作业13
1.读取
1 def load(path): 2 with open(path) as f: 3 label, data = [], [] 4 csv_reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter='\t') 5 for line in csv_reader: 6 label.append(line[0]) # Label 7 data.append(pretreatment(line[1])) # Feature 8 return label, data
2.数据预处理
1 def pretreatment(text): 2 # Tokenize 3 tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] 4 stops = stopwords.words('english') 5 # Remove stop words 6 tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] 7 # Convert to lower case if token's length greater than 3 8 tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token) >= 3] 9 lmtzr = WordNetLemmatizer() 10 tag = nltk.pos_tag(tokens) 11 tokens = [lmtzr.lemmatize(token, pos=get_wordnet_pos(tag[i][1])) for i, token in enumerate(tokens)] 12 preprocessed = ' '.join(tokens) 13 return preprocessed
3.数据划分—训练集和测试集数据划分
1 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, label, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=label)
4.文本特征提取
观察邮件与向量的关系
向量还原为邮件
1 def to_feature_matrix(x_train, x_test): 2 tfidf = TfidfVectorizer() 3 X_train = tfidf.fit_transform(x_train) 4 X_test = tfidf.transform(x_test) 5 return X_train, X_test, tfidf 6 7 def vec2word(x_train, X_train, model): 8 vec = X_train.toarray()[0] 9 pos_of_positive = np.flatnonzero(X_train.toarray()[0]) 10 words = [k for k, v in model.vocabulary_.items() if v in pos_of_positive] 11 print("Vector:\t\t\t\t\t{}\n" 12 "Positions of Positive:\t{}\n" 13 "Values of Positive:\t\t{}\n" 14 "Positive Words:\t\t\t{}\n" 15 "Original Words:\t\t\t{}\n".format(vec, pos_of_positive, 16 vec[pos_of_positive], words, x_train[0]))
4.模型选择
1 def predict(type, x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test): 2 model = None 3 if type == 'MultinomialNB': 4 model = MultinomialNB() 5 elif type == 'GaussianNB': 6 model = GaussianNB() 7 model.fit(x_train, y_train) 8 y_pre = model.predict(x_test) 9 print('Samples: {}, Correct: {}'.format(len(y_test), (y_pre == y_test).sum())) 10 return y_pre
5.模型评价:混淆矩阵,分类报告
混淆矩阵(confusion-matrix):
TP(True Positive):真实为0,预测也为0
FN(False Negative):真实为0,预测为1
FP(False Positive):真实为1,预测为0
TN(True Negative):真实为1,预测也为1
准确率:代表分类器对整个样本判断正确的比重。
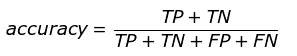
精确率:指被分类器判断正例中的正样本的比重。
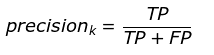
召回率:指被预测为正例的占总的正例的比重。
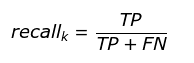
F值:精确率和召回率的调和平均数,最大为1,最小为0。

代码:
1 def model_report(ypre_mnb, y_test): 2 conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, ypre_mnb) 3 print("Confusion matrix:\n", conf_matrix) 4 report = classification_report(y_test, ypre_mnb) 5 print("Classification Report:\n", report) 6 print("Accuracy Rate:", (conf_matrix[0][0] + conf_matrix[1][1]) / np.sum(conf_matrix))
运行结果:
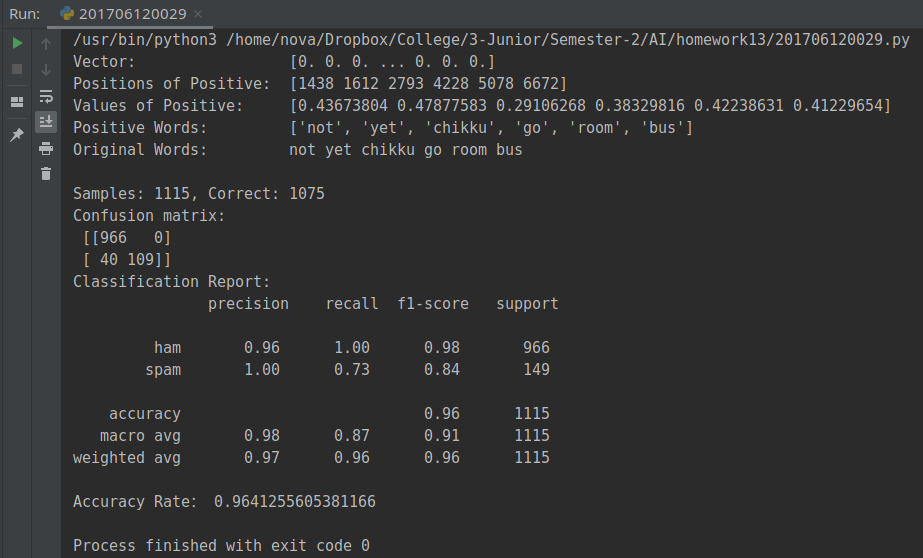
6.比较与总结
如果用CountVectorizer进行文本特征生成,与TfidfVectorizer相比,效果如何?
CountVectorizer:只考虑词汇在文本中出现的频率,属于词袋模型特征。
TfidfVectorizer: 除了考量某词汇在文本出现的频率,还关注包含这个词汇的所有文本的数量。能够削减高频没有意义的词汇出现带来的影响, 挖掘更有意义的特征。文本条目越多,Tfid的效果会越显著。
CountVectorizer与TfidfVectorizer相比,对于负类的预测更加准确,而正类的预测则稍逊色。但总体预测正确率也比TfidfVectorizer稍高,相比之下似乎CountVectorizer更适合进行预测。
完整代码:
1 import csv 2 import numpy as np 3 import nltk 4 from nltk.corpus import stopwords 5 from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer 6 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 7 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer 8 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB 9 from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB 10 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report 11 12 # Set nltk data path 13 nltk.data.path.append("/home/nova/Data/homework/AI/nltk_data-gh-pages/packages") 14 15 def pretreatment(text): 16 # Tokenize 17 tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] 18 stops = stopwords.words('english') 19 # Remove stop words 20 tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] 21 # Convert to lower case if token's length greater than 3 22 tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token) >= 3] 23 lmtzr = WordNetLemmatizer() 24 tag = nltk.pos_tag(tokens) 25 tokens = [lmtzr.lemmatize(token, pos=get_wordnet_pos(tag[i][1])) for i, token in enumerate(tokens)] 26 preprocessed = ' '.join(tokens) 27 return preprocessed 28 29 def load(path): 30 with open(path) as f: 31 label, data = [], [] 32 csv_reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter='\t') 33 for line in csv_reader: 34 label.append(line[0]) # Label 35 data.append(pretreatment(line[1])) # Feature 36 return label, data 37 38 def get_wordnet_pos(treebank_tag): 39 if treebank_tag.startswith('J'): 40 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.ADJ 41 elif treebank_tag.startswith('V'): 42 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.VERB 43 elif treebank_tag.startswith('N'): 44 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.NOUN 45 elif treebank_tag.startswith('R'): 46 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.ADV 47 else: 48 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.NOUN 49 50 # To feature matrix 51 def to_feature_matrix(x_train, x_test): 52 tfidf = TfidfVectorizer() 53 X_train = tfidf.fit_transform(x_train) 54 X_test = tfidf.transform(x_test) 55 return X_train, X_test, tfidf 56 57 def vec2word(x_train, X_train, model): 58 vec = X_train.toarray()[0] 59 pos_of_positive = np.flatnonzero(X_train.toarray()[0]) 60 words = [k for k, v in model.vocabulary_.items() if v in pos_of_positive] 61 print("Vector:\t\t\t\t\t{}\n" 62 "Positions of Positive:\t{}\n" 63 "Values of Positive:\t\t{}\n" 64 "Positive Words:\t\t\t{}\n" 65 "Original Words:\t\t\t{}\n".format(vec, pos_of_positive, 66 vec[pos_of_positive], words, x_train[0])) 67 68 # Using MultinomialNB 69 def predict(type, x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test): 70 model = None 71 if type == 'MultinomialNB': 72 model = MultinomialNB() 73 elif type == 'GaussianNB': 74 model = GaussianNB() 75 model.fit(x_train, y_train) 76 y_pre = model.predict(x_test) 77 print('Samples: {}, Correct: {}'.format(len(y_test), (y_pre == y_test).sum())) 78 return y_pre 79 80 # Report 81 def model_report(ypre_mnb, y_test): 82 conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, ypre_mnb) 83 print("Confusion matrix:\n", conf_matrix) 84 report = classification_report(y_test, ypre_mnb) 85 print("Classification Report:\n", report) 86 print("Accuracy Rate:", (conf_matrix[0][0] + conf_matrix[1][1]) / np.sum(conf_matrix)) 87 88 if __name__ == '__main__': 89 # Load dataset 90 label, data = load('./SMSSpamCollection') 91 # Train-test split 92 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, label, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=label) 93 # Samples to feature matrix 94 X_train, X_test, tfidf = to_feature_matrix(x_train, x_test) 95 # Vector to words 96 vec2word(x_train, X_train, tfidf) 97 # Predict with MultinomialNB model 98 y_pre = predict('MultinomialNB', X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test) 99 # Evaluate the model 100 model_report(y_pre, y_test)


