python面向对象之继承
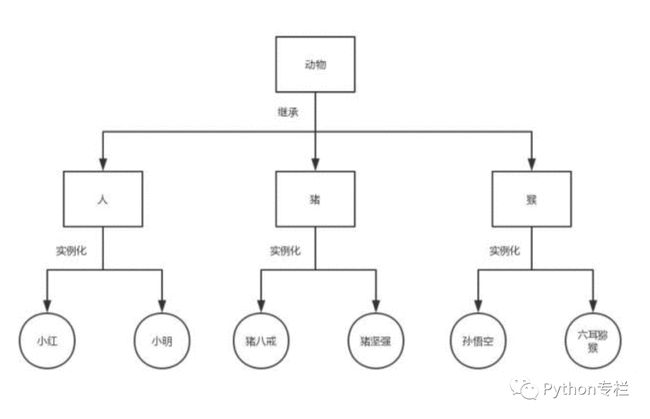
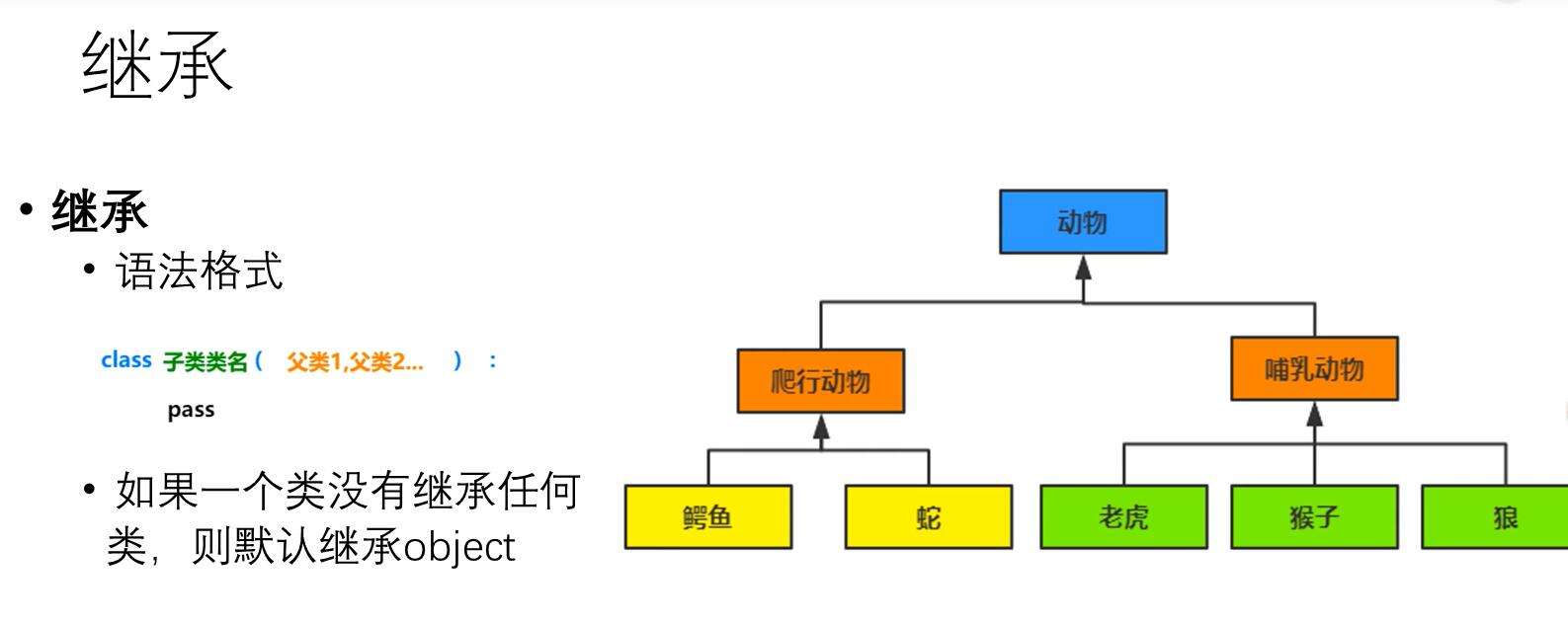
python面向对象之继承· 继承 · 类的继承 · 单继承下属性查找 · 多继承下属性的查找 · super()和mro列表 · 多态与多态性 一、继承1.什么是继承?继承就是新建类的一种方式,新建的类我们称为子类或者叫派生类,被继承的类我们称为父类或基类 子类可以使用父类中的属性或者方法 2.为什么要用继承?类解决了对象与对象之间的代码冗余问题 继承解决的是类与类之间的代码冗余问题 3.如何使用继承?新式类:继承了object类的子子孙孙都是新式类 经典类:没有继承了object类的子子孙孙都是经典类 新式类与经典类只有在python2中区分
二、类的继承# 以学生选课系统为例 # 父类,公共类 class People(): school = 'SH' def __init__(self, name, age, gender): self.name = name self.age = age self.gender = gender # 学生类 class Student(People): def __init__(self, name, age, gender, course=None): if course is None: course = [] People.__init__(self, name, age, gender) self.courses = course def choose_course(self, course): self.courses.append(course) print('%s 选课成功 %s' % (self.name, self.courses)) stu = Student('ly', 19, 'male') # teacher类 class Teacher(People): def __init__(self, name, age, gender, level): self.level = level People.__init__(self, name, age, gender) def score(self, stu_obj, score): stu_obj.score = score # 给学生打分 print('%s给%s打了%s分' % (self.name, stu_obj.name, score)) tea = Teacher('ly', 19, 'male', 10) print(tea.name) print(tea.level) 三、单继承下属性查找class Foo: def f1(self): print('Foo.f1') def f2(self): # print('Foo.f2') self.f1() class Bar(Foo): def f1(self): print('Bar.f1') obj = Bar() # {} obj.f2() # 练习 class Foo: def __f1(self): # _Foo__f1() print('Foo.f1') def f2(self): # print('Foo.f2') self.__f1() # _Foo__f1() class Bar(Foo): def __f1(self): # # _Bar__f1() print('Bar.f1') obj = Bar() # {} obj.f2() 四、多继承下的属性查找
# 新式类:按照广度优先查询 # 经典类:按照深度优先查询 class A(object): def test(self): print('from A') class B(A): # def test(self): # print('from B') pass class C(A): # def test(self): # print('from C') pass class D(B): # def test(self): # print('from D') pass class E(C): # def test(self): # print('from E') pass class F(D, E): # def test(self): # print('from F') pass f1 = F() f1.test() 五、super()和mro列表class People(): school = 'SH' def __init__(self, name, age, gender): self.name = name self.age = age self.gender = gender class Teacher(People): def __init__(self, name, age, gender, level): self.level = level super().__init__(name, age, gender) # super的使用 # mro列表练习1 class A: def test(self): print('from A.test') super().test() class B: def test(self): print('from B') class C(A, B): pass c = C() c.test() # mro列表练习2 class B: def test(self): print('B---->test') def aaa(self): print('B---->aaa') class A: def test(self): print('A---->test') super().aaa() class C(A, B): def aaa(self): print('C----->aaa') c = A() # c.test() # 打印结果: print(A.mro()) 六、多态与多态性
1.什么是多态水:液态水,固态水,气态水 动物:人、猪、狗、猫 # 抽象类: 抽象类只能被继承,不能被实例化 class Animal(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta): @abc.abstractmethod # 该方法已经是抽象方法了 def speak(self): pass @abc.abstractmethod def login(self):pass class People(Animal): def speak(self): # print('嗷嗷嗷') pass def login(self): pass class Pig(Animal): def speak(self): print('哼哼哼') class Dog(Animal): def speak(self): print('汪汪汪') obj = People() obj.speak() # 多态练习 class Pig(): def speak(self): print('哼哼哼') class Dog(): def speak(self): print('汪汪汪') class Txt(): def speak(self): print('Txt') obj = People() obj1 = Pig() obj2 = Dog() obj3 = Txt() # 多态带来的特性:在不用考虑对象数据类型的情况下,直接调用对应的函数 def animal(animal): return animal.speak() animal(obj) animal(obj1) animal(obj2) animal(obj3) # 父类限制子类的行为 class Animal(): def speak(self): raise Exception("必须实现speak方法")
|



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号