库函数总结
C++ cctype头文件内的判断类函数
isalpha(x) 判断大小写字母
islower(x) 判断小写字母
isupper(x) 判断大写字母
isblank(x) 判断space和\t
isspace(x) 判断(space 、\t、\r、\n)
(tolower/toupper)实现字母的大小写转换
常用到的是在ctype.h(C++中是cctype)库文件下定义的函数方法
C:
函数实现原型:
int tolower(int c)//小写
{
if ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z'))
return c + ('a' - 'A');
return c;
}
int toupper(int c)//大写
{
if ((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z'))
return c + ('A' - 'a');
return c;
}
demo-C语言实现
#include<string.h> //strlen
#include<stdio.h> //printf
#include<ctype.h> //tolower
int main()
{
int i;
char string[] = "THIS IS A STRING";
printf("%s\n", string);
for (i = 0; i < strlen(string); i++)
{
string[i] = tolower(string[i]);
}
printf("%s\n", string);
printf("\n");
}
demo-C++的实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str= "THIS IS A STRING";
for (int i=0; i <str.size(); i++)
str[i] = tolower(str[i]);
cout<<str<<endl;
return 0;
}
next_permutation()
对于next_permutation函数,其函数原型为:
#include
bool next_permutation(iterator start,iterator end)
当当前序列不存在下一个排列时,函数返回false,否则返回true
而prev_permutation函数就要反过来了,当上一个排序不存在时返回false,否则返回true
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num[5]={1,2,3}; //此时应该是升序,中间出现逆序的会无法出现全部排序
do
{
cout<<num[0]<<" "<<num[1]<<" "<<num[2]<<endl;
}while(next_permutation(num,num+3));
return 0;
}
运行以后可以发现,next_permutation(num,num+n)函数是对数组num中的前n个元素进行全排列,同时并改变num数组的值。
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。
prev_premutation()与next...相反
qsort()
函数声明
void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void*))
参数
- **base **-- 指向要排序的数组的第一个元素的指针。
- **nitems **-- 由 base 指向的数组中元素的个数。
- **size **-- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
- **compar **-- 用来比较两个元素的函数。
返回值
该函数不返回任何值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int values[] = { 88, 56, 100, 2, 25 };
int cmpfunc (const void * a, const void * b)
{
return ( *(int*)a - *(int*)b );
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("排序之前的列表:\n");
for( n = 0 ; n < 5; n++ ) {
printf("%d ", values[n]);
}
qsort(values, 5, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
printf("\n排序之后的列表:\n");
for( n = 0 ; n < 5; n++ ) {
printf("%d ", values[n]);
}
return(0);
}
C++ rand 与 srand 的用法
计算机的随机数都是由伪随机数,即是由小M多项式序列生成的,其中产生每个小序列都有一个初始值,即随机种子。(注意: 小M多项式序列的周期是65535,即每次利用一个随机种子生成的随机数的周期是65535,当你取得65535个随机数后它们又重复出现了。)
我们知道 rand() 函数可以用来产生随机数,但是这不是真正意义上的随机数,是一个伪随机数,是根据一个数(我们可以称它为种子)为基准以某个递推公式推算出来的一系列数,当这系列数很大的时候,就符合正态公布,从而相当于产生了随机数,但这不是真正的随机数,当计算机正常开机后,这个种子的值是定了的,除非你破坏了系统。
rand()
功能: 随机数发生器
用法:
int rand(void)
所在头文件: stdlib.h
rand() 的内部实现是用线性同余法做的,它不是真的随机数,因其周期特别长,故在一定的范围里可看成是随机的。
rand() 返回一随机数值的范围在 0 至 RAND_MAX 间。RAND_MAX 的范围最少是在 32767 之间(int)。用 unsigned int 双字节是 65535,四字节是 4294967295 的整数范围。0~RAND_MAX 每个数字被选中的机率是相同的。
用户未设定随机数种子时,系统默认的随机数种子为 1。
rand() 产生的是伪随机数字,每次执行时是相同的; 若要不同, 用函数 srand() 初始化它。
srand()
功能: 初始化随机数发生器
用法:
void srand(unsigned int seed)
所在头文件: stdlib.h
srand() 用来设置 rand() 产生随机数时的随机数种子。参数 seed 必须是个整数,如果每次 seed 都设相同值,rand() 所产生的随机数值每次就会一样。
使用当前时钟作为随机数种子
rand() 产生的随机数在每次运行的时候都是与上一次相同的。若要不同, 用函数 srand() 初始化它。可以利用 srand((unsigned int)(time(NULL)) 的方法,产生不同的随机数种子,因为每一次运行程序的时间是不同的。
产生随机数的用法
- 给srand()提供一个种子,它是一个unsigned int类型;
- 调用rand(),它会根据提供给srand()的种子值返回一个随机数(在0到RAND_MAX之间);
- 根据需要多次调用rand(),从而不间断地得到新的随机数;
- 无论什么时候,都可以给srand()提供一个新的种子,从而进一步"随机化"rand()的输出结果。
0~RAND_MAX 之间的随机数程序
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++ )
cout << rand() << '/t';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
产生一定范围随机数的通用表示公式
要取得 [a,b) 的随机整数,使用 (rand() % (b-a))+ a;
要取得 [a,b] 的随机整数,使用 (rand() % (b-a+1))+ a;
要取得 (a,b] 的随机整数,使用 (rand() % (b-a))+ a + 1;
通用公式: a + rand() % n;其中的 a 是起始值,n 是整数的范围。
要取得 a 到 b 之间的随机整数,另一种表示:a + (int)b * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1)。
要取得 0~1 之间的浮点数,可以使用 rand() / double(RAND_MAX)。
stringstream
stringstream是 C++ 提供的另一个字串型的串流(stream)物件,和之前学过的iostream、fstream有类似的操作方式。要使用stringstream, 必須先加入這一行:include
stringstream主要是用在將一個字串分割,可以先用 clear( )以及 str( ) 將指定字串設定成一开始的內容,再用 >> 把个別的资料输出,例如:string s; stringstream ss; int a, b, c; getline(cin, s); ss.clear(); ss.str(s); ss >> a >> b >> c;下面我們看到一個使用
stringstream的例子:題目:输入的第一行有一个数字 N 代表接下來有 N 行資料,每一行資料里有不固定個數的整數(最多 20 個,每行最大 200 個字元),請你寫一個程式將每行的总和印出來。
輸入:
3
1 2 3
20 17 23 54 77 60
111 222 333 444 555 666 777 888 999輸出:
6
251
4995程式如下:
string s; stringstream ss; int n, i, sum, a; cin >> n; getline(cin, s); // 讀取換行 for (i=0; i<n; i++) { getline(cin, s); ss.clear(); ss.str(s); sum=0; while (1) { ss >> a; if ( ss.fail() ) break; sum+=a; } cout << sum << endl; }
[stringstream使用详解](https://blog.csdn.net/xw20084898/article/details/21939811)
string substr()函数
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
产生子串
返回一个新建的
初始化为string对象的子串的拷贝
string对象。
子串是,在字符位置pos开始,跨越len个字符(或直到字符串的结尾,以先到者为准)对象的部分。
参数
pos
第一个字符的位置被复制为子串。
如果这是等于字符串的长度,该函数返回一个空字符串。
如果这是大于字符串的长度,它会抛出out_of_range。
注意:第一个字符表示为值0(不是1)。
len
字符数在子包括(如果字符串是短,尽可能多的字符可以在需要使用)。
字符串::非营利值表示的所有字符,直到字符串的结尾。
返回值
A string object with a substring of this object.
实例
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string x="Hello_World";
/*默认截取从0到npos.重载原型为string substr(_off=0,_count=npos);npos一般表示为string类中不存在的位置,_off表示字符串的开始位置,_count截取的字符的数目*/
cout<<x.substr()<<endl;
cout<<x.substr(5)<<endl;//截取x[5]到结尾,即npos.重载原型为string substr(_off,_count=npos)
cout<<x.substr(0,5)<<endl;//以x[0]为始,向后截取5位(包含x[0]),重载原型string substr(_off,_count)
/*
备注:
指定的截取长度加起始位置即_off+_count>源字符串的长度,则子字符串将延续到源字符串的结尾
*/
}
string append() 函数
函数原型
basic_string &append( const basic_string &str );
basic_string &append( const char *str );
basic_string &append( const basic_string &str, size_type index, size_type len );
basic_string &append( const char *str, size_type num );
basic_string &append( size_type num, char ch );
basic_string &append( input_iterator start, input_iterator end );
可实现的功能
在字符串的末尾添加str,
在字符串的末尾添加str的子串,子串以index索引开始,长度为len
在字符串的末尾添加str中的num个字符,
在字符串的末尾添加num个字符ch,
在字符串的末尾添加以迭代器start和end表示的字符序列.
append函数常用的三个功能:
- 直接添加另一个完整的字符串:如str1.append(str2);
- 添加另一个字符串的某一段子串:如str1.append(str2, 11, 7);
- 添加几个相同的字符:如str1.append(5, ‘.’);注意,个数在前字符在后.上面的代码意思为在str1后面添加5个"."
实例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str1="I like C++";
string str2=",I like the world.";
string str3="Hello";
string str4("Hi");
str1.append(str2);
str3.append(str2, 11, 7);
str4.append(5, '.');
cout<<str1<<endl;
cout<<str3<<endl;
cout<<str4<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果
I like C++,I like the world.
Hello World.
Hi.....
substr()和append()结合使用
题目描述
- 连续输入字符串,请按长度为8拆分每个字符串后输出到新的字符串数组;
- 长度不是8整数倍的字符串请在后面补数字0,空字符串不处理。
实现方法1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
int count = 0;
int remain_num = 0;
while (cin >> str) {
count = str.size() / 8;
remain_num = str.size() % 8;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
string full,temp;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
temp = str[j];
full += temp;
}
cout << full << endl;
str.erase(str.begin(), str.begin() + 8);
}
if(remain_num){
string remain(8-remain_num, '0');
str += remain;
cout << str << endl;
}
}
}
实现方法2
使用str.size()方法可以轻松的实现在一段字符串中提取部分内容
使用str.append()方法可以轻松实现拓展字符串
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
while (cin >> str) {
int remain_num = str.size() % 8;
while (str.size() >= 8) {
cout << str.substr(0, 8) << endl;
str = str.substr(8);//注意此处代表提取,从str[8]开始到str结尾的内容
}
if (remain_num) {
str.append(8 - remain_num, '0');
cout << str << endl;
}
}
}
C++11特性的to_string
头文件 #include
to_string最常用的就是把int型变量或者数字转化为string类型
double、float也是可以的
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1=to_string(123);
cout<<s1<<endl;
string s2=to_string(4.5);
cout<<s2<<endl;
cout<<s1+s2<<endl;
printf("%s\n",(s1+s2).c_str());//想使用printf输出string的时候要加个.c_str()
}
count函数
头文件 algorithm
功能类似于find。这个函数使用一对迭代器和一个值做参数,返回这个值出现次数的统计结果。
编写程序读取一系列int型数据,并将它们存储到vector对象中,然后统计某个指定的值出现了多少次。
cout<<count(ivec.begin() , ivec.end() , searchValue)
具体实现:
//读取一系列int数据,并将它们存储到vector对象中,
//然后使用algorithm头文件中定义的名为count的函数,
//统计某个指定的值出现了多少次
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ival , searchValue;
vector<int> ivec;
//读入int型数据并存储到vector对象中,直至遇到文件结束符
cout<<"Enter some integers(Ctrl+Z to end): "<<endl;
while(cin >> ival)
ivec.push_back(ival);
cin.clear(); // 使输入流重新有效
//读入欲统计其出现次数的int值
cout<<"Enter an integer you want to search: "<<endl;
cin>>searchValue;
//使用count函数统计该值出现的次数并输出结果
cout<<count(ivec.begin() , ivec.end() , searchValue)
<<" elements in the vector have value "
<<searchValue<<endl;
return 0;
}
count_if函数
count_if :返回区间中满足指定条件的元素数目。
template
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
bool greater10(int value)
{
return value >10;
}
int main()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v1;
vector<int>::iterator Iter;
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(10);
cout << "v1 : ";
for (Iter = v1.begin(); Iter != v1.end(); Iter++)
cout << *Iter << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int>::size_type result1 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater10); //count_if算法返回使谓词函数返回条件成立的元素个数
cout << "The number of elements in v1 greater than 10 is: "
<< result1 << "." << endl;
return 0;
}
谓词(predicate):是做某些检测的函数,返回用于条件判断的类型,指出条件是否成立。
总结:
count : 在序列中统计某个值出现的次数count_if : 在序列中统计与某谓词匹配的次数
greater()与less()函数
greater和less是头文件
中定义的两个结构,它们通过重载了()运算符来实现比较功能。
greater的定义如下:
template <class T> struct greater {
bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const {return x>y;}
typedef T first_argument_type;
typedef T second_argument_type;
typedef bool result_type;
};
less的定义如下:
template <class T> struct less {
bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const {return x<y;}
typedef T first_argument_type;
typedef T second_argument_type;
typedef bool result_type;
};
具体使用
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>//因为用了sort()函数
#include<functional>//因为用了greater<int>()
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int a[]={3,1,4,2,5};
int i;
int len=sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);//这里切记要除以sizeof(int)!
sort(a ,a + len, greater<int>());//内置类型的由大到小排序
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
sort(a, a + len, less<int>());//内置类型的由小到大排序
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
priority_queue用法
头文件 : #include<queue>
定义: priority_queue<int> p;
优先输出大数据
priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>
Type为数据类型, Container为保存数据的容器,Functional为元素比较方式。
如果不写后两个参数,那么容器默认用的是vector,比较方式默认用operator<,也就是优先队列是大顶堆,队头元素最大。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main(){
priority_queue<int> p;
p.push(1);
p.push(2);
p.push(8);
p.push(5);
p.push(43);
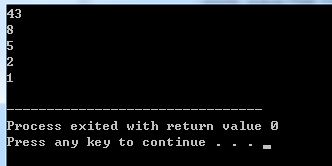
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout<<p.top()<<endl;
p.pop();
}
return 0;
}
优先输出小数据
方法一
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > p;
举例
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main(){
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >p;
p.push(1);
p.push(2);
p.push(8);
p.push(5);
p.push(43);
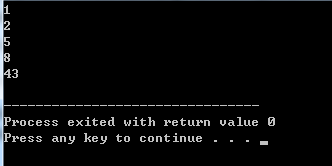
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout<<p.top()<<endl;
p.pop();
}
return 0;
}
方法二:自定义优先级,重载默认的 < 符号
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int x,y;
Node(int a=0, int b=0):
x(a), y(b) {}
};
struct cmp{
bool operator()(Node a, Node b){
if(a.x == b.x) return a.y>b.y;
return a.x>b.x;
}
};
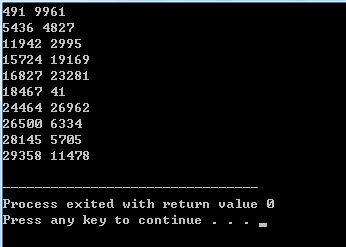
int main(){
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp>p;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
p.push(Node(rand(), rand()));
while(!p.empty()){
cout<<p.top().x<<' '<<p.top().y<<endl;
p.pop();
}//while
//getchar();
return 0;
}
STL适合场景
| vector | deque | list | set | mulitset | map | mulitmap | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 内存结构 | 单端数组 | 双端数组 | 双向链表 | 二叉树 | 二叉树 | 二叉树 | 二叉树 |
| 可随机存储 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 对key而言,不是 | 否 |
| 元素搜索速度 | 慢 | 慢 | 非常慢 | 快 | 快 | 对key而言,快 | 对key而言,快 |
| 元素插删位置 | 尾端 | 头尾两端 | 任何位置 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
list 表单
vector 顺序方面元素
deque 队列
map 关键字-值,字典
set 在文本处理过程中,可以用来保存想要忽略的单词。
isdigit()检查所传的字符是否是十进制数字字符
描述
C 库函数 void isdigit(int c) 检查所传的字符是否是十进制数字字符。
十进制数字是:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
函数声明
int isdigit(int c);
返回值: 如果 c 是一个数字,则该函数返回非零值,否则返回 0。
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
int var1 = 'h';
int var2 = '2';
if( isdigit(var1) )
{
printf("var1 = |%c| 是一个数字\n", var1 );
}
else
{
printf("var1 = |%c| 不是一个数字\n", var1 );
}
if( isdigit(var2) )
{
printf("var2 = |%c| 是一个数字\n", var2 );
}
else
{
printf("var2 = |%c| 不是一个数字\n", var2 );
}
return(0);
}
结果
var1 = |h| 不是一个数字
var2 = |2| 是一个数字
stoi 函数解析
功能
将 n 进制的字符串转化为十进制
用法
stoi(字符串,起始位置,n进制),将 n 进制的字符串转化为十进制
示例:
stoi(str, 0, 2); //将字符串 str 从 0 位置开始到末尾的 2 进制转换为十进制
头文件
#include <string>
实例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "1010";
int a = stoi(str, 0, 2);
cout << a << endl;
}
//输出10
iota函数
函数原型
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
void iota (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, T val);
等价于
template<class _FwdIt,class _Ty> inline
void _Iota(_FwdIt _First, _FwdIt _Last, _Ty _Val)
{ // compute increasing sequence into [_First, _Last)
for (; _First != _Last; ++_First, ++_Val)
*_First = _Val;
}
参数:
-
first,last:
分别指向序列中初始及末尾位置的正向迭代器(Forward Iterators)。这个范围即 [first,last) ,包括 first 到 last 间的所有元素,包括 first 指向的元素,但不包括 last 指向的元素。
-
val:用于累加的初始值。
功能
用顺序递增的值赋值指定范围内的元素 。
实例
// iota example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <numeric> // std::iota
int main () {
int numbers[10];
std::iota (numbers,numbers+10,100);
std::cout << "numbers:";
for (int& i:numbers) std::cout << ' ' << i;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
numbers: 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109