利用链地址法实现 hash表
链地址法也成为拉链法。
其基本思路是:将全部具有同样哈希地址的而不同keyword的数据元素连接到同一个单链表中。假设选定的哈希表长度为m,则可将哈希表定义为一个有m个头指针组成的指针数组T[0..m-1]。凡是哈希地址为i的数据元素,均以节点的形式插入到T[i]为头指针的单链表中。而且新的元素插入到链表的前端,这不仅由于方便。还由于常常发生这种事实:新近插入的元素最优可能不久又被訪问。
链地址法特点
(1)拉链法处理冲突简单。且无堆积现象,即非同义词决不会发生冲突,因此平均查找长度较短;
(2)因为拉链法中各链表上的结点空间是动态申请的。故它更适合于造表前无法确定表长的情况。
(3)开放定址法为降低冲突。要求装填因子α较小。故当结点规模较大时会浪费非常多空间。而拉链法中可取α≥1,且结点较大时,拉链法中添加的指针域可忽略不计,因此节省空间;
(4)在用拉链法构造的散列表中,删除结点的操作易于实现。仅仅要简单地删去链表上对应的结点就可以。而对开放地址法构造的散列表,删除结点不能简单地将被删结点的空间置为空,否则将截断在它之后填人散列表的同义词结点的查找路径。这是由于各种开放地址法中,空地址单元(即开放地址)都是查找失败的条件。
因此在用开放地址法处理冲突的散列表上运行删除操作。仅仅能在被删结点上做删除标记,而不能真正删除结点。
下面简单的对hash表中数据存储进行实现,功能主要包括将数组元素存储在hash表中
用两个结点分别记录key值元素与目标数组元素,数据结构定义为
// 存储目标数组中元素的结点 typedef struct ArcNode{ int data; // 元素值 struct ArcNode * Next; }ArcNode, *pArcNode; // 存储hash链key值数组的结点 typedef struct RouNode{ int key; // key值 ArcNode * link; }RouNode, *pRouNode;
代码具体执行结果如下
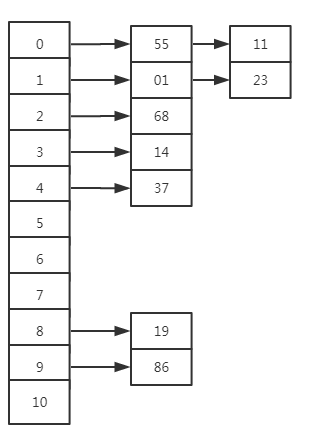
key of the node is 0, the hash number:55 11 key of the node is 1, the hash number:1 23 key of the node is 2, the hash number:68 key of the node is 3, the hash number:14 key of the node is 4, the hash number:37 key of the node is 5, the hash number: key of the node is 6, the hash number: key of the node is 7, the hash number: key of the node is 8, the hash number:19 key of the node is 9, the hash number:86 key of the node is 10, the hash number:
代码执行结果图示如下
完整代码

// hash link+array // 链地址法实现 # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # define NUM 11 // 表示 hash 链的长度 # define Maxsize 9 // 表示需要hash处理数组的长度 // 存储目标数组中元素的结点 typedef struct ArcNode{ int data; // 元素值 struct ArcNode * Next; }ArcNode, *pArcNode; // 存储hash链key值数组的结点 typedef struct RouNode{ int key; // key值 ArcNode * link; }RouNode, *pRouNode; pRouNode creat_Array(int num); // 创建hash表中key值数组,并初始化指针域为空 pArcNode creat_node(int val); // 创建一个无连接的新结点,并将数组元素保存在结点中 void traverse_node(pRouNode Array); // 遍历整个hash链表 int get_key(int val); // 计算数组元素的key值 pRouNode link_node(pRouNode Array, int val); // 对某个单一的数值进行hash处理 pRouNode link_array(pRouNode Array, int A[]); // 将整个数组依次进行hash int main(void) { int A[Maxsize] = {1,55,14,19,23,37,11,68,86}; pRouNode Array = creat_Array(NUM); link_array(Array, A); traverse_node(Array); return 0; } pRouNode creat_Array(int num) { int i; pRouNode Array = (pRouNode)malloc(sizeof(RouNode)*num); for (i=0; i<NUM; i++) { Array[i].key = i; Array[i].link = NULL; } return Array; } pArcNode creat_node(int val) { pArcNode NODE = (pArcNode)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); NODE->data = val; NODE->Next = NULL; return NODE; } void traverse_node(pRouNode Array) { int i; for (i=0; i<NUM; i++) { printf("key of the node is %d, the hash number:",Array[i].key); pArcNode pNew = Array[i].link; while (NULL != pNew) { printf("%d ",pNew->data); pNew = pNew->Next; } printf("\n"); } return ; } int get_key(int val) // 计算数组元素的 key值 { return val%NUM; } pRouNode link_node(pRouNode Array, int val) { if (NULL != Array[get_key(val)].link) { pArcNode pNew = Array[get_key(val)].link; while (NULL != pNew->Next) { pNew = pNew->Next; } pNew->Next = creat_node(val); } else { pArcNode pNew = creat_node(val); Array[get_key(val)].link = pNew; } return Array; } pRouNode link_array(pRouNode Array, int A[]) { int i = 0; for (i; i<Maxsize; i++) { link_node(Array, A[i]); } return Array; }
RRR
本人计算机小白一枚,对编程有浓厚兴趣,在此贴出自己的计算机学习历程,还有很多不足,望多多指教!
读书后发现好多的内容与具体专业有偏差,没来得及完成,虽然“有时间我就会做...”是人生最大的谎言,但有时间我会继续搞定未完成的内容,有始有终,兴趣使然!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号