高级语言程序设计课程第五次个人作业
高级语言程序设计课程第五次个人作业
- 这个作业属于哪个课程:2024高级语言程序设计
- 这个作业要求在哪里:高级语言程序设计课程第五次个人作业
- 学号:032201218
- 姓名:陈彦哲
一、编写并运行书本第8章8.11编程练习题目中的第1~8题
8.11.1
题目:
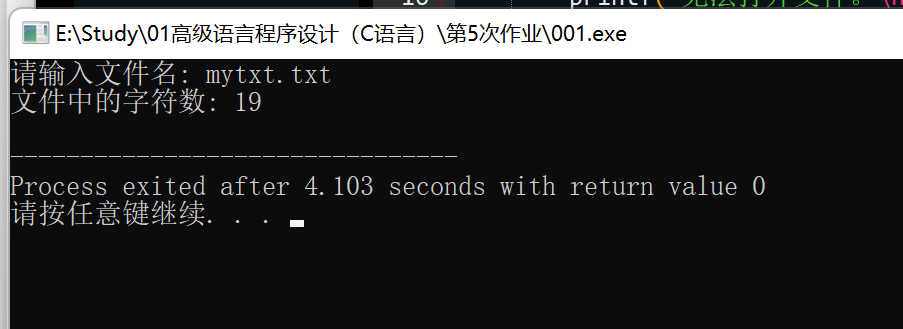
设计一个程序,统计在读到文件结尾之前读取的字符数。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *file;
char filename[100];
int count = 0;
char ch;
printf("请输入文件名: ");
scanf("%s", filename);
// 打开文件
file = fopen(filename, "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("无法打开文件。\n");
return 1;
}
// 逐个读取字符,直到文件结尾
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF) {
count++;
}
// 关闭文件
fclose(file);
printf("文件中的字符数: %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
思路:
根据题意理解即可。
问题:不知道怎么逐个读取字符
解决:while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF) { count++; }用这个方法解决了
8.11.2
题目:
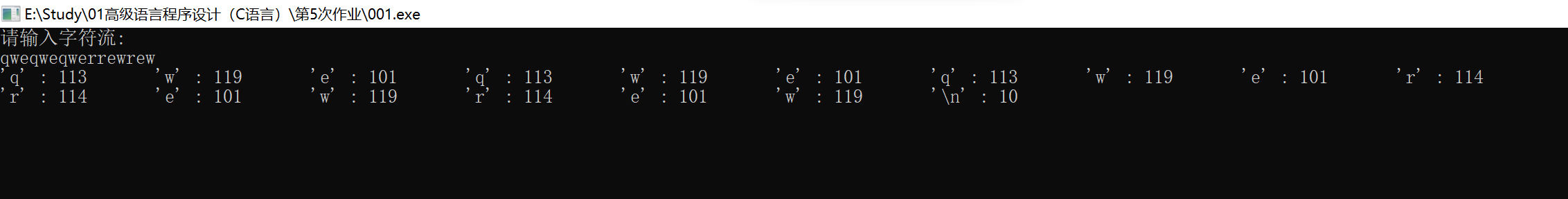
编写一个程序,在遇到 EOF 之前,把输入作为字符流读取。程序要 打印每个输入的字符及其相应的ASCII十进制值。注意,在ASCII序列中,空 格字符前面的字符都是非打印字符,要特殊处理这些字符。如果非打印字符 是换行符或制表符,则分别打印\n或\t。否则,使用控制字符表示法。例 如,ASCII的1是Ctrl+A,可显示为^A。注意,A的ASCII值是Ctrl+A的值加上 64。其他非打印字符也有类似的关系。除每次遇到换行符打印新的一行之 外,每行打印10对值。(注意:不同的操作系统其控制字符可能不同。)
#include <stdio.h>
void PrintChar(int ch) {
if (ch >= 32 && ch <= 126) {
printf("'%c' : %d\t", ch, ch);
}
// 特殊处理换行符和制表符
else if (ch == '\n') {
printf("'\\n' : %d\t", ch);
} else if (ch == '\t') {
printf("'\\t' : %d\t", ch);
}
else {
printf("^%c : %d\t", ch + 64, ch);
}
}
int main() {
int ch, count = 0;
printf("请输入字符流:\n");
// 逐个读取字符直到遇到EOF
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF) {
PrintChar(ch);
count++;
// 每10个字符换行
if (count % 10 == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
}
// 如果最后一行未满10个字符,手动换行
if (count % 10 != 0) {
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:不知道怎么处理非打印字符
解决:用printf("^%c : %d\t", ch + 64, ch);即可
8.11.3
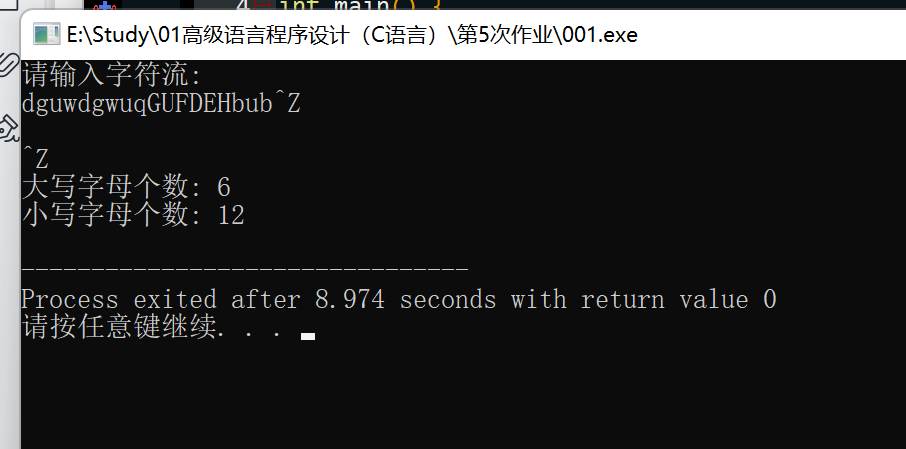
题目:编写一个程序,在遇到 EOF 之前,把输入作为字符流读取。该程序 要报告输入中的大写字母和小写字母的个数。假设大小写字母数值是连续 的。或者使用ctype.h库中合适的分类函数更方便。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main() {
int ch;
int upperCount = 0;
int lowerCount = 0;
printf("请输入字符流:\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF) {
if (isupper(ch)) {
upperCount++;
} else if (islower(ch)) {
lowerCount++;
}
}
printf("大写字母个数: %d\n", upperCount);
printf("小写字母个数: %d\n", lowerCount);
return 0;
}
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
8.11.4
题目:编写一个程序,在遇到EOF之前,把输入作为字符流读取。该程序要 报告平均每个单词的字母数。不要把空白统计为单词的字母。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main() {
int ch;
int wordCnt = 0;
int letterCnt = 0;
int inWord = 0;
printf("请输入字符流:\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF) {
if (isalpha(ch)) {
letterCnt++;
if (!inWord) {
inWord = 1;
wordCnt++;
}
} else if (isspace(ch)) {
inWord = 0;
}
}
if (wordCnt > 0) {
printf("平均每个单词的字母数: %.2f\n", (double)letterCnt / wordCnt);
} else {
printf("没有检测到单词\n");
}
return 0;
}
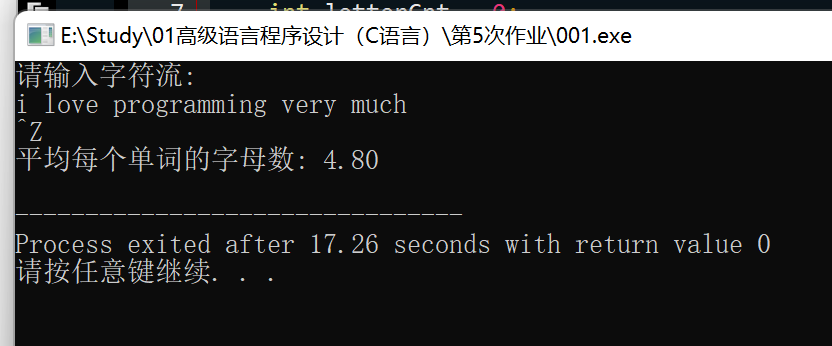
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
8.11.5
题目:修改程序清单8.4的猜数字程序,使用更智能的猜测策略。例如,程序 最初猜50,询问用户是猜大了、猜小了还是猜对了。如果猜小了,那么下一 次猜测的值应是50和100中值,也就是75。如果这次猜大了,那么下一次猜 测的值应是50和75的中值,等等。使用二分查找(binary search)策略,如 果用户没有欺骗程序,那么程序很快就会猜到正确的答案。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int low = 1;
int high = 100;
int guess;
char res;
printf("想一个1到100之间的数字,输入h表示高了,l表示低了,r表示正确\n");
while (low <= high) {
guess = (low + high) / 2;
printf("答案是%d吗,输入h表示高了,l表示低了,r表示正确:", guess);
res = getchar();
// 跳过多余的字符
while (getchar() != '\n');
// 二分法查找
if (res == 'r') {
printf("猜对了!\n");
break;
} else if (res == 'h') {
high = guess - 1;
} else if (res == 'l') {
low = guess + 1;
} else {
printf("无效输入,请输入h、l或r\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
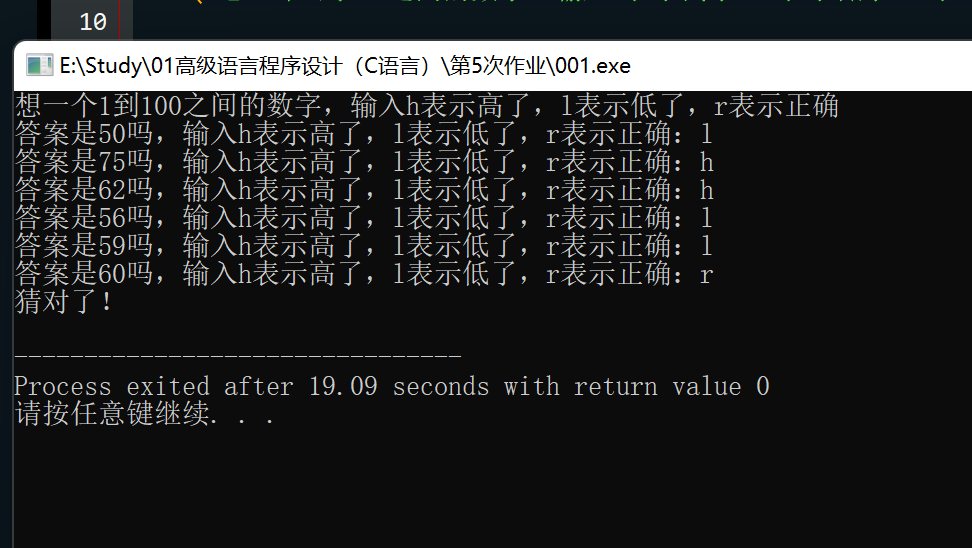
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
8.11.6
题目:修改程序清单8.8中的get_first()函数,让该函数返回读取的第1个非空 白字符,并在一个简单的程序中测试
#include <stdio.h>
char get_first() {
int ch;
// 跳过空白字符
while ((ch = getchar()) == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n')
continue;
// 清空缓冲区中的其他字符
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
return ch;
}
int main() {
char firstChar;
printf("请输入一些字符:\n");
firstChar = get_first();
printf("第一个非空白字符是: %c\n", firstChar);
return 0;
}
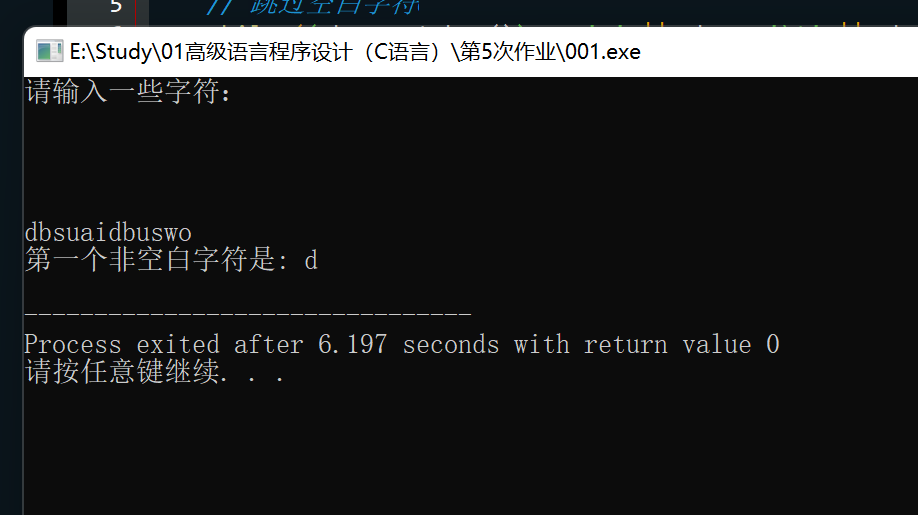
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
8.11.7
题目:修改第7章的编程练习8,用字符代替数字标记菜单的选项。用q代替5 作为结束输入的标记。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define l1 8.75
#define l2 9.33
#define l3 10.00
#define l4 11.20
int main() {
double pay = 0, tax = 0, nce = 0;
double n;
char choice;
while (1) {
printf("****************************************************************\n");
printf("Enter the letter corresponding to the desired pay rate or action:\n");
printf("a) $8.75/hr b) $9.33/hr\n");
printf("c) $10.00/hr d) $11.20/hr\n");
printf("q) quit\n");
printf("****************************************************************\n");
printf("请选择时薪等级:");
scanf(" %c", &choice); // 注意空格以跳过前面的空白字符
if (choice == 'q') {
break;
}
printf("请输入一周工作的小时数:");
scanf("%lf", &n);
double level;
switch (choice) {
case 'a': level = l1; break;
case 'b': level = l2; break;
case 'c': level = l3; break;
case 'd': level = l4; break;
default:
printf("请输入正确的字符:\n");
continue;
}
// 算工资
if (n <= 40) {
pay = level * n;
} else {
pay = level * 40 + (n - 40) * 1.5 * 10.00;
}
// 算税率
if (pay <= 300) {
tax = 0.15 * pay;
} else if (pay > 300 && pay <= 450) {
tax = 300 * 0.15 + (pay - 300) * 0.2;
} else {
tax = 300 * 0.15 + 150 * 0.2 + (pay - 450) * 0.25;
}
// 算净收入
nce = pay - tax;
printf("工资总额:%lf\n", pay);
printf("税金:%lf\n", tax);
printf("净收入:%lf\n", nce);
}
return 0;
}
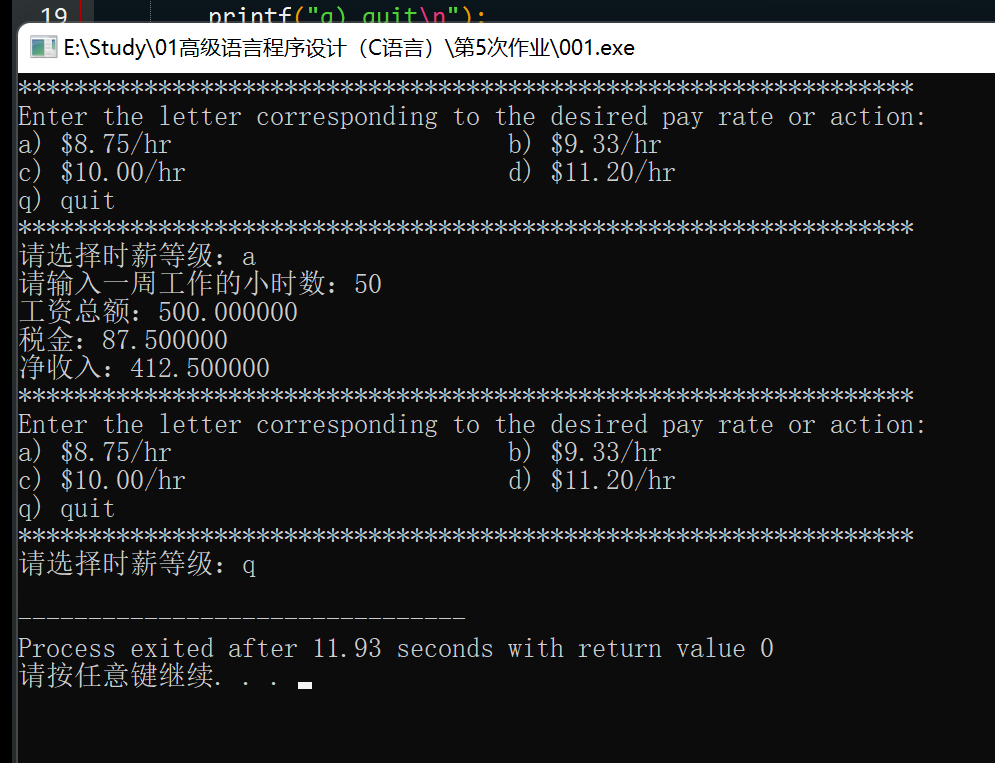
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
8.11.8
题目:
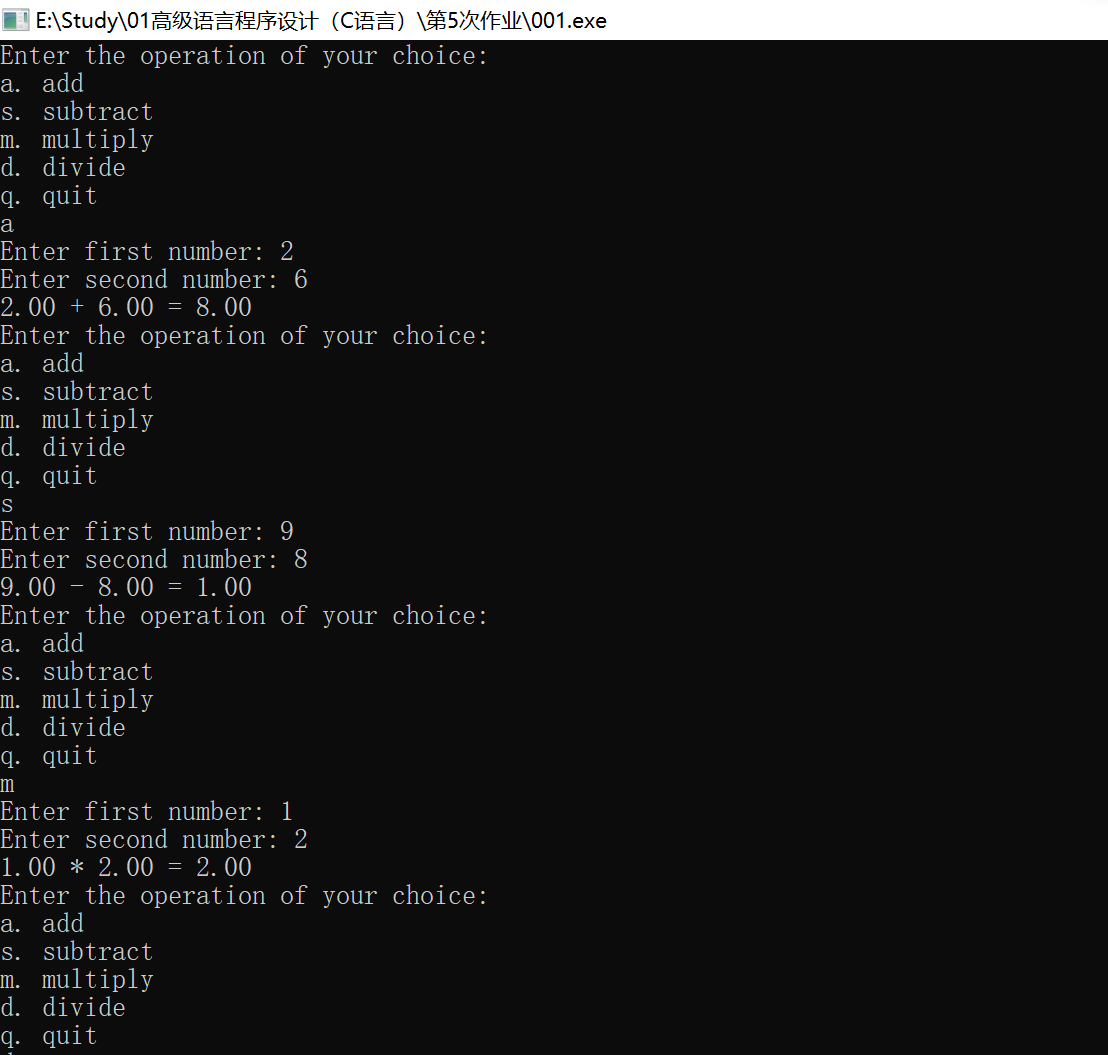
编写一个程序,显示一个提供加法、减法、乘法和除法的菜单。获得用户选择的选项后,程序提示用户输入两个数字,然后执行用户选择的操作。该程序只接受菜单提供的选项。程序使用 float 类型的变量存储用户输入的数字,如果用户输入失败,则允许再次输入。在进行除法运算时,如果用户输入0作为第2个数(除数),程序应提示用户重新输入一个新值。
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add
s. subtract
m. multiply
d. divide
q. quit
a
Enter first number: 22.4
Enter second number: one
one is not a number. Please enter a number, such as 2.5, -1.78E8, or 3: 1
22.4 + 1 = 23.4
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add
s. subtract
m. multiply
d. divide
q. quit
d
Enter first number: 18.4
Enter second number: 0
Enter a number other than 0: 0.2
18.4 / 0.2 = 92
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add
s. subtract
m. multiply
d. divide
q. quit
q
Bye.
#include <stdio.h>
float getNumber() {
float num;
while (1) {
// 典型的通过输入的有效元素的个数来判断输入是否合法
if (scanf("%f", &num) != 1) {
printf("输入非法,请重试: ");
while (getchar() != '\n'); // 清空输入缓冲区
} else {
break;
}
}
return num;
}
int main() {
char choice;
while (1) {
printf("Enter the operation of your choice:\n");
printf("a. add\ns. subtract\nm. multiply\nd. divide\nq. quit\n");
// 在scanf中添加一个空格,以跳过输入缓冲区的前导空白字符
scanf(" %c", &choice);
if (choice == 'q') {
printf("Bye.\n");
break;
}
float num1, num2;
printf("Enter first number: ");
num1 = getNumber();
printf("Enter second number: ");
num2 = getNumber();
switch (choice) {
case 'a':
printf("%.2f + %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 + num2);
break;
case 's':
printf("%.2f - %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 - num2);
break;
case 'm':
printf("%.2f * %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 * num2);
break;
case 'd':
while (num2 == 0) {
printf("除数不能为0,请重新输入: ");
num2 = getNumber();
}
printf("%.2f / %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 / num2);
break;
default:
printf("请输入有效的操作符\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}

思路:按题意理解即可
问题:不知道怎么清空输入缓存区
解决:通过while (getchar() != '\n'); 解决
二、编写并运行书本第9章9.11编程练习题目中的第1~11题
9.11.1
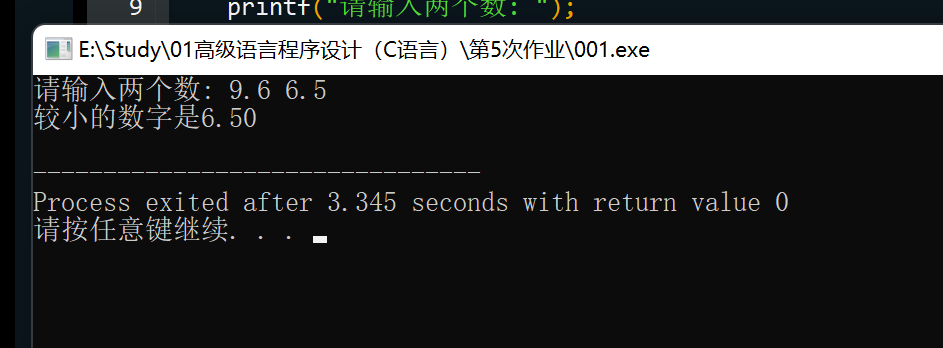
题目:设计一个函数min(x, y),返回两个double类型值的较小值。在一个简单 的驱动程序中测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
double min(double x, double y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
int main() {
double a, b;
printf("请输入两个数: ");
scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b);
printf("较小的数字是%.2f\n", min(a, b));
return 0;
}
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决办法:无
9.11.2
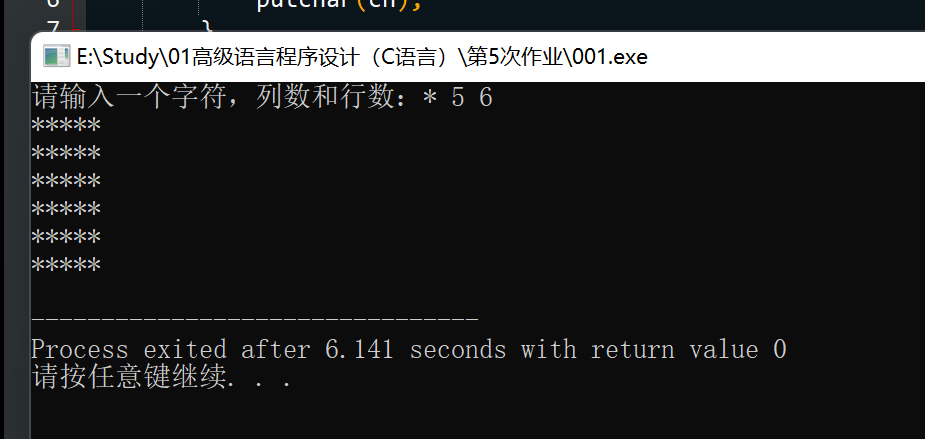
题目:设计一个函数chline(ch, i, j),打印指定的字符j行i列。在一个简单的驱 动程序中测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
void chline(char ch, int cols, int rows) {
for (int r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
putchar(ch);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
int main() {
char ch;
int cols, rows;
printf("请输入一个字符,列数和行数:");
scanf(" %c %d %d", &ch, &cols, &rows);
chline(ch, cols, rows);
return 0;
}
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.3
题目:
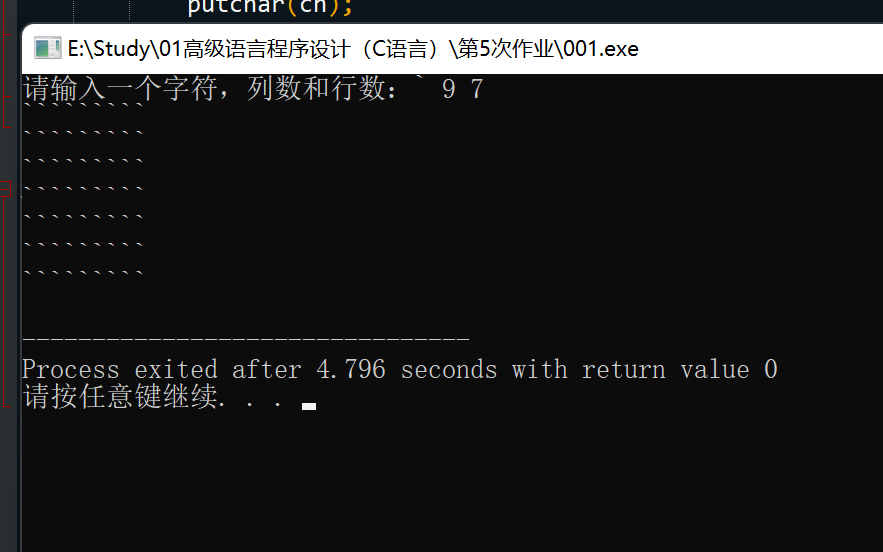
编写一个函数,接受3个参数:一个字符和两个整数。字符参数是待 打印的字符,第1个整数指定一行中打印字符的次数,第2个整数指定打印指 定字符的行数。编写一个调用该函数的程序。
#include <stdio.h>
void printChars(char ch, int cols, int rows) {
for (int r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
putchar(ch);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
int main() {
char ch;
int cols, rows;
printf("请输入一个字符,列数和行数:");
scanf(" %c %d %d", &ch, &cols, &rows);
printChars(ch, cols, rows);
return 0;
}
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.4
题目:两数的调和平均数这样计算:先得到两数的倒数,然后计算两个倒数 的平均值,最后取计算结果的倒数。编写一个函数,接受两个double类型的 参数,返回这两个参数的调和平均数
#include <stdio.h>
double harmonicMean(double x, double y) {
return 2.0 * x * y / (x + y);
}
int main() {
double a, b;
printf("请输入两个数:");
scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b);
printf("这两个数的调和平均数是:%.2f\n", harmonicMean(a, b));
return 0;
}
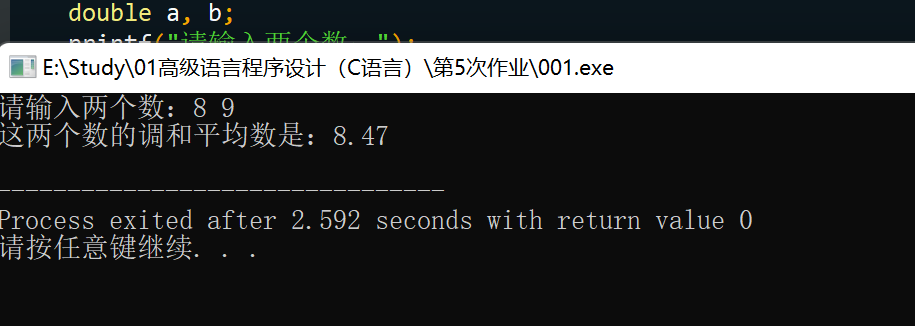
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.5
题目:
编写并测试一个函数larger_of(),该函数把两个double类型变量的值替 换为较大的值。例如, larger_of(x, y)会把x和y中较大的值重新赋给两个变 量
#include <stdio.h>
void larger_of(double *x, double *y) {
double t = *x > *y ? *x : *y;
*x = t;
*y = t;
}
int main() {
double a, b;
printf("请输入两个数:");
scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b);
larger_of(&a, &b);
printf("修改后的两个数是:%.2f 和 %.2f\n", a, b);
return 0;
}

思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.6
题目:编写并测试一个函数,该函数以3个double变量的地址作为参数,把最小值放入第1个函数,中间值放入第2个变量,最大值放入第3个变量。
#include <stdio.h>
void mySort(double nums[3]) {
double temp;
// 比较并交换
if (nums[0] > nums[1]) {
temp = nums[0];
nums[0] = nums[1];
nums[1] = temp;
}
if (nums[0] > nums[2]) {
temp = nums[0];
nums[0] = nums[2];
nums[2] = temp;
}
if (nums[1] > nums[2]) {
temp = nums[1];
nums[1] = nums[2];
nums[2] = temp;
}
}
int main() {
double nums[3];
printf("请输入三个数:");
scanf("%lf %lf %lf", &nums[0], &nums[1], &nums[2]);
mySort(nums);
printf("排序后的数值为:%.2f, %.2f, %.2f\n", nums[0], nums[1], nums[2]);
return 0;
}
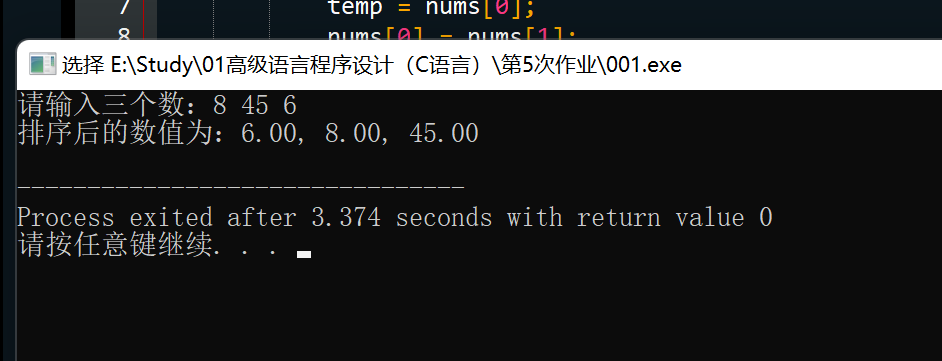
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.7
题目:编写一个函数,从标准输入中读取字符,直到遇到文件结尾。程序要 报告每个字符是否是字母。如果是,还要报告该字母在字母表中的数值位 置。例如,c和C在字母表中的位置都是3。合并一个函数,以一个字符作为 参数,如果该字符是一个字母则返回一个数值位置,否则返回-1。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int getPosition(char ch) {
if (isalpha(ch)) {
return isupper(ch) ? ch - 'A' + 1 : ch - 'a' + 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
char ch;
printf("请输入字符:");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF) {
if (ch == '\n') continue;
int pos = getPosition(ch);
if (pos != -1)
printf("%c 是字母,位置为:%d\n", ch, pos);
else
printf("%c 不是字母\n", ch);
}
return 0;
}

思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.8
题目:
第6章的程序清单6.20中,power()函数返回一个double类型数的正整数 次幂。改进该函数,使其能正确计算负幂。另外,函数要处理0的任何次幂 都为0,任何数的0次幂都为1(函数应报告0的0次幂未定义,因此把该值处理为1)。要使用一个循环,并在程序中测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
double power(double base, int exp) {
if (base == 0 && exp == 0) {
printf("0的0次幂未定义,在本题设置为1\n");
return 1;
}
double result = 1.0;
int absExp;
if (exp > 0) {
absExp = exp;
} else {
absExp = -exp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < absExp; i++) {
result *= base;
}
return exp < 0 ? 1.0 / result : result;
}
int main() {
double base;
int exp;
while (1) {
printf("请输入底数和指数:");
if (scanf("%lf %d", &base, &exp) != 2) {
break;
}
printf("%.2f 的 %d 次幂 = %.5f\n", base, exp, power(base, exp));
}
return 0;
}
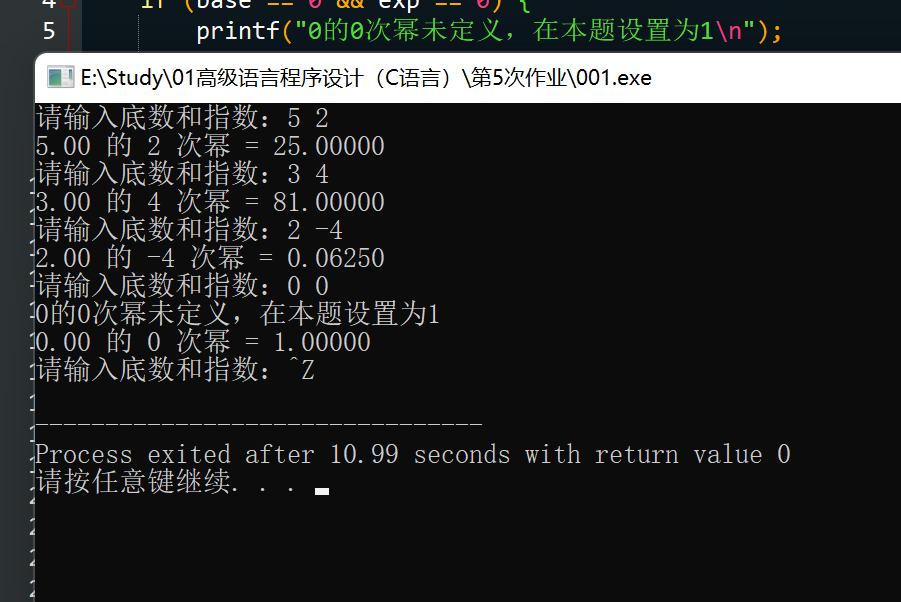
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决办法:无
9.11.9
题目:
使用递归函数重写编程练习8。
#include <stdio.h>
double power(double base, int exp) {
if (base == 0 && exp == 0) {
printf("0的0次幂未定义,在本题设置为1\n");
return 1;
} else if (exp == 0) {
return 1;
} else if (exp > 0) {
return base * power(base, exp - 1);
} else {
return 1.0 / power(base, -exp);
}
}
int main() {
double base;
int exp;
while (1) {
printf("请输入底数和指数:");
if (scanf("%lf %d", &base, &exp) != 2) {
break;
}
printf("%.2f 的 %d 次幂 = %.5f\n", base, exp, power(base, exp));
}
return 0;
}
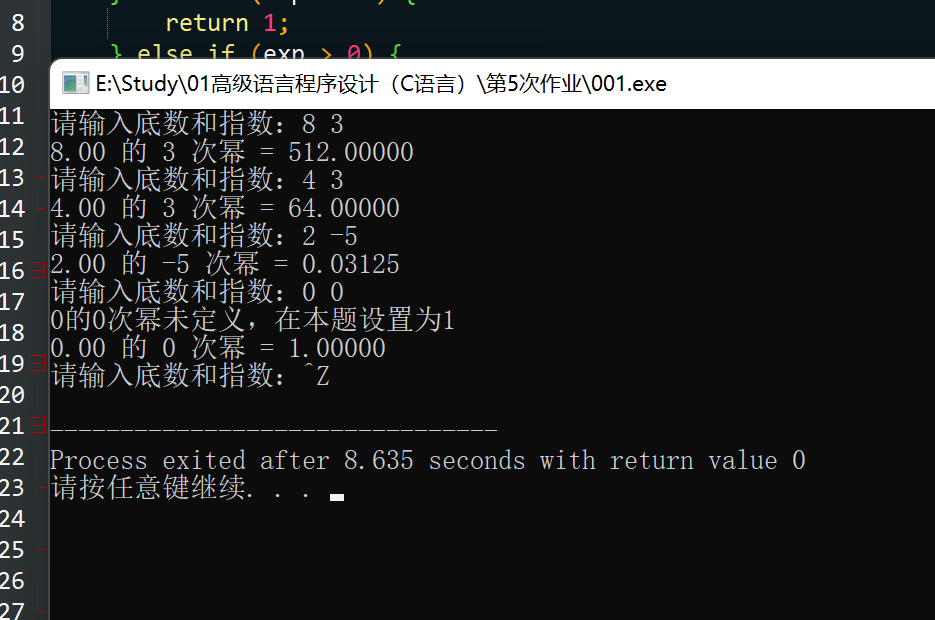
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.10
题目:
A为了让程序清单9.8中的to_binary()函数更通用,编写一个to_base_n() 函数接受两个在2~10范围内的参数,然后以第2个参数中指定的进制打印第 1个参数的数值。例如,to_base_n(129, 8)显示的结果为201,也就是129的 八进制数。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
void to_base_n(int num, int base) {
if (num == 0) {
return;
}
to_base_n(num / base, base);
printf("%d", num % base);
}
int main() {
int num, base;
printf("请输入一个数字和进制(2-10):");
scanf("%d %d", &num, &base);
if (base < 2 || base > 10) {
printf("无效的进制\n");
return 1;
}
to_base_n(num, base);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
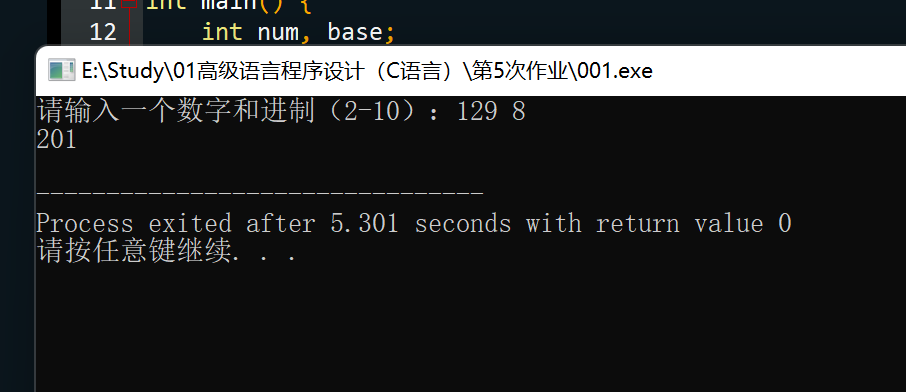
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
9.11.11
题目:
编写并测试Fibonacci()函数,该函数用循环代替递归计算斐波那契 数
#include <stdio.h>
double fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
double a = 0, b = 1, temp;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
temp = a + b;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
return b;
}
int main() {
int n;
printf("请输入斐波那契数列的项数:");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Fibonacci(%d) = %.0f\n", n, fibonacci(n));
return 0;
}
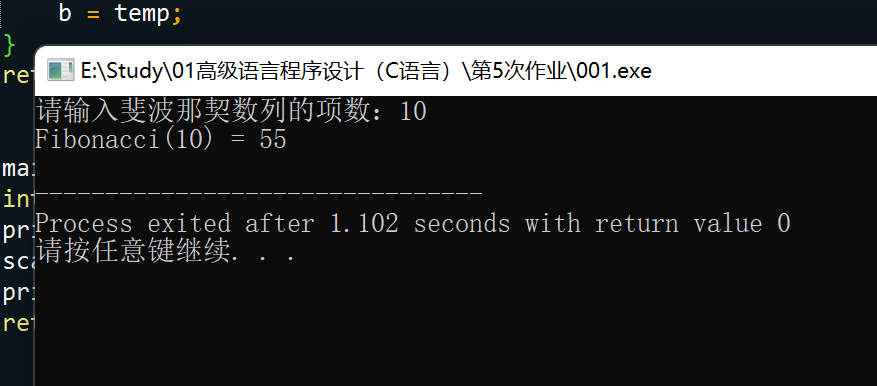
思路:按题意理解即可
问题:无
解决:无
三、总结思考:
- 学会了逐个读取字符,请点击这里跳转
- 复习了函数和文件流的用法
- 学会了用
printf("^%c : %d\t", ch + 64, ch);处理非打印字符 - 学会了用
while (getchar() != '\n');清空输入缓存区,收获良多


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号