MySql基础常用集合-3
一、存储引擎
关系数据库表是用于存储和组织信息的数据结构,可以将表理解为由行和列组成的表格。有的表简单,有的表复杂,有的表根本不用来存储任何长期的数据,有的表读取时非常快,但是插入数据时去很差;而我们在实际开发过程中,就可能需要各种各样的表,不同的表,就意味着存储不同类型的数据,数据的处理上也会存在着差异,那么。对于MySQL来说,它提供了很多种类型的存储引擎,我们可以根据对数据处理的需求,选择不同的存储引擎,从而最大限度的利用MySQL强大的功能,而像SqlServer和Oracle只提供一种存储引擎,InnoDB是MySql中最常用和最通用的存储引擎。
二、Charset和collation
Charset指的是字符集,比如:utf-8、GB2312等等。
Collation指的是排序规则,一个字符集可以用很多个排序规则
比如:
Utf-8字符集有如下排序规则:utf8_general_ci、 utf8_unicode_ci,通常我们使用utf8_unicode_ci
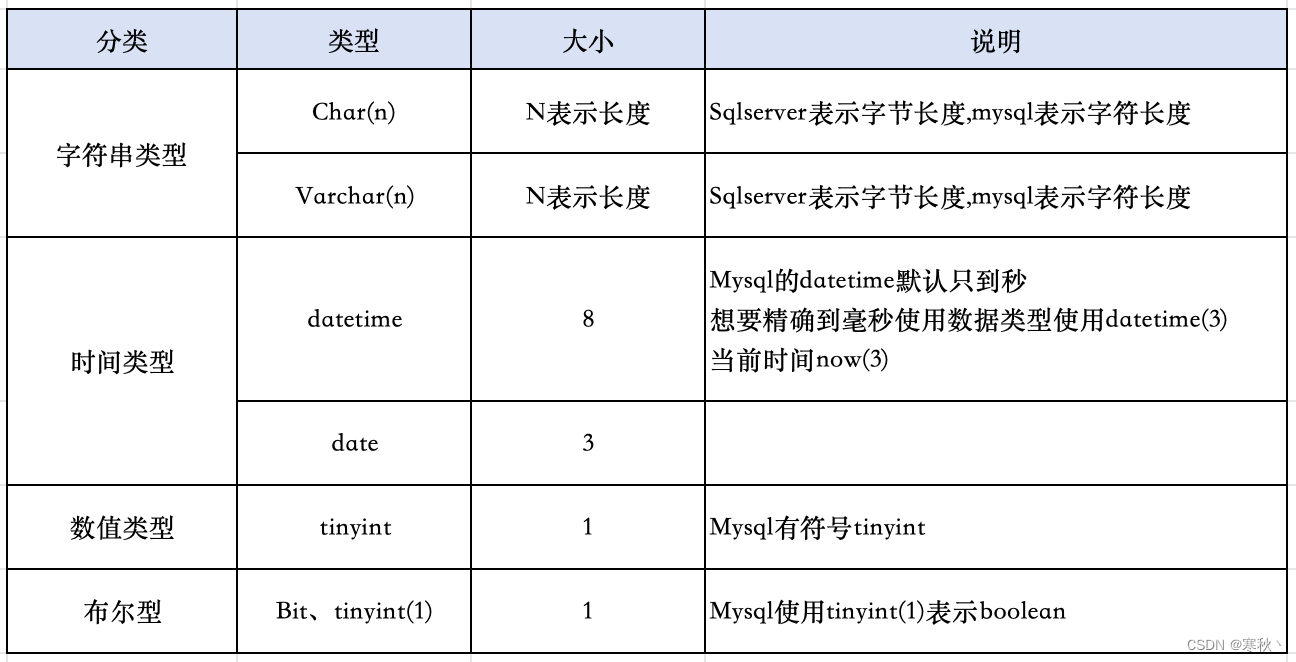
三、常用数据类型
四、函数
字符串位置
# MySql
Select position('c' in 'abcdef')
# SqlServer
select CHARINDEX('c','abcdef')
字符串截取
# MySql
Select substring('abcdef',2,3)
# SqlServer
Select substring('abcdef',2,3)
去掉空格
# MySql
Select rtrim(ltrim(' a bcd '))
# SqlServer
Select rtrim(ltrim(' a bcd '))
获取字符串长度
# MySql
Select length('abcdef')
# SqlServer
Select len('abcdef')
字符串替换
# MySql
select replace('abcdef','c','C')
# SqlServer
select replace('abcdef','c','C')
字符串英文大小写
# MySql
select upper(lower('ABC'))
# SqlServer
select upper(lower('ABC'))
类型转换
# MySql
select convert('11',SIGNED)
select cast('11' as SIGNED)
# SqlServer
select convert(int, '11')
select cast('11' as int)
日期转换
# MySql
select DATE_FORMAT(now(),'%Y-%m-%d')
select DATE_FORMAT(now(),'%Y%m%d')
# SqlServer
Select convert(varchar(10),getdate(),120)
Select convert(varchar(10),getdate(),112)
null值判断
# MySql
Select ifnull(1,0)
# SqlServer
Select isnull(1,0)
五、流程控制
Mysql (只能在存储过程或者函数中使用)
if then
elseif then
else
end if
while 1=1 do
end while
SqlServer(可以任意使用)
if
begin
end
else if
begin
end
else
begin
end
while 1=1
begin
select 1
end
六、临时表
MySql:
Create temporary table tmp
(
Name varchar(50)
)
Create temporary table tmp
Select * from table
SqlServer:
Create table #t
(
name varchar(50)
)
Select id
into #t1
from table
七、存储过程
Mysql:
delimiter //
create procedure myproc
(
a int
)
begin
select a+1;
end;//
SqlServer:
Create procedure myproc
(
@a int
)
As
Begin
Select @a+1;
end
八、创建函数
MySql:
delimiter //
Create function myfun()
returns varchar(100)
reads sql data
begin
return 'aaa';
end;//
SqlServer:
Create function myfun()
Returns varchar(100)
as
Begin
Return ‘aaa’
end
九、注释
MySql:
# select * from table limit 1
-- select * from table
/*select top 1 *
From table limit 1*/
SqlServer:
--select top 1 * from table
/*select top 1 *
From table*/
十、查询前几条
MySql:
Select *
From table
Limit 10
SqlServer:
Select top 10 *
From table
十一、休眠
MySql:
Select sleep(1000)
SqlServer:
Waitfor time '10:00'
Waitfor delay '1:00'
十二、打印
MySql:
Select @p
SqlServer:
Print @p
十三、MySql锁
数据库常用到的锁主要有,共享锁、更新锁、排它锁
共享锁默认所有查询语句都会发出共享锁,并且语句执行完就释放了,加上共享锁之后可以查询不允许修改了,例如:
Select * from table where code = 2
更新锁需要在查询的时候加上表提示,例如:
Select * from table where code = 2 for update
更新锁可以查询不能修改保持到事务结束。
排它锁是一般执行update和delete的时候会发出排它锁,加上排它锁之后,别的事务既不能读也不能修改。
经常用到的命令:
查看所有执行中的语句
Show processlist
查询所有执行中的事务
select * from information_schema.INNODB_TRX;
查询持有锁或等待锁信息
Select * from information_schema.innodb_locks
查询锁等待关系
Select * from information_schema.innodb_lock_waits
尽量使用主键或者唯一索引加锁
避免较慢的查询
避免多表连接查询
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiangxi1204/article/details/138705278





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现