;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
arr[ nums[i] ]++;
if(nums[i]==target&&arr[nums[i]]==1)
c=i;
}
if(c!=-1)
return new int[]{c ,(c+arr[target]-1)};
else
return new int[]{-1,-1};
}
}
//https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/solution/zai-pai-xu-shu-zu-zhong-cha-zhao-yuan-su-de-di-3-4/
//他不是找目标位置,而是找第一个等于的位置和第一个>的位置
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int leftIdx = binarySearch(nums, target, true);//第一个=target的位置
int rightIdx = binarySearch(nums, target, false) - 1;//第一个》target-1的位置
if (leftIdx <= rightIdx && rightIdx < nums.length && nums[leftIdx] == target && nums[rightIdx] == target) {
return new int[]{leftIdx, rightIdx};
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target, boolean lower) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1, ans = nums.length;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target || (lower && nums[mid] >= target)) {
right = mid - 1;
ans = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}74. 搜索二维矩阵
class Solution {//自己写的
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int[] arr=new int[matrix.length];
if(matrix.length==1){//特殊情况,只有一个数组
for(int index:matrix[0] )
if(index==target)
return true;
return false;
}
for(int i=0;i<matrix.length-1;i++)
if(matrix[i][0]<=target&&matrix[i+1][0]>target)
{
for(int index:matrix[i] )
if(index==target)
return true;
}
else{//二维数组最后一行
for(int index:matrix[i+1] )
if(index==target)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/solution/sou-suo-er-wei-ju-zhen-by-leetcode-solut-vxui/
思路
若将矩阵每一行拼接在上一行的末尾,则会得到一个升序数组,我们可以在该数组上二分找到目标元素。
代码实现时,可以二分升序数组的下标,将其映射到原矩阵的行和列上。
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;//m,n代表行和列
int low = 0, high = m * n - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
int x = matrix[mid / n][mid % n];//映射
if (x < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (x > target) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
思路与算法
由于矩阵 matrix 中每一行的元素都是升序排列的,因此我们可以对每一行都使用一次二分查找,判断 target 是否在该行中,从而判断 target 是否出现。
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
for (int[] row : matrix) {
int index = search(row, target);
if (index >= 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
int num = nums[mid];
if (num == target) {
return mid;
} else if (num > target) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int x = 0, y = n - 1;
while (x < m && y >= 0) {
if (matrix[x][y] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[x][y] > target) {
--y;
} else {
++x;
}
}
return false;
}
}高精度
BigInteger 只可用于整数 构造方法
BigInteger(byte[] val)
将包含BigInteger的二进制补码二进制表达式的字节数组转换为BigInteger
BigInteger(int numBits, Random rnd)
构造一个随机生成的BigInteger,均匀分布在0到(2 numBits - 1)的范围内。
BigInteger(String val)
将BigInteger的十进制字符串表示形式转换为BigInteger。
加法 add( )
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.add(b));
reader.close();
}
}减法 subtract( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.subtract(b));
reader.close();
}
}乘法 multiply( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.multiply(b));
reader.close();
}
}除法 divideAndRemainder( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
//divide 返回值为 a/b
BigInteger[] c = a.divideAndRemainder(b); //返回值为数组,分别为a/b和a%b
System.out.println(c[0]);
System.out.println(c[1]);
reader.close();
}
}取余 mod( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.mod(b));
reader.close();
}
}BigDecimal 处理浮点数运算
构造方法
BigDecimal(char[] in)
一个转换的字符数组表示 BigDecimal成 BigDecimal ,接受字符作为的相同序列 BigDecimal(String)构造。
BigDecimal(char[] in, int offset, int len)
一个转换的字符数组表示 BigDecimal成 BigDecimal ,接受字符作为的相同序列 BigDecimal(String)构造,同时允许一个子阵列被指定。
BigDecimal(double val)
将 double转换为 BigDecimal ,这是 double的二进制浮点值的精确十进制表示
BigDecimal(int val)
将 int成 BigDecimal
BigDecimal(long val)
将 long成 BigDecimal
BigDecimal(String val)
加法 add( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.add(b));
reader.close();
}
}取余 remainder( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.remainder(b));
reader.close();
}
}除法 divide( )
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(reader.readLine());
System.out.println(a.divide(b));
reader.close();
}
}AcWing 791. 高精度加法
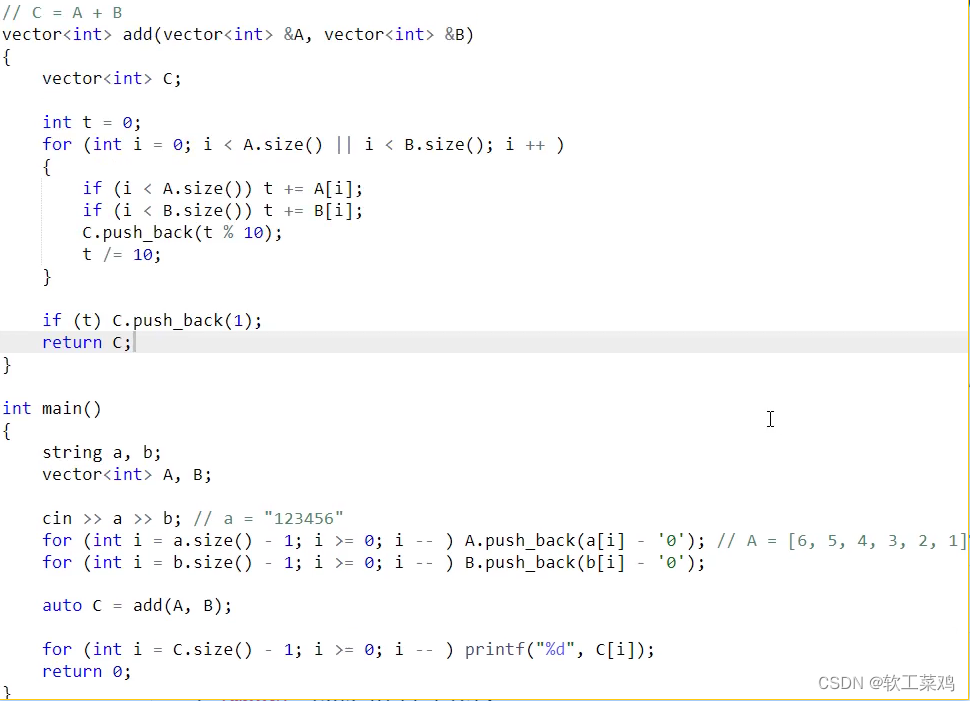
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = scanner.next();
String b = scanner.next();
//String表示长度用length这个方法,集合中用size这个方法
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>(a.length());
List<Integer> B = new ArrayList<>(b.length());
//add可以直接将数放到末尾,新开空间。
//因为数组添加设置为最后一位方便,因为数组扩容修改超级快
//charAt返回指定下标下面的char值,后面减去0是为了把字符变成数字
for(int i = a.length() - 1;i >= 0; i --) A.add(a.charAt(i) - '0');
for(int i = b.length() - 1;i >= 0; i --) B.add(b.charAt(i) - '0');
List<Integer> C = add(A,B);
for(int i = C.size() - 1;i >= 0; i--){
System.out.print(C.get(i) + "");
}
}
public static List<Integer> add(List<Integer> A ,List<Integer> B){
List<Integer> C = new ArrayList<>();
int t = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < A.size() || i < B.size();i++){
if(i < A.size()) t += A.get(i);
if(i < B.size()) t += B.get(i);
C.add(t % 10);
t = t/10;
}
if(t != 0) C.add(1);//判断t要不要借位
return C;
}
}AcWing 792. 高精度减法
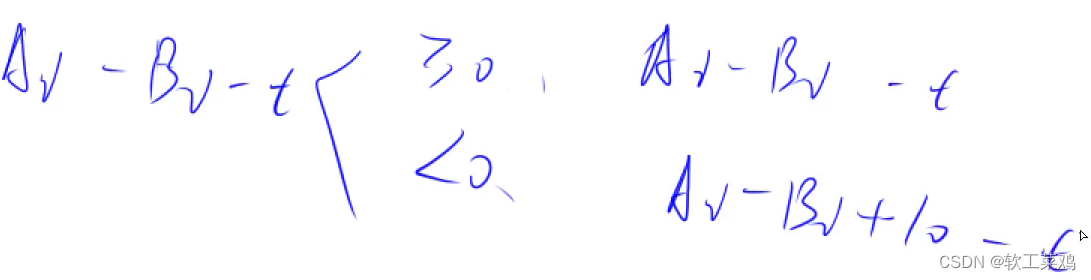
t作为 结果i位置 的值 的标志有两种可能:>=0 或 <0 ;
(t+10)%10: >=0 时,10抵消=本身; <0,t=t+10;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = scanner.next();
String s2 = scanner.next();
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> B = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = s1.length() - 1;i >= 0;i --) A.add(s1.charAt(i) - '0');
for(int i = s2.length() - 1;i >= 0; i --) B.add(s2.charAt(i) - '0');
if(!cmp(A,B)){
System.out.print("-");
}
List<Integer> C = sub(A,B);
for(int i = C.size() - 1;i >= 0; i --){
System.out.print(C.get(i));
}
}
public static List<Integer> sub(List<Integer> A,List<Integer> B){
if(!cmp(A,B)){
return sub(B,A);
}
List<Integer> C = new ArrayList<>();
int t = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < A.size();i ++){
//这里应该是A.get(i) - B.get(i) - t ,因为可能B为零,
//所以判断一下是不是存在
t = A.get(i) - t;
if(i < B.size()) t -= B.get(i);
//B > 当前位数,说明B[i]此时不为0;得-
C.add((t + 10) % 10);
if(t < 0) t = 1;
else t = 0;
}
//删除前导0
while(C.size() > 1 && C.get(C.size() - 1) == 0) C.remove(C.size() - 1);
return C;
}
public static boolean cmp(List<Integer> A,List<Integer> B){
if(A.size() != B.size()) return A.size() > B.size();
for(int i = A.size() - 1;i >= 0;i --){
if(A.get(i) != B.get(i))
return A.get(i) > B.get(i);
}
return true;
}
}AcWing 793. 高精度乘法
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = scanner.next();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>(a.length());
for(int i = a.length() - 1; i >= 0;i --) A.add(a.charAt(i) - '0');
List<Integer> C = mul(A,b);
for(int i = C.size() - 1 ;i >= 0;i --){
System.out.print(C.get(i));
}
}
public static List<Integer> mul(List<Integer> A ,int b){
List<Integer> C = new ArrayList<>();
int t = 0;
//t不为0 就是 最高位还有进位!
for(int i = 0;i < A.size() || t != 0;i ++ ){
if(i < A.size()) t += A.get(i) * b;
C.add(t % 10);
t /= 10;// 第i+1位 的 进位数
}
while(C.size() > 1 && C.get(C.size() - 1) == 0) C.remove(C.size() - 1);
return C;
}
}AcWing 794. 高精度除法


import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] arg){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = scanner.next();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>(a.length());
for(int i = a.length() - 1;i >= 0;i --) A.add(a.charAt(i) - '0');
List<Integer> C = div(A,b);
for(int i = C.size() - 2;i >= 0;i --) System.out.print(C.get(i));
System.out.println();
System.out.print(C.get(C.size() - 1));
}
public static List<Integer> div(List<Integer> A,int b){
List<Integer> C = new ArrayList<>();
int r = 0;//余数
for(int i = A.size() - 1 ;i >= 0; i --){
r = r * 10 + A.get(i);
C.add(r / b);//add 商
r %= b;
}
Collections.reverse(C);//for从高位add的所有要reverse
while(C.size() > 1 && C.get(C.size() - 1) == 0) //去掉前导0
C.remove(C.size() - 1);
C.add(r);
return C;
}
}本文来自博客园,作者:软工菜鸡,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/SElearner/p/17676642.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号