ServletContext
***使用ServletContext可实现不同客户端获取到相同的服务器数据 (如文章浏览次数, 点赞数等)
实例:
1. 先访问下面servlet在服务器创建ServletContext以便让不同客户端使用:
public class TestServletContext extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //获取ServletContext对象 (三种方式) ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext(); ServletContext sc2 = this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); ServletContext sc3 = req.getSession().getServletContext(); //使用ServletContext对象完成数据共享 键的类型为String, 值的类型为Object sc.setAttribute("name", "尼古拉斯 凯奇"); resp.getWriter().write("ServletContext对象已经创建, 其他用户都可以获取到此值--尼古拉斯 凯奇"); } }
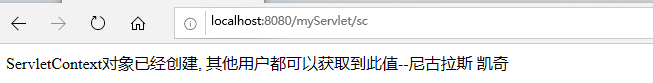
2. 访问之后, 清除浏览器缓存(即cookie, 模拟不同浏览器访问), 再访问下面servlet, 获取到name的值, 实现了不同客户端访问相同的服务器数据:
public class TestServletContext2 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext(); Object name = sc.getAttribute("name"); resp.getWriter().write("获取到的ServletContext的值是: " + name); } }
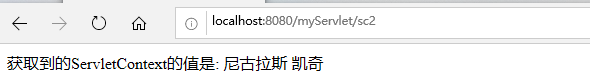
***使用ServletContext也可以获取到web.xml中的全局配置数据:
web.xml中配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0">
注:一组<context-param>标签只能存储一组键值对数据, 多组可声名多个<context-param>进行存储
<context-param> <param-name>name</param-name> <param-value>Ryan</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>city</param-name> <param-value>杭州</param-value> </context-param> <!--配置servlet类路径--> <servlet>
......
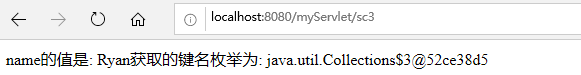
public class TestServletContext3 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext(); //根据键的名字返回web.xml中配置的全局数据的值, 返回String类型, 如果数据不存在返回null. String name = sc.getInitParameter("name"); resp.getWriter().write("name的值是: " + name); //返回键名的枚举. Enumeration<String> ipa = sc.getInitParameterNames(); resp.getWriter().write("获取的键名枚举为: " + ipa); } }
浏览器访问此servlet后可获取web.xml中的相关值:
***获取项目根目录下资源的绝对路径
String rp = sc.getRealPath("/aaa.text");
System.out.println(rp);

另外还可以获取项目根目录下资源的流对象:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号