运用数据库来存储小信息
本次的任务是
将学生信息存入数据库
显示所有学生信息列表
删除数据库表中第一条信息
就是你输入什么 手机就可以把输入的内容存储在数据库里
方便读取和删除
嗯 就这样
这个有点小麻烦 还有数据库语句什么的

还是谈正事 布局代码就不详写了 直接贴上主要的小部分
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="55dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_add"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:onClick="onClick"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="增加一条信息" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_del"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:onClick="onClick"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="删除一条信息" />
</LinearLayout>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</ListView>
easy easy
来贴Java代码部分
让其读取到输入的内容并且保存
然后再点读取的时候将它弄出来
嗯 还行吧
等等 还得把不想要的删除掉
操作数据库Java代码
public class InfoDAO {
private MainDbHelper helper;
private SQLiteDatabase db;
public InfoDAO (Context context) {
helper = new MainDbHelper(context);
}
public void insert(String name){
db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "insert into student(name) values('"+name+"')";
db.execSQL(sql);
}
public Cursor selectAll() {
db = helper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("student", null, null, null, null, null, null);
return cursor;
}
public void delete(String id) {
db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "delete from student where _id="+String.valueOf(id);
db.execSQL(sql);
}
}
创建和打开数据库
public class MainDbHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private String sql = "create table student(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name txt)";
public MainDbHelper(Context context) {
super(context, "student", null, 1);
}
//当APP中没有数据库或者数据库版本为1的时候会被调用,且只调用一次
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) {
sqLiteDatabase.execSQL(sql);
}
@Override
//升级数据库表.当newVersion > oldVersion,会被调用
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
sqLiteDatabase.execSQL("drop table if exists student");
onCreate(sqLiteDatabase);
}
}
再来一个自定义的Adapter用来解析cursor类型的数据UoCursorAdapter继承自CursonAdapter类
public class UoCursorAdapter extends CursorAdapter {
public UoCursorAdapter(Context context, Cursor cursor) {
super(context, cursor, 0);
}
@Override
public View newView(Context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
return LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.activity_info,viewGroup,false);
}
@Override
public void bindView(View view, Context context, Cursor cursor) {
TextView name = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
name.setText(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name")));
}
}
最后是主类Java代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_add;
private EditText et_name;
InfoDAO infoDAO;
Cursor cursor;
UoCursorAdapter uoCursorAdapter;
private ListView list_info;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
et_name = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_name);
list_info = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.list_info);
infoDAO = new InfoDAO(this);
cursor = infoDAO.selectAll();
if(cursor!=null) {
uoCursorAdapter = new UoCursorAdapter(this, cursor);
list_info.setAdapter(uoCursorAdapter);
}
}
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_add:
String name = et_name.getText().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "姓名,班级不能为空",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
infoDAO.insert(name);
cursor = infoDAO.selectAll();
if(cursor!=null) {
uoCursorAdapter = new UoCursorAdapter(this, cursor);
list_info.setAdapter(uoCursorAdapter);
}
break;
case R.id.btn_del:
if(cursor!=null){
if(cursor.moveToFirst()){
infoDAO.delete(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("_id")));
cursor = infoDAO.selectAll();
}
}
uoCursorAdapter = new UoCursorAdapter(this,cursor);
list_info.setAdapter(uoCursorAdapter);
break;
}
}

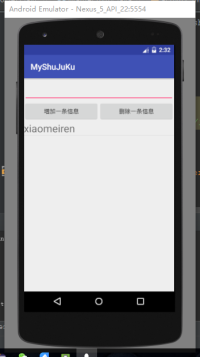
结束了
说实话 写博客 越写越简单短小 不过这篇算比较多的 因为数据库很烦啊 哈哈哈



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号