BZOJ4541[HNOI2016]矿区(对偶图)
题目链接
前置知识
平面图转对偶图
简单理解“对偶图”就是,原图边把平面切成了很多块,对偶图中的点代表这些块(最外面的无穷域也可以算作一个块),相邻的块(即有公共边)之间连边,如下图(左边原图,右边对偶图):
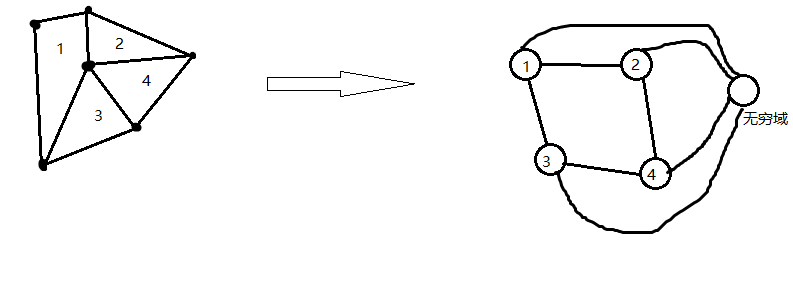
不难发现原图中的每条边都对应了新图中的一条边
那么如何将一个平面图转成对偶图呢
先把无向边拆成两条有向边,这样每条边都可以被分配到一个块里
我们发现若一个点的入边\(i\)和出边\(j\)同属一个“块”,那么对这个点连出的边极角排序后,\(i\)的反向边一定和\(j\)相邻,那么我们可以借助极角排序先求出一个\(next\)数组,\(next[i]\)表示和边\(i\)同属一个块,且紧跟在\(i\)后的那条边
随后我们枚举每条未分配边,不断跳\(next\),把经过的边和这条边自身分配给一个新“块”,显然会有一个时刻跳回这条边自己,这时退出,继续枚举未分配边,直到把所有边分配
接下来枚举每条边,把它和它的反向边所分配的“块”连边即可
代码在最下方题解代码中
解析
先求对偶图
然后以无穷域为根求出一棵生成树,每个节点维护子树内面积和、面积的平方和
枚举所求区域的边界,若一个块在边界的父亲位置,减去儿子的贡献,若在儿子位置,加上儿子的贡献
结合画图比较好理解(其实是我不知道怎么讲比较清楚)
代码
PS.注意开long long,我因为P没开long long RE了半个下午。。。。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#define MAXN 200005
#define MAXM 1200005
#define sqr(x) ((x) * (x))
typedef long long LL;
const double eps = 1e-10;
struct Point {
int x, y;
Point(int _x = 0, int _y = 0):x(_x), y(_y) {};
} pt[MAXN];
struct Edge {
int u, v, id;
double ang;
Edge() { memset(this, 0, sizeof(Edge)); }
Edge(int _u, int _v, int _id) { u = _u, v = _v, id = _id, ang = atan2(pt[v].y - pt[u].y, pt[v].x - pt[u].x); }
bool operator <(const Edge &e) const { return fabs(ang - e.ang) < eps ? v < e.v : ang < e.ang; }
} edge[MAXM];
std::vector<Edge> G[MAXN], tree[MAXM];
int N, M, Q, root, tot, cnt, next[MAXM], area[MAXM], qry[MAXM], fa[MAXM];
LL up[MAXM], s[MAXM], P;
char vis[MAXM], in_tree[MAXM];
char gc();
LL read();
void print(LL);
void build();
void dfs(int);
LL gcd(LL x, LL y) { return y ? gcd(y, x % y) : x; }
int main() {
//freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
N = read(), M = read(), Q = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) pt[i].x = read(), pt[i].y = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) {
int a = read(), b = read();
edge[tot] = Edge(a, b, tot), G[a].push_back(edge[tot]), ++tot;
edge[tot] = Edge(b, a, tot), G[b].push_back(edge[tot]), ++tot;
}
build();
dfs(root);
while (Q--) {
int c = (read() + P) % N + 1;
LL ans0 = 0, ans1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < c; ++i) qry[i] = (read() + P) % N + 1;
qry[c] = qry[0];
for (int i = 1; i <= c; ++i) {
Edge tmp = Edge(qry[i - 1], qry[i], 0);
int t = (*std::lower_bound(G[qry[i - 1]].begin(), G[qry[i - 1]].end(), tmp)).id;
if (!in_tree[t]) continue;
if (fa[area[t]] == area[t ^ 1]) ans0 += up[area[t]], ans1 += s[area[t]];
else ans0 -= up[area[t ^ 1]], ans1 -= s[area[t ^ 1]];
}
LL d = gcd(ans0, ans1);
print(P = ans0 / d); putchar(' '); print(ans1 / d); putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
inline char gc() {
static char buf[1000000], *p1, *p2;
if (p1 == p2) p1 = (p2 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1000000, stdin);
return p1 == p2 ? EOF : *p2++;
}
inline LL read() {
LL res = 0, op; char ch = gc();
while (ch != '-' && (ch < '0' || ch > '9')) ch = gc();
op = (ch == '-' ? ch = gc(), -1 : 1);
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') res = (res << 1) + (res << 3) + ch - '0', ch = gc();
return res * op;
}
inline void print(LL x) {
static int buf[30];
if (!x) putchar('0');
else {
if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
while (x) buf[++buf[0]] = x % 10, x /= 10;
while (buf[0]) putchar('0' + buf[buf[0]--]);
}
}
inline LL get_square(int i, int j, int k) {
LL x1 = pt[j].x - pt[i].x, x2 = pt[k].x - pt[i].x;
LL y1 = pt[j].y - pt[i].y, y2 = pt[k].y - pt[i].y;
return x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
}
void build() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) std::sort(G[i].begin(), G[i].end());
for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i) {
int v = edge[i].v;
std::vector<Edge>::iterator p = std::lower_bound(G[v].begin(), G[v].end(), edge[i ^ 1]);
if (p == G[v].begin()) p = G[v].end();
--p, next[i] = p->id;
}
for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i) {
if (area[i]) continue;
area[i] = area[next[i]] = ++cnt;
for (int j = next[i]; edge[j].v ^ edge[i].u; j = next[j], area[j] = cnt)
s[cnt] += get_square(edge[i].u, edge[j].u, edge[j].v);
if (s[cnt] <= 0) root = cnt;
}
for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i)
tree[area[i]].push_back(Edge(area[i], area[i ^ 1], i));
}
void dfs(int u) {
up[u] = sqr(s[u]), s[u] <<= 1, vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < tree[u].size(); ++i) {
Edge e = tree[u][i];
if (!vis[e.v]) {
in_tree[e.id] = in_tree[e.id ^ 1] = 1, fa[e.v] = u;
dfs(e.v);
s[u] += s[e.v], up[u] += up[e.v];
}
}
}

