Java如何使用KEPserver 实现OPC通信
一.PLC和OPC
使用的PLC:西门子PLC S7-200 SMART
使用的OPC server软件:
KEPServer V6 百度网盘 密码:2080 (备注:KEPserver 需要付费的 正版价格8800元/1个电脑 ,非正版使用期为一个月,过期后KEPserver 使用2小时后 KEPserver 失效——————目前没见过破解永久使用权的)
二.连接测试
OPC是工业控制和生产自动化领域中使用的硬件和软件的接口标准,以便有效地在应用和过程控制设备之间读写数据。O代表OLE(对象链接和嵌入),P (process过程),C (control控制)。
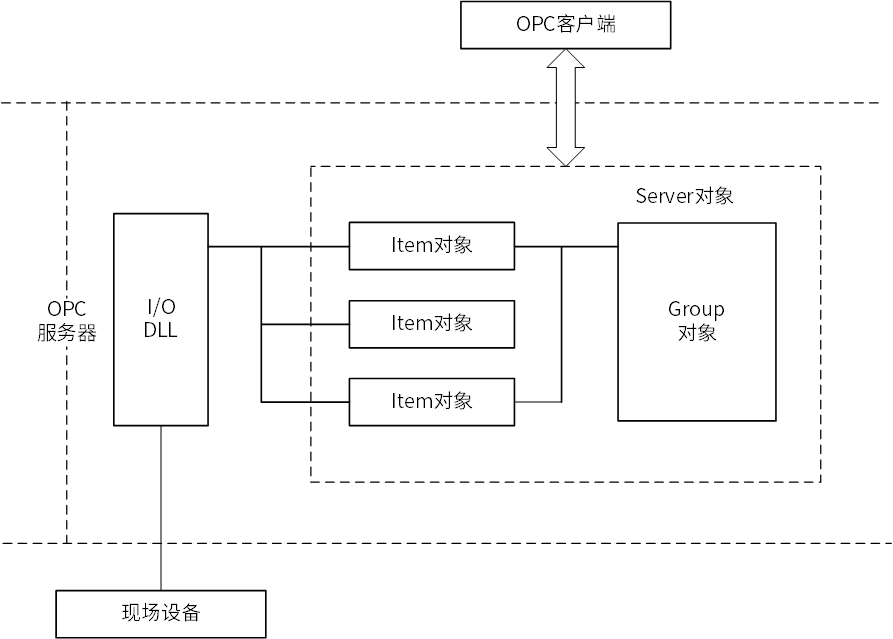
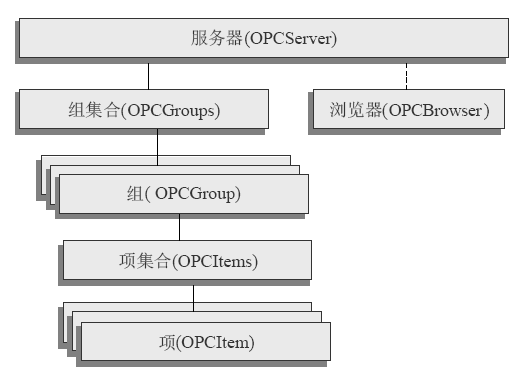
OPC服务器包括3类对象(Object):服务器对象(Server)、项对象(Item)和组对象(Group)。
OPC标准采用C/S模式,OPC服务器负责向OPC客户端不断的提供数据。
什么是OPC?(原文介绍)
Server和Client
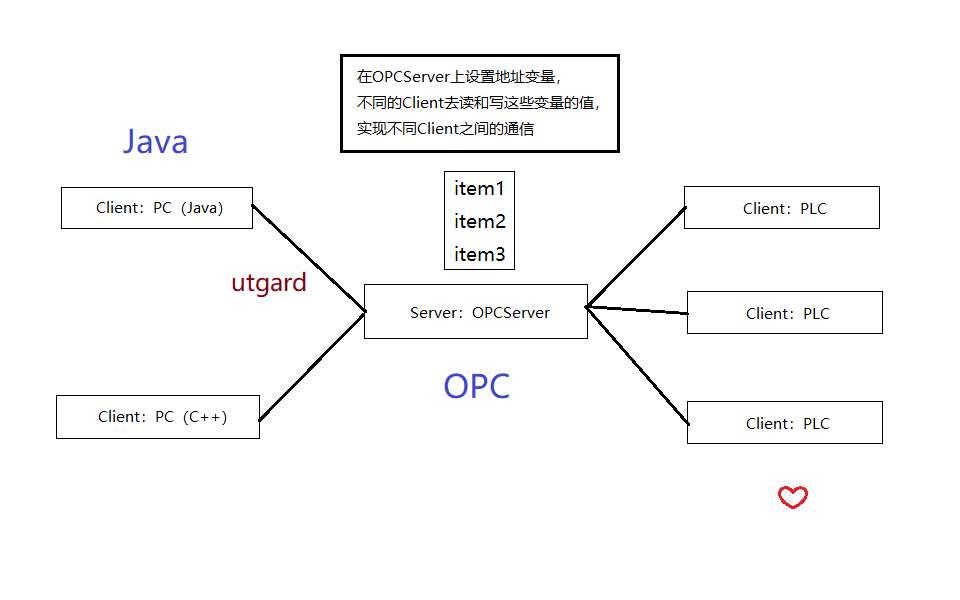
要实现的是Client(Java)和Client(PLC)之间的通信
中间借助OPCServer,Server上设定好地址变量,不同的Client读写这些变量值实现通信。
示意图如下
OPC和DCOM配置:通信不成功都是配置的问题。。。
配置OPCserver
一般一个电脑(win10)同时安装Server(比如KEPServer)和Client(Java编写的),就配置这个电脑就行
如果是在两个电脑上,那就都需要配置。
三.实现通信
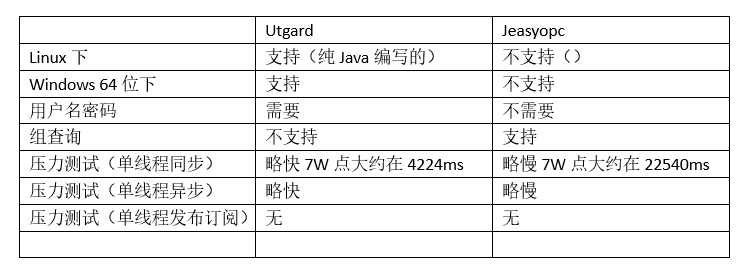
Utgard:
- 最重要参考:Java OPC client开发踩坑记
- Github上的:资料下载
- Java语言开发OPC之Utgard的数据访问方式
- Utgard访问OPC server
Github上的
- 最全面的测试(Utgard和JeasyOPC测试):OPC_Client
- Utgard测试
四.实现过程
1.opc的概念
2.关于OPC UA
- OPC UA的西门子PLC至少是s7-1500
3.关于Utgard
- utgard是一个开源的项目,基于j-interop做的,用于和OPC SERVER通讯。
- j-interop是纯java封装的用于COM/DCOM通讯的开源项目,这样就不必使用JNI
4.关于JeasyOPC
- JeasyOPC源码下载
- 借助一个dll库来实现的和OPCServer的通信,但是JCustomOpc.dll,,太老了,而且支持只32位系统
五.maven依赖
1 <!--utgard --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.openscada.external</groupId> 4 <artifactId>org.openscada.external.jcifs</artifactId> 5 <version>1.2.25</version> 6 </dependency> 7 <dependency> 8 <groupId>org.openscada.jinterop</groupId> 9 <artifactId>org.openscada.jinterop.core</artifactId> 10 <version>2.1.8</version> 11 </dependency> 12 <dependency> 13 <groupId>org.openscada.jinterop</groupId> 14 <artifactId>org.openscada.jinterop.deps</artifactId> 15 <version>1.5.0</version> 16 </dependency> 17 <dependency> 18 <groupId>org.openscada.utgard</groupId> 19 <artifactId>org.openscada.opc.dcom</artifactId> 20 <version>1.5.0</version> 21 </dependency> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>org.openscada.utgard</groupId> 24 <artifactId>org.openscada.opc.lib</artifactId> 25 <version>1.5.0</version> 26 </dependency> 27 <dependency> 28 <groupId>org.bouncycastle</groupId> 29 <artifactId>bcprov-jdk15on</artifactId> 30 <version>1.61</version> 31 </dependency> 32 <dependency> 33 <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> 34 <artifactId>logback-core</artifactId> 35 <version>1.3.0-alpha4</version> 36 </dependency> 37 <dependency> 38 <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> 39 <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> 40 <version>1.3.0-alpha4</version> 41 <scope>test</scope> 42 </dependency>
说明
对地址变量进行读取数值和写入数值操作,一般分循环和批量两种方式,(同步和异步就不讨论了)
- 循环读取:Utgard提供了一个AccessBase类来循环读取数值
- 循环写入:启动一个线程来循环写入数值
- 批量读取:通过组(Group),增加项(Item)到组,然后对Item使用read()
- 批量写入:通过组(Group),增加项(Item)到组,然后对Item使用write()
读取PLC 的点位值
1 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 2 3 import org.jinterop.dcom.common.JIException; 4 import org.jinterop.dcom.core.JIString; 5 import org.jinterop.dcom.core.JIVariant; 6 import org.openscada.opc.lib.common.ConnectionInformation; 7 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.AccessBase; 8 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.DataCallback; 9 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.Item; 10 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.ItemState; 11 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.Server; 12 import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.SyncAccess; 13 14 public class UtgardTutorial1 { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 17 // 连接信息 18 final ConnectionInformation ci = new ConnectionInformation(); 19 ci.setHost("192.168.0.1"); // 电脑IP 20 ci.setDomain(""); // 域,为空就行 21 ci.setUser("OPCUser"); // 电脑上自己建好的用户名 (之前DCOM 配置过) 22 ci.setPassword("123456"); // 密码(用户名密码) 23 24 // 使用MatrikonOPC Server的配置 25 // ci.setClsid("F8582CF2-88FB-11D0-B850-00C0F0104305"); // MatrikonOPC的注册表ID,可以在“组件服务”里看到 26 // final String itemId = "u.u"; // MatrikonOPC Server上配置的项的名字按实际 27 28 // 使用KEPServer的配置 29 ci.setClsid("7BC0CC8E-482C-47CA-ABDC-0FE7F9C6E729"); // KEPServer的注册表ID,可以在“组件服务”里看到 30 final String itemId = "u.u.u"; // KEPServer上配置的项的名字,没有实际PLC,用的模拟器:simulator (KEPserver 建立通道,建立设备,建立点位)通过标记点位名字定位要读取的值 31 // final String itemId = "通道 1.设备 1.标记 1"; 32 33 // 启动服务 34 final Server server = new Server(ci, Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()); 35 36 try { 37 // 连接到服务 38 server.connect(); 39 // add sync access, poll every 500 ms,启动一个同步的access用来读取地址上的值,线程池每500ms读值一次 40 // 这个是用来循环读值的,只读一次值不用这样 41 final AccessBase access = new SyncAccess(server, 500); 42 // 这是个回调函数,就是读到值后执行这个打印,是用匿名类写的,当然也可以写到外面去 43 access.addItem(itemId, new DataCallback() { 44 @Override 45 public void changed(Item item, ItemState itemState) { 46 int type = 0; 47 try { 48 type = itemState.getValue().getType(); // 类型实际是数字,用常量定义的 49 } catch (JIException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 System.out.println("监控项的数据类型是:-----" + type); 53 System.out.println("监控项的时间戳是:-----" + itemState.getTimestamp().getTime()); 54 System.out.println("监控项的详细信息是:-----" + itemState); 55 56 // 如果读到是short类型的值 57 if (type == JIVariant.VT_I2) { 58 short n = 0; 59 try { 60 n = itemState.getValue().getObjectAsShort(); 61 } catch (JIException e) { 62 e.printStackTrace(); 63 } 64 System.out.println("-----short类型值: " + n); 65 } 66 67 // 如果读到是字符串类型的值 68 if(type == JIVariant.VT_BSTR) { // 字符串的类型是8 69 JIString value = null; 70 try { 71 value = itemState.getValue().getObjectAsString(); 72 } catch (JIException e) { 73 e.printStackTrace(); 74 } // 按字符串读取 75 String str = value.getString(); // 得到字符串 76 System.out.println("-----String类型值: " + str); 77 } 78 } 79 }); 80 // start reading,开始读值 81 access.bind(); 82 // wait a little bit,有个10秒延时 83 Thread.sleep(10 * 1000); 84 // stop reading,停止读取 85 access.unbind(); 86 } catch (final JIException e) { 87 System.out.println(String.format("%08X: %s", e.getErrorCode(), server.getErrorMessage(e.getErrorCode()))); 88 } 89 } 90 }
注意:if(type == JIVariant.VT_BSTR)//返回数字队形返回值的类型 这里的对应的类型不是java的类型
类型对照表:
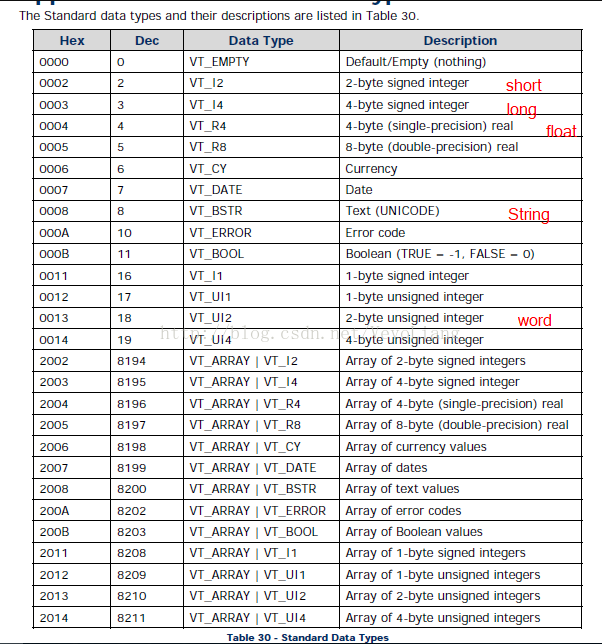
读取数值与写入数值
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.jinterop.dcom.common.JIException; import org.jinterop.dcom.core.JIVariant; import org.openscada.opc.lib.common.ConnectionInformation; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.AccessBase; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.DataCallback; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.Group; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.Item; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.ItemState; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.Server; import org.openscada.opc.lib.da.SyncAccess; public class UtgardTutorial2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 连接信息 final ConnectionInformation ci = new ConnectionInformation(); ci.setHost("192.168.0.1"); // 电脑IP ci.setDomain(""); // 域,为空就行 ci.setUser("OPCUser"); // 用户名,配置DCOM时配置的 ci.setPassword("123456"); // 密码 // 使用MatrikonOPC Server的配置 // ci.setClsid("F8582CF2-88FB-11D0-B850-00C0F0104305"); // MatrikonOPC的注册表ID,可以在“组件服务”里看到 // final String itemId = "u.u"; // 项的名字按实际 // 使用KEPServer的配置 ci.setClsid("7BC0CC8E-482C-47CA-ABDC-0FE7F9C6E729"); // KEPServer的注册表ID,可以在“组件服务”里看到 final String itemId = "u.u.u"; // 项的名字按实际,没有实际PLC,用的模拟器:simulator // final String itemId = "通道 1.设备 1.标记 1"; // create a new server,启动服务 final Server server = new Server(ci, Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()); try { // connect to server,连接到服务 server.connect(); // add sync access, poll every 500 ms,启动一个同步的access用来读取地址上的值,线程池每500ms读值一次 // 这个是用来循环读值的,只读一次值不用这样 final AccessBase access = new SyncAccess(server, 500); // 这是个回调函数,就是读到值后执行再执行下面的代码,是用匿名类写的,当然也可以写到外面去 access.addItem(itemId, new DataCallback() { @Override public void changed(Item item, ItemState state) { // also dump value try { if (state.getValue().getType() == JIVariant.VT_UI4) { // 如果读到的值类型时UnsignedInteger,即无符号整形数值 System.out.println("<<< " + state + " / value = " + state.getValue().getObjectAsUnsigned().getValue()); } else { System.out.println("<<< " + state + " / value = " + state.getValue().getObject()); } } catch (JIException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); // Add a new group,添加一个组,这个用来就读值或者写值一次,而不是循环读取或者写入 // 组的名字随意,给组起名字是因为,server可以addGroup也可以removeGroup,读一次值,就先添加组,然后移除组,再读一次就再添加然后删除 final Group group = server.addGroup("test"); // Add a new item to the group, // 将一个item加入到组,item名字就是MatrikonOPC Server或者KEPServer上面建的项的名字比如:u.u.TAG1,PLC.S7-300.TAG1 final Item item = group.addItem(itemId); // start reading,开始循环读值 access.bind(); // add a thread for writing a value every 3 seconds // 写入一次就是item.write(value),循环写入就起个线程一直执行item.write(value) ScheduledExecutorService writeThread = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); writeThread.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { final JIVariant value = new JIVariant("24"); // 写入24 try { System.out.println(">>> " + "写入值: " + "24"); item.write(value); } catch (JIException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 启动后5秒第一次执行代码,以后每3秒执行一次代码 // wait a little bit ,延时20秒 Thread.sleep(20 * 1000); writeThread.shutdownNow(); // 关掉一直写入的线程 // stop reading,停止循环读取数值 access.unbind(); } catch (final JIException e) { System.out.println(String.format("%08X: %s", e.getErrorCode(), server.getErrorMessage(e.getErrorCode()))); } } }
数组类型
如果地址变量的数据类型是数组类型呢?
1 // 读取Float类型的数组 2 if (type == 8196) { // 8196是打印state.getValue().getType()得到的 3 JIArray jarr = state.getValue().getObjectAsArray(); // 按数组读取 4 Float[] arr = (Float[]) jarr.getArrayInstance(); // 得到数组 5 String value = ""; 6 for (Float f : arr) { 7 value = value + f + ","; 8 } 9 System.out.println(value.substring(0, value.length() - 1); // 遍历打印数组的值,中间用逗号分隔,去掉最后逗号 10 } 11 12 // 写入3位Long类型的数组 13 Long[] array = {(long) 1,(long) 2,(long) 3}; 14 final JIVariant value = new JIVariant(new JIArray(array)); 15 item.write(value);
| 值(十进制) | 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | VT_EMPTY | 默认/空(无) |
| 2 | VT_I2 | 2字节有符号整数 |
| 3 | VT_I4 | 4字节有符号整数 |
| 4 | VT_R4 | 4字节实数 |
| 5 | VT_R8 | 8字节实数 |
| 6 | VT_C | currency |
| 7 | VT_DATE | 日期 |
| 8 | VT_BSTR | 文本 |
| 10 | VT_ERROR | 错误代码 |
| 11 | VT_BOOL | 布尔值(TRUE = -1,FALSE = 0) |
| 17 | VT_I1 | 1个字节有符号字符 |
| 18 | VT_UI1 | 1个字节无符号字符 |
| 19 | VT_UI2 | 2字节无符号整数 |
| 20 | VT_UI4 | 4字节无符号整数 |
| +8192 | VT_ARRAY | 值数组(即8200 =文本值数组) |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号