C,C++语法基础 | STL容器,位运算与常用库函数 | 08
STL容器,位运算与常用库函数 | 08
Vector
存在于头文件#include<vector>.
vector是变长数组(也就是动态数组),支持随机访问(就是可以通过下标进行访问).不支持在任意位置O(1)插入. 为了保证效率,元素的增删一般应该在末尾进行.
下面是vector的声明
#include<vector> // 头文件
vector<int> a; // 相当于一个长度动态变化的int数组
vector<int> a[100]; // 第一维为固定100的长度,第二维长度动态变化的int数组
struct rec{int x;int y;};
vector<rec> c; // 自定义结构体类型也可以保存在vector中
Vector常用函数
size()/empty()
size()函数返回vector的实际长度(包含的元素个数),empty()函数返回一个bool值,表明vector是否为空. 二者的时间复杂度都为O(1).
所有的STL容器都支持这两个方法,还以也相同,之后我们就不再重复.
clear()
clear()函数把vector清空
需要注意了,基本都是有clear()函数的,除了stack,queue,priority_queue这3个函数是没有clear()函数的.需要清空的话就只能重新定义了.
迭代器
迭代器就像STL容器的指针,可以用星号*操作符解除引用.
一个保存int的vector的迭代器声明方法为: vector<int>::iterator it,这里其实可以使用auto it.
vector的迭代器是"随机访问迭代器",可以把vector的迭代器与一个整数相加减,其行为和指针移动类似.it+2,*(it+2)
begin/end 和 front/back()
begin()函数返回指向vector中第一个元素的迭代器. *a.begin()与a[0]的作用相同.
所有容器都是[a.begin(),a.end()),所以*a.end()是越界访问.
a.front()是返回第一个元素,而a.begin()是返回第一个元素的指针,理解清楚. a.back()和a.end()是一个道理.
push_back()和pop_back()
a.push_back(x) 把元素x插入到vector a的尾部
a.pop_back(x) 删除vector a的最后一个元素
Vector的遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> a({1,2,3});
// 传统容器遍历
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// // 迭代器遍历(基本很少使用这种方式来遍历)
for(vector<int>::iterator it=a.begin();it!=a.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// // 使用auto写法
for(auto it=a.begin();it<a.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// foreach写法
for(int x:a){
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
queue
首先引入头文件#include<queue>,其中包含循环队列queue和优先队列priority_queue两个容器.
声明方式如下:
#include<queue>
queue<int> q; // 定义int的循环队列
struct rec{int x;int y;};
queue<rec> q; // 定义自定义结构体的队列
priority_queue<int> q; // 大根堆
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q; // 小根堆(这个需要背记的),c99是不支持小根堆的这种写法.
注意: 如果优先队列中使用自定义类型(结构体),那么就需要重载运算符.
结构体语法bool operator 运算符 (const 结构体名称& a) const{ 元素 运算符 a.xx }
struct Rec{
int a,b;
bool operator > (const Rec& t) const{
return a > t.a;
}
};
priority_quue<Rec,vector<Rec>,greater<Rec>> d;
d.push({1,2});
循环队列 queue
q.push() 从队尾插入
q.pop() 从对头弹出
q.front() 返回队头元素
q.back() 返回队尾元素
优先队列 priority_queue
q.push() 把元素插入堆
q.pop() 删除堆顶元素
q.top() 查询堆顶元素(最大值)
stack
引入头文件#include<stack>
s.push() 向栈顶插入
s.pop() 弹出栈顶元素
s.top() 查看栈顶元素
deque
引入头文件#include<deque>
双端队列deque是一个支持在两端高效插入或删除的连续性存储空间. 它像是vector和queue的结合.与vector相比,deque在头部增删元素仅需要O(1)的时间,与queue相比,deque像数组一样支持随机访问.
[] 随机访问
begin/end 返回deque的头尾迭代器
front/back 队头/队尾元素
push_back 从队尾入队
push_front 从队首入队
pop_back 从队尾出队
pop_front 从队头出队
clear 清空队列
set
引入头文件#include<set>,主要包括set和multiset两个容器,分别是"有序集合"和"有序多重集合",即前者的元素不能重复,而后者可以包含若干个相等的元素.
multiset的作用就是可以维护一个含有重复元素的有序序列,set是维护一个不含有重复元素的有序序列.
size/empty/clear 与vector类似
set<int>::iterator it=s.begin() 迭代器操作也和vector类似
s.begin()/s.end() 返回集合的首尾迭代器,时间复杂度为O(1)
s.insert(x) 把一个元素x插入到集合s中,时间复杂度为O(logn),在set中,如果该元素存在,则不会重复插入该元素,对集合的状态无影响.
s.find(x) 在集合中查找等于x的元素,并返回指向该元素的迭代器. 若不存在,则返回s.end(), 时间复杂度为O(logn). s.find(x) == s.end() 为没有找到.
lower_bound/upper_bound
这两个函数的用法很类似! 不要混淆了! 与find(x)很类似,但是查找条件略有不同,事件复杂度为O(logn)
s.lower_bound(x) 查找大于等于x的元素中最小的一个,并返回指向该元素的迭代器.
s.upper_bound(x) 查找大于x的元素中最小的一个,并返回指向该元素的迭代器.
erase(it)/erase(x)
it是一个迭代器,s.erase(it)从集合s中删除迭代器it指向的元素,时间复杂度为O(logn)
设x是一个元素,s.erase(x)从s中删除所有等于x的元素,时间复杂度为O(k+logn),其中k是被删除的元素的个数.
count s.count(x)返回集合s总等于x的元素个数,时间复杂度为O(k+logn),其中k为元素x的个数.
map
引入#include<map>头文件.
map容器是一个键值对key-value的映射,其内部实现是一颗以key为关键码的红黑树. Map的key和value可以是任意类型,其中key必须定义小于号运算符.
c++中的map其实和Python中的dict用法非常类似.
map<string,int> m;
m["yxc"] = 2; // 这样就插入一个新值了
set/empty/clear/begin/end 均与set类似.
insert/erase 均与set类似,但是参数是二元组.
// 插入二元组
map<string,vector<int>> a;
a.insert({"a",{1,2,3}});
find(x) 查找key为x的二元组.
[]操作符
h[key]返回key映射的value的引用,时间复杂度为O(logn).
[]操作符是map最吸引人的地方,我们可以很方便地通过h[key]来得到key对应的value,还可以对h[key]进行赋值操作,改变key对应的value.
map的遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// c99 c11
unordered_map<double,string> a;
a[300] = "e";
a[50] = "c";
a[1] = "a";
a[2] = "b";
for(auto i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
cout << i->first << " " << i->second <<endl;
return 0;
}
unordered_set
引入头文件#include<unordered_set>,这个底层实现是哈希表,之前的#include<set>底层实现是红黑树. 里面有unrodered_set和unordered_multiset
unordered_set与set比较,处理没有lower_bound/upper_bound(因为这是二分操作,需要有序),其余的操作都是一样的. 但是unordered_set基本的操作都是O(1)的,而set的基本操作都是O(logn)的.
unordered_map
引入头文件include<unordered_map>.
这个和map的操作是一样的,但是底层是哈希表,效率更高.
需要注意的是,这个在C11才支持unordered_map,蓝桥杯和NOIP都是C99的标准,是不支持的.
pair
pair是一个二元组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
pair<int,string> p = {1,"x"};
cout << p.first << " " << p.second << endl;
return 0;
}
如果是在c99需要使用函数mark_pair()来进行赋值.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
pair<int,string> p = make_pair(1,"x");
cout << p.first << " " << p.second << endl;
return 0;
}
pair是支持比较的,都已经实现好了,按照双关键字进行比较.
位运算
& 与
| 或
~ 非
^ 异或
>> 右移
<< 左移
常用操作: (这个记住了,算法题会经常使用)
(1) 求x的第k位数字 x>>k&1

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 0b11011;
cout << (1 & (a >> 4)) << endl;
return 0;
}
(2) lowbit(x)==x&-x 返回x的最后一个1
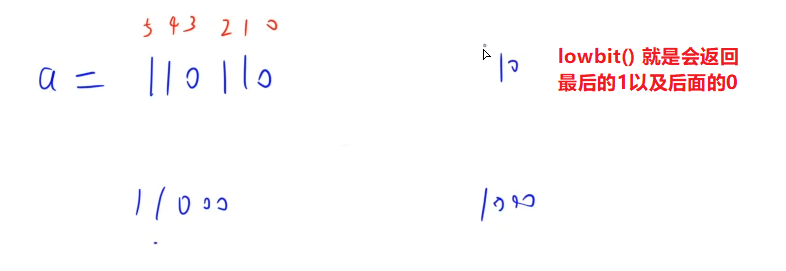
reverse
各种常用函数基本都在#include<algorithm>
reverse(起始指针,终止指针),注意是左闭右开的.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 反转数组
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
reverse(a,a+5);
for(int x:a)cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
// 反转vector
vector<int> b({1,2,3,4,5});
reverse(b.begin(),b.end());
for(int x:a)cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
unique
返回去重之后的尾迭代器(或指针),仍然为前闭后开,即这个迭代器是去重之后末尾元素的下一个位置. 该函数常用于离散化,利用迭代器(或指针)的减法,可计算出去重后的元素个数.
// m是去重后的元素个数
vector<int> a({1,1,2,2,3,3});
int m = unique(a.begin(),a.end())-a.begin();
int b[] = {1,1,2,2,3,3};
int n = unique(a,a+6)-a;
// 遍历去重的元素 0~m m+1~a.end() 就是重复的元素
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) cout << a[i] << " ";
其实如果是使用vector的话,那么更好的做法就是在使用完unique之后,就把需要的元素进行删除.
vector<int> a({1,1,2,2,3,3,3});
a.erase(unique(a.begin(),a.end()),a.end()); // 直接删除后边不要的元素
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[] = {1,2,1,2,2,2,3,4,4,4,5,5};
int m = unique(a,a+sizeof(a)/sizeof(int))-a;
cout << "m:" << m << endl;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int> b({1,2,1,2,2,2,3,4,4,4,5,5});
int n = unique(b.begin(),b.end())-b.begin();
cout << "n:" << n << endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cout << b[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
random_shuffle
random_shuffle的用法和reverse是一样的,但是一般使用的不多,都是用于自己生成数据的情况.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
random_shuffle(a,a+sizeof(a)/sizeof(int));
for(int x:a)cout << x << ' ';
return 0;
}
随机数有随机种子,如果想要每次运行都不一样,需要加入下面代码
#include<ctime>
srand(time(0)); // time(0)是返回从1970/1/1 到现在的秒数
sort
sort(起始指针,结束指针) 升序排序
sort(起始指针,结束指针,greater<int>() 降序排序
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b){ // 定义比较函数都是 <
return a < b;
}
int main(){
srand(time(0));
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int len = sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);
random_shuffle(a,a+len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)cout << a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
sort(a,a+len);// 升序排序
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)cout << a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
sort(a,a+len,greater<int>()); // 降序排序
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)cout << a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
sort(a,a+len,cmp); // 降序排序
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)cout << a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
如果想要给自定义结构体排序的话,就需要自己定义一个排序函数. (如果部自己定一个比较函数的,就需要在结构体内部重载运算符. )
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct rec{
int x,y;
}a[5];
bool cmp(rec a,rec b){
return a.x < b.x;
}
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)a[i].x=-i,a[i].y=i;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)printf("(%d,%d) ",a[i].x,a[i].y);
cout << endl;
sort(a,a+5,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)printf("(%d,%d) ",a[i].x,a[i].y);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
lower_bound/upper_bound 二分
使用二分搜索的前提是序列已经有序了.
// 找到查找值的下标
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int t = lower_bound(a,a+5,3)-a;
习题八
数字在排序数组中出现的次数
class Solution {
public:
int getNumberOfK(vector<int>& nums , int k) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int x:nums)if(x==k)cnt++;
return cnt;
}
};
0到n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> s;
for(int i=0;i<=nums.size();i++)s.insert(i);
for(int x:nums)s.erase(x);
return *s.begin(); // 剩下返回的需要使用迭代器来找
}
};
最简单的做法就是首先把0~n-1都放在一个哈希表中,然后遍历序列进行删除,最后剩下的那个就是答案.
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
这个其实可以使用类似快速排序的双指针,只不过快排是左右二分大小,这个是左右二分奇偶.
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
int i=0,j=array.size()-1;
while(i<j){
while(i<j && (array[i]&1))i++;
while(i<j && !(array[j]&1))j--;
if(i<j)swap(array[i],array[j]);
}
}
};
从尾到头打印链表

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> a;
ListNode* p = head;
while(p){
a.push_back(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
reverse(a.begin(),a.end());
return a;
}
};
用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈来实现队列,其中的一个栈来做缓冲.
第一个栈来做主要操作,第二个栈来做缓冲.
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> s1,s2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
// 初始化可以不用管
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
while(s1.size() > 1)s2.push(s1.top()),s1.pop();
int t = s1.top();
s1.pop(); // y总是把 top() 和 pop() 分开的
while(s2.size())s1.push(s2.top()),s2.pop();
return t;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
while(s1.size() > 1)s2.push(s1.top()),s1.pop();
int t = s1.top();
while(s2.size())s1.push(s2.top()),s2.pop();
return t;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return s1.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
最小的k个数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
sort(input.begin(),input.end());
vector<int> res;
for(auto i=input.begin();i<input.begin()+k;i++)res.push_back(*i);
return res;
}
};
和为S的两个数字

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findNumbersWithSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_set<int> S;
for(int x:nums){
if(S.count(target - x)){// 判断存不存在可以使用 set.count()
return {target -x ,x};
}else{
S.insert(x);
}
}
}
};
数字排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res;
do{
res.push_back(nums);
}while(next_permutation(nums.begin(),nums.end()));
return res;
}
};
这个全排列除了可以使用暴力搜索之外,还可以使用STL的next_permutation(起始指针,结束指针),每次传入数组,都会返回数组的下一个大小的排列,如果已经是最大排列,那么就会返回false, 所以可以使用do...while来使用.
二进制中1的个数

直接每位取出二进制数的位数,如果是1的话就计数加一.
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
if(n >> i & 1)cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};
还有就是使用lowbit(),每次都返回最后一个1以及后面的二进制,可以直接减去.
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while(n)cnt++,n-= -n & n;
return cnt;
}
};
三元组排序

首先可以在结构体中重载运算符,后者自己定义一个排序函数.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
struct D{
int x;
double y;
string z;
// bool operator < (const D& t) const{
// return x < t.x;
// }
}a[N];
bool cmp(D a,D b){
return a.x < b.x;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y >> a[i].z;
// sort(a,a+n);
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d %.2lf %s\n",a[i].x,a[i].y,a[i].z.c_str()); // 注意最后要有string.c_str()
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号