JAVA使用下面的方法头编写方法,返回两个数组列表的并集

import java.util.Set; import java.util.List; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.TreeSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedList; public class GAGA { public static void main(String args[]) { getList(); } // 获取两个ArrayList的差集、交集、去重并集(数据量大小不限制) private static void getList() { List<String> firstArrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> secondArrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> defectList = new ArrayList<String>();//差集List List<String> collectionList = new ArrayList<String>();//交集List List<String> unionList = new ArrayList<String>();//去重并集List try { firstArrayList.add("3"); firstArrayList.add("5"); firstArrayList.add("45"); firstArrayList.add("4"); firstArrayList.add("3"); secondArrayList.add("33"); secondArrayList.add("51"); secondArrayList.add("5"); secondArrayList.add("4"); secondArrayList.add("13"); // 获取差集 defectList = receiveDefectList(firstArrayList, secondArrayList); Iterator<String> defectIterator = defectList.iterator(); System.out.println("===================差集==================="); while(defectIterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(defectIterator.next()); } // 获取交集 collectionList = receiveCollectionList(firstArrayList, secondArrayList); Iterator<String> collectionIterator = collectionList.iterator(); System.out.println("===================交集==================="); while(collectionIterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(collectionIterator.next()); } // 获取去重并集 unionList = receiveUnionList(firstArrayList, secondArrayList); Iterator<String> unionIterator = unionList.iterator(); System.out.println("===================去重并集==================="); while(unionIterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(unionIterator.next()); } }catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @方法描述:获取两个ArrayList的差集 * @param firstArrayList 第一个ArrayList * @param secondArrayList 第二个ArrayList * @return resultList 差集ArrayList */ public static List<String> receiveDefectList(List<String> firstArrayList, List<String> secondArrayList) { List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<String>(); LinkedList<String> result = new LinkedList<String>(firstArrayList);// 大集合用linkedlist HashSet<String> othHash = new HashSet<String>(secondArrayList);// 小集合用hashset Iterator<String> iter = result.iterator();// 采用Iterator迭代器进行数据的操作 while(iter.hasNext()){ if(othHash.contains(iter.next())){ iter.remove(); } } resultList = new ArrayList<String>(result); return resultList; } /** * @方法描述:获取两个ArrayList的交集 * @param firstArrayList 第一个ArrayList * @param secondArrayList 第二个ArrayList * @return resultList 交集ArrayList */ public static List<String> receiveCollectionList(List<String> firstArrayList, List<String> secondArrayList) { List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<String>(); LinkedList<String> result = new LinkedList<String>(firstArrayList);// 大集合用linkedlist HashSet<String> othHash = new HashSet<String>(secondArrayList);// 小集合用hashset Iterator<String> iter = result.iterator();// 采用Iterator迭代器进行数据的操作 while(iter.hasNext()) { if(!othHash.contains(iter.next())) { iter.remove(); } } resultList = new ArrayList<String>(result); return resultList; } /** * @方法描述:获取两个ArrayList的去重并集 * @param firstArrayList 第一个ArrayList * @param secondArrayList 第二个ArrayList * @return resultList 去重并集ArrayList */ public static List<String> receiveUnionList(List<String> firstArrayList, List<String> secondArrayList) { List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<String>(); Set<String> firstSet = new TreeSet<String>(firstArrayList); for(String id : secondArrayList) { // 当添加不成功的时候 说明firstSet中已经存在该对象 firstSet.add(id); } resultList = new ArrayList<String>(firstSet); return resultList; } }
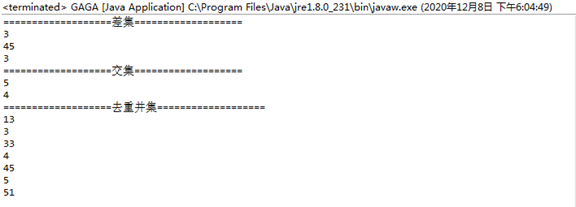
输出结果如图:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号