DS博客作业02--栈和队列
| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 韩龙飞 |
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结(0-5分)
1.1 栈
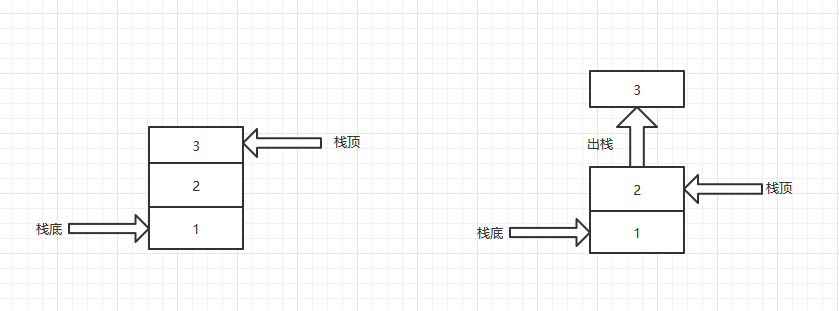
定义:栈是一种只能在一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
组成成分:栈顶(Top)、栈底(Bottom)
特点:后进先出(Last In First Out,LIFO)
基本操作:初始化、销毁、进栈、出栈、取栈顶元素
1.1.1 顺序栈
- 结构体
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top; //栈顶指针
}Stack,*SqStack;
- 初始化函数
void InitStack(SqStack &s) {
s = new Stack;
s->top = -1;
}
- 进栈
![]()
bool Push(SqStack &s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == MaxSize-1) {
return false;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = e;
return true;
}
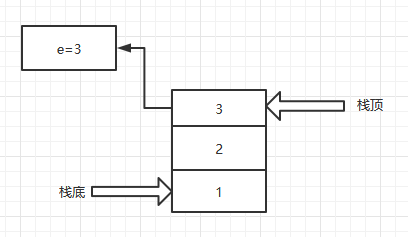
- 出栈
![]()
bool Pop(SqStack &s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == -1) {
return false;
}
e=s->data[s->top];
s->top--
return true;
}
- 取栈顶元素
![]()
bool GetTop(SqStack &s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == -1) {
return false;
}
e = s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
1.1.2 链栈
- 结构体
typrdef struct linkNode
{
ElemType data;
struct linkNode *next;
}LiNode,*Listack;
- 初始化
void CreatStack(LiStack &s)
{
s=new LiNode;
s->next=NULL;
}
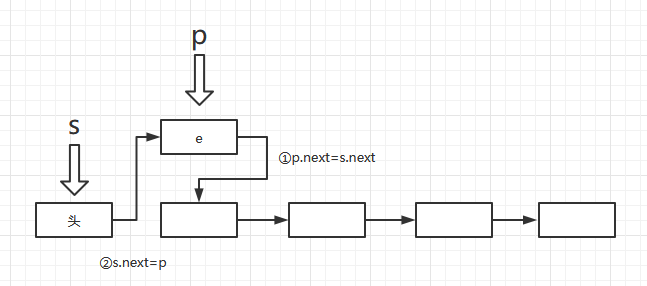
- 进栈
![]()
void Push(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
LiStack p;
p = new LiNode;
p->data = e;
p->next = S->next;
S->next = p;
}
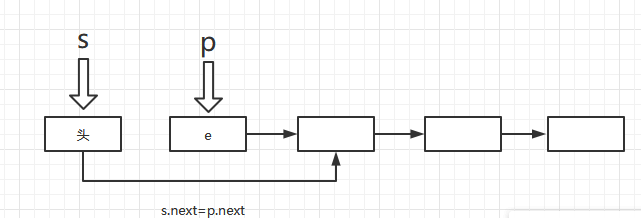
- 出栈
![]()
bool Pop(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
LiStack p;
if (S->next == NULL)return false;
p = S->next;
e = p->data;
S->next = p->next;
delete p;
return true;
}
- 取栈顶元素
bool DetTop(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
if (S->next == NULL)return false;
e = S->next->data;
return true;
}
1.2 栈的应用
1.2.1 将算术表达式转换为后缀表达式
优先级:(>*=/>+=- )不进栈
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Stacak {
char* base;
char* top;
void Init(int m)
{
base = (char*)malloc(m * sizeof(char));
top = base;
}
void Pop() {
--top;
}
void Push(char e) {
*top++ = e;
}
bool Empty() {
if (top == base) return true;
return false;
}
char Top() {
return *(top - 1);
}
};
bool isNum(char c)
{
if (c == '.' || ('0' <= c && c <= '9')) return true;
return false;
}
bool flag;
void pr()
{
if (flag)
printf(" ");
}
int main() {
Stacak S;
S.Init(1000);
char s[1000];
int p[1000];
scanf("%s", s);
p['*'] = p['/'] = 2;
p['+'] = p['-'] = 1;
while (!S.Empty()) {
printf("%c\n", S.Top());
S.Pop();
}
for (int i = 0; s[i];) {
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') {
if (i == 0) {// -1+3
if (s[i] == '-') {
printf("-");
flag = true;
}
i++;
while (isNum(s[i])) {//处理多位
printf("%c", s[i]);
flag = true;
i++;
}
}
else if (s[i - 1] == '(') {//1+(-2)
pr();
if (s[i] == '-') {
printf("-");
flag = true;
}
i++;
while (isNum(s[i])) {
printf("%c", s[i]);
flag = true;
i++;
}
}
else if (s[i - 1] == '+' || s[i - 1] == '-' || s[i - 1] == '*' || s[i - 1] == '/') {//-1--1
pr();
if (s[i] == '-') {
printf("-");
flag = true;
}
i++;
while (isNum(s[i])) {
printf("%c", s[i]);
flag = true;
i++;
}
}
else {
while (!S.Empty() && p[S.Top()] >= p[s[i]] && S.Top() != '(') {
pr();
printf("%c", S.Top());
S.Pop();
flag = true;
}
S.Push(s[i]);
i++;
}
}
else if (s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/') {
while (!S.Empty() && p[S.Top()] >= p[s[i]] && S.Top() != '(') {
pr();
printf("%c", S.Top());
S.Pop();
flag = true;
}
S.Push(s[i]);
i++;
}
else if ('0' <= s[i] && s[i] <= '9') {
pr();
while (isNum(s[i])) {
printf("%c", s[i]);
i++;
flag = true;
}
}
else if (s[i] == '(') {
S.Push(s[i]);
i++;
}
else if (s[i] == ')') {
while (S.Top() != '(') {
pr();
printf("%c", S.Top());
S.Pop();
flag = true;
}
S.Pop();
i++;
}
}
while (!S.Empty()) {
pr();
printf("%c", S.Top());
S.Pop();
flag = true;
}
printf("\n");
}
1.2.2 迷宫问题
利用栈可以存储先前走过的路径,当遇到死路时可返回以寻找新的可行路线,这种方法又叫回溯法。
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int mg[10][10]= {{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
};//地图
int M=8;//行数
int N=8;//列数
typedef struct
{
int i;//当前方块行号
int j;//当前方块列号
int di;//下一个可走的相邻方块的方位号
} Box; //定义方块类型
typedef struct
{
Box data[100];
int top;//栈顶指针
} StType; //定义顺序栈类型
bool mgpath(int xi,int yi,int xe,int ye)//求解路径为:(xi,yi)->(xe,ye)
{
int i,j,k,di,find;
StType st;//定义栈st
st.top=-1;//初始化栈顶指针
st.top++;//初始方块进栈
st.data[st.top].i=xi;
st.data[st.top].j=yi;
st.data[st.top].di=-1;
mg[xi][yi]=-1;
while(st.top>-1)//栈不为空时循环
{
i=st.data[st.top].i;
j=st.data[st.top].j;
di=st.data[st.top].di;//取栈顶方块
if(i==xe&&j==ye)//找到出口,输出路径
{
printf("迷宫路径如下:\n");
for(k=0; k<=st.top; k++)
{
printf("\t(%d,%d)",st.data[k].i,st.data[k].j);
if((k+1)%5==0)
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
return true;
}
find=0;
while(di<4&&find==0)//站下一个可走方块
{
di++;
switch(di)
{
case 0:
i=st.data[st.top].i-1;
j=st.data[st.top].j;
break;
case 1:
i=st.data[st.top].i;
j=st.data[st.top].j+1;
break;
case 2:
i=st.data[st.top].i+1;
j=st.data[st.top].j;
break;
case 3:
i=st.data[st.top].i;
j=st.data[st.top].j-1;
break;
}
if(mg[i][j]==0)
find=1;//找下一个可走相邻方块
}
if(find==1)//找到了下一个可走方块
{
st.data[st.top].di=di;//修改原栈顶元素的di值
st.top++;//下一个可走方块进栈
st.data[st.top].i=i;
st.data[st.top].j=j;
st.data[st.top].di=-1;
mg[i][j]=-1;//避免重复走到该方块
}
else//没有路径可走则退栈
{
mg[st.data[st.top].i][st.data[st.top].j]=0;//让该位置变为其他路径可走方块
st.top--;//将该方块退栈
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
if(!mgpath(1,1,M,N))
printf("无解");
return 0;
}
1.3 队列

定义:队列是一种只能在一端进行插入操作,在另一端进行删除操作的受限线性表
组成:队首(Front)、队尾(Rear)
特点:先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)
基本操作:初始化、销毁、进队、出队、判断是否为空
1.3.1 顺序队
- 结构体
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
ElemType front, rear;
}Queue,*SqQueue;
- 初始化
void CreatQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{
Q == new Queue;
Q->front = Q->rear = -1;
}
- 进队
bool EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType e)
{
if (Q->rear + 1 == MaxSize)return false;
Q->rear++;
Q->data[Q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
- 出队
bool DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType& e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)return false;
Q->front++;
e = Q->data[Q->front];
return true;
}
1.3.2 环形队列
顺序队的出队只是指针的挪动,并没有真正删除空间,因此由于队满条件的不严谨,会出现rear==MaxSize-1成立时队列中还有空位置的情况,这种现象称为假溢出
而环形队列可以解决这样的问题
与顺序队列不同的地方:
队头指针front循环增1:front=(front+1)%MaxSize
队头指针rear循环增1:rear=(rear+1)%MaxSize
队满:(rear+1)%MaxSize=front
初始化:rear=front=0
1.3.3 链队列
- 结构体
//定义节点结构
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}QueueNode;
//定义头节点
typedef struct {
QueueNode* front;
QueueNode* rear;
}LinkQueue;
- 初始化
void InitQueue(LinkQueue* Q)
{
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
}
- 进队
void EnLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType v)
{
QueueNode* p;
p = new QueueNode;
p->data = v;
p->next = NULL;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))
Q->front = Q->rear = p;
else
{
Q->rear->next = p; //将新的节点连接到队列
Q->rear = p; //指向队列尾
}
}
- 出队
bool DeLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType &e)
{
QueueNode* s;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))return false;
s = Q->front;
e = s->data;
if (Q->front == Q->rear) //判断队列是否只有一个节点
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
else
Q->front = s->next;
delete s;
return true;
}
1.3.4 队列应用
1.3.4.1 报数问题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{ ElemType data[MaxSize]; //存放队中元素
int front,rear; //队头和队尾指针
} SqQueue; //顺序队类型
void InitQueue(SqQueue *&q) //初始化队列
{ q=(SqQueue *)malloc (sizeof(SqQueue));
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue *&q) //销毁队列
{
free(q);
}
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue *q) //判断队列是否为空
{
return(q->front==q->rear);
}
bool enQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType e) //进队列
{ if ((q->rear+1)%MaxSize==q->front) //队满上溢出
return false;
q->rear=(q->rear+1)%MaxSize;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
bool deQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType &e) //出队列
{ if (q->front==q->rear) //队空下溢出
return false;
q->front=(q->front+1)%MaxSize;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
void number(int n)
{
int i; ElemType e;
SqQueue *q; //环形队列指针
InitQueue(q); //初始化队列
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) //构建初始序列
enQueue(q,i);
printf("报数出列顺序:");
while (!QueueEmpty(q)) //队列不空循环
{
deQueue(q,e); //出队一个元素e
printf("%d ",e); //输出元素编号
if (!QueueEmpty(q)) //队列不空
{
deQueue(q,e); //出队一个元素e
enQueue(q,e); //将刚出列的元素进队
}
}
printf("\n");
DestroyQueue(q); //销毁队列q
}
int main()
{
int i,n=8;
printf("初始序列:");
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d ",i);
printf("\n");
number(n);
return 0;
}
2.PTA实验作业(4分)
2.1 符号配对
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
伪代码
建栈s
输入字符串
for i=0 to str为空
if 当前字符为左括号(大中小)
进栈
else if 当前字符为"/"下一个字符为"*"
'<'进栈且i+1
else if 当前字符为右括号(大或中或小)
if 栈不为空且栈顶字符对应为左符号(大或中或小)
出栈
else
输出no
if 栈空
打印规定格式字符(?-)
else
打印栈顶字符
end if
end if
end if
if 栈空且flag为1
输出"YES"
else if flag为0
输出no和规定格式字符
end for
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
①利用了库函数,节省自定义函数的时间
②栈空条件的判断要时刻注意
③利用栈的性质,栈顶元素一定是与右符号对应的左符号。
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
建两个队列qa和qb
定义整型变量n、number、e分别为顾客人数、编号、和存储数据变量
for i to n-1
输入编号
if 编号为偶数
进qb队列
else
进qa队列
end if
end for
for i to n-1
if qa、qb不为空
if i为0
输出队首元素
else
if i%3等于2
输出" "和qb队首元素
else
输出" "和qa队首元素
end if
end if
end if
if qa为空qb不为空
输出qb队首元素
end if
if qb为空qa不为空
输出qa队首元素
end if
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
①利用了队列函数
②利用队列特性先进先出
3.阅读代码(0--1分)
3.1 代码
class Solution {
public:
void move(int n, vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C){
if(n == 1){
C.push_back(A.back());
A.pop_back();
} else{
move(n - 1, A, C, B);
move(1, A, B, C);
move(n - 1, B, A, C);
}
}
void hanota(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C) {
int n = A.size();
move(n, A, B, C);
}
};
3.2 设计思路
利用了c++中的vector库函数,运用递归的方式把题目从n转化为了两块需要转移的部分
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点
优点:使用了vector库函数,利用了递归的解法
难点:递归的使用




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号