算法第四版 谢路云译 第一章参考答案(java实现) 持续更新中 欢迎评论留意见
算法第四版教材相关配置,感谢知乎答主:
算法第四版所用到需要下载的库
在Eclipse中调用Algs4库
-
1.1.1 给出以下表达式的值:
a. ( 0 + 15 ) / 2
b. 2.0e-6 * 100000000.1
c. true && false || true && true
答案:a.7(类型是整型,所以输出为7)
b.200.0000002 (
2.0e-6 表示 2.0*10的-6次方,为 0.000002
0.000002 * 100000000.1 = 200.0000002
)
c.ture
-
1.1.2 给出以下表达式的类型和值:
a. (1 + 2.236)/2
b. 1 + 2 + 3 + 4.0
c. 4.1 >= 4
d. 1 + 2 + "3"
答案:a.1.618(浮点型) b. 10.0 c.true d.33
-
1.1.3 编写一个程序,从命令行得到三个整数参数。如果它们都相等则打印 equal ,否则 打印 not equal。
答案:java代码,这里了解了“==”与“equals”的区别。https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pfLGs6x-_-YbPist1nTkUQ
import java.util.Scanner;
public class E {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入三个整数");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
String string1 = scanner1.next();
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
String string2 = scanner2.next();
Scanner scanner3 = new Scanner(System.in);
String string3 = scanner3.next();
Integer number1 = Integer.valueOf(string1);
Integer number2 = Integer.valueOf(string2);
Integer number3 = Integer.valueOf(string3);
if(number1 .equals(number2) && number1 .equals(number3) && number2 .equals(number3)) {
System.out.println("equal");
} else {
System.out.println("not equal");
}
}
}
-
1.1.4 下列语句各有什么问题(如果有的话)?
a. if (a > b) then c = 0;
b. if a > b { c = 0; }
c. if (a > b) c = 0;
d. if (a > b) c = 0 else b = 0;
答案:a.java中没有then关键字,Visual Basic中有
b.a>b缺少()
c.正确
d.c=0缺少;(分号)
-
1.1.5 编写一段程序,如果 double 类型的变量 x 和 y 都严格位于 0 和 1 之间则打印 true,否则打印 false。
答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class E {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入两个数字");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
String string1 = scanner1.next();
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
String string2 = scanner2.next();
double x=Double.valueOf(string1);
double y=Double.valueOf(string2);
if(x>=0&&x<=1&&y>=0&&y<=1)
System.out.println(true);
else
System.out.println(false);
}
}
-
1.1.6 下面这段程序会打印出什么?
int f = 0;
int g = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 15; i++)
{
StdOut.println(f);
f = f + g;
g = f - g;
}
答案:一段斐波那契数列。
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
34
55
89
144
233
377
610
-
1.1.7 分别给出以下代码段打印出的值:
//a.
double t = 9.0;
while (Math.abs(t - 9.0/t) > .001)
t = (9.0/t + t) / 2.0;
StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", t);
//b.
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
sum++;
StdOut.println(sum);
//c.
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i *= 2)
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++)
sum++;
StdOut.println(sum);
答案:a.3.00009 b.499500((999+1)*999/2) c.10000
-
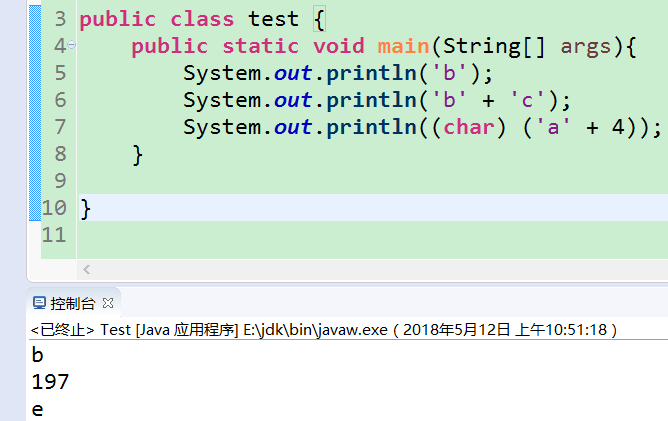
1.1.8 下列语句会打印出什么结果?给出解释
a. System.out.println('b');
b. System.out.println('b' + 'c');
c. System.out.println((char) ('a' + 4));
答案:a.b b.197 c.e (b的ASCII码为98,c的为99)
-
1.1.9 编写一段代码,将一个正整数 N 用二进制表示并转换为一个 String 类型的值 s。
答案:Java 有一个内置方法 Integer.toBinaryString(N) 专门完成这个任务,但该题的目的就是给出这个方法的其他实现方法。
下面就是一个特别简洁的答案:
String s = "";
for (int n = N; n > 0; n /= 2)
s = (n % 2) + s;
答案:
public static String decimalToBinary(int n) {
String resultString = "";
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--)
resultString = resultString + (n >>> i & 1);
return resultString;
}
-
1.1.10 下面这段代码有什么问题?
int[] a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = i * i;
答案:它没有用 new 为 a[] 分配内存,这段代码会产生一个 variable a might not have been initialized 的编译错误。
-
1.1.11 编写一段代码,打印出一个二维布尔数组的内容。其中,使用 * 表示真,空格表示假。打印出行号和列号。
答案:
private static void printout(boolean[][] a1){
for (int i = 0; i < a1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a1[i].length; j++) {
if (a1[i][j]){
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.CHINA,"%d %d *",i+1,j+1));
} else {
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.CHINA,"%d %d /",i+1,j+1));
}
}
}
}
-
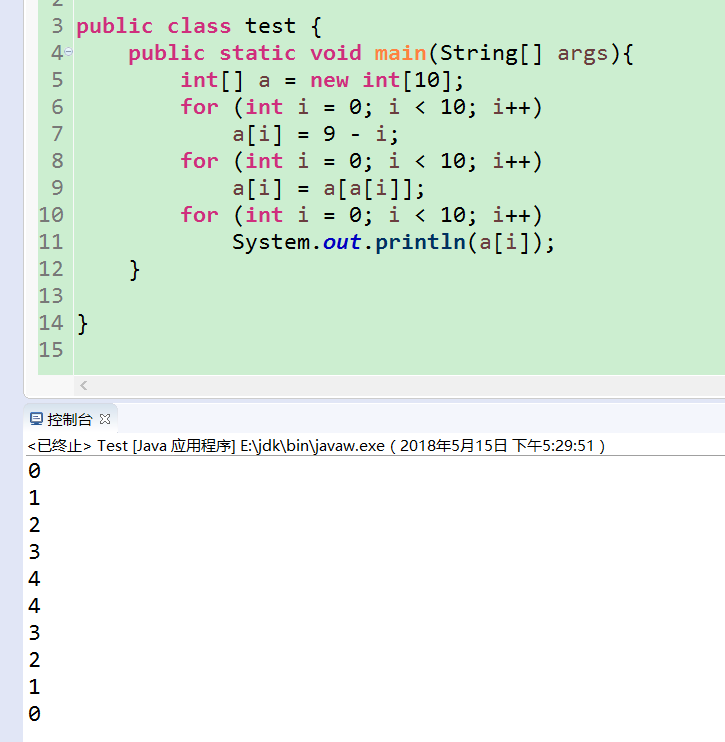
1.1.12 以下代码段会打印出什么结果?
int[] a = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = 9 - i;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = a[a[i]];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.println(a[i]);//如书中所示打印i,则题目无意义
答案:
-
1.1.13 编写一段代码,打印出一个 M 行 N 列的二维数组的转置(交换行和列)。
答案:
int[ ][ ] a={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
int[][] temp = new int[a[0].length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a[0].length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
temp[i][j] = a[j][i];
System.out.print(temp[i][j] + " ");
if(j == a.length - 1)
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
-
1.1.14 编写一个静态方法 lg(),接受一个整型参数 N,返回不大于 log2N (以2为底N的对数)的最大整数。不要使用 Math 库。
答案:
public static int lg(int N){
// m = log a N
int a=2; //a为底数
int m=0;
for(;N>1;N/=a){
m++;
}
return m;
}
- 1.1.15 编写一个静态方法 histogram(),接受一个整型数组 a[] 和一个整数 M 为参数并返回一个大小为 M 的数组,其中第 i 个元素的值为整数 i 在参数数组中出现的次数。如果 a[] 中的值均在 0 到 M-1之间,返回数组中所有元素之和应该和 a.length 相等。
-
1.1.16 给出 exR1(6) 的返回值:
public static String exR1(int n) { if (n <= 0) return ""; return exR1(n-3) + n + exR1(n-2) + n; }
答案:

-
1.1.17 找出以下递归函数的问题:
public static String exR2(int n) {
String s = exR2(n - 3) + n + exR2(n - 2) + n;
if (n <= 0)
return "";
return s;
}
答案:这段代码中的基础情况永远不会被访问。调用 exR2(3) 会产生调用 exR2(0)、exR2(-3) 和exR2(-6),循环往复直到发生 StackOverflowError。
-
1.1.18 请看以下递归函数:
public static int mystery(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) return 0;
if (b % 2 == 0) return mystery(a+a, b/2);
return mystery(a+a, b/2) + a;
}
mystery(2, 25) 和 mystery(3, 11) 的返回值是多少?
给定正整数 a 和 b,mystery(a,b)计算的结果是什么?
将代码中的 + 替换为 * 并将 return 0 改为 return 1,然后回答相同的问题。
答案:
public static int mystery(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0)
return 0;
if (b % 2 == 0)
return mystery(a+a, b/2);
return mystery(a+a, b/2) + a;
}
public static int mystery1(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0)
return 1;
if (b % 2 == 0)
return mystery1(a*a, b/2);
return mystery1(a*a, b/2) * a;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(mystery(2,25)); // 输出50
System.out.println(mystery(3,11)); //输出33
System.out.println(mystery1(2,25)); // 输出33554432
System.out.println(mystery1(3,11)); //输出177147
}
-
1.1.19 在计算机上运行以下程序:
public class Fibonacci {
public static long F(int N) {
if (N == 0)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
return 1;
return F(N - 1) + F(N - 2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int N = 0; N < 100; N++)
StdOut.println(N + " " + F(N));
}
}
计算机用这段程序在一个小时之内能够得到 F(N) 结果的最大 N 值是多少?开发 F(N) 的一个更好的实现,用数组保存已经计算过的值。
答案:
public class Fibonacci {
public static long F(int N) {
if (N == 0) return 0;
if (N == 1) return 1;
return F(N-1) + F(N-2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int N = 0; N < 100; N++)
System.out.println(N + " " + F(N));
}
}//递归影响速度,斐波拉契数列,改良可以考虑取消递归
-
1.1.20 编写一个递归的静态方法计算ln(N!)的值。
答案:
public static double log(int N) {
if (N == 0)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
return 0;
return (log(N - 1) + Math.log(N));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
double result = log(4);
System.out.println(result);
}
-
1.1.21 编写一段程序,从标准输入按行读取数据,其中每行都包含一个名字和两个整数。然后用printf() 打印一张表格,每行的若干列数据包括名字、两个整数和第一个整数除以第二个整数 的结果,精确到小数点后三位。可以用这种程序将棒球球手的击球命中率或者学生的考试分数制成表格。
答案:(必须超过两组数据,否则抛出数组越界异常)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int M = 3;
int index = 0;
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] strs = new String[M];
while (index < M)
strs[index++] = reader.readLine();
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; ++i) {
String[] arr = strs[i].split("\\s+");
double temp = Double.parseDouble(arr[1]) / Double.parseDouble(arr[2]);
System.out.printf("%-10s %-10s %-10s %-13.3f\n", arr[0], arr[1], arr[2], temp);
}
}
-
1.1.21 使用1.1.6.4 节中的 rank()递归方法重新实现 BinarySearch 并跟踪该方法的调用。每当该方法被调用时,打印出它的参数 lo 和 hi 并按照递归的深度缩进。提示 :为递归方法加一个参数来保存递归的深度。
答案:1.1.6.4介绍的二分法的递归实现如下:
public static int rank(int key, int[] a) {
return rank(key, a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi) {
//如果key存在于a[]中,它的索引不会小于lo且不会大于hi
if (lo > hi)
return -1;
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if(key < a[mid])
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - 1);
else if (key > a[mid])
return rank(key, a, mid + 1, hi);
else
return mid;
}
public static int rank (int key,int[] a) {
return rank(key,a,0,16,1);
}
public static int rank (int key,int[] a,int lo,int hi,int deep) {
if (hi < lo) return - 1;
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
for(int i = 0 ; i < deep ; i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println("lo: "+lo+" hi: "+hi);
if (key < a[mid])
return rank (key,a,lo,mid - 1,deep + 1);
else if (key > a[mid])
return rank (key,a,mid + 1,hi,deep + 1);
else
return mid;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16};
rank(10,array);
}
/**打印出的结果
lo: 0 hi: 16
lo: 9 hi: 16
lo: 9 hi: 11
**/
-
1.1.23 为 BinarySearch 的测试用例添加一个参数:+ 打印出标准输入中不在白名单上的值; -,则打印出标准输入中在名单上的值。
-
1.1.24 给出使用欧几里得算法计算 105 和 24 的最大公约数的过程中得到的一系列 p 和 q 的值。扩展该算法中的代码得到一个程序Euclid,从命令行接受两个参数,计算它们的最大公约数并打印出每次调用递归方法时的两个参数。使用你的程序计算 1 111 111 和 1 234 567 的最大公约数。
答案:
public static int gcd(int m,int n) {
int rem = 0;
int M = m;
int N = n;
if (m < n) {
M = n ;
N = m ;
}
rem = M % N ;
if (0 == rem)
return N;
System.out.println("m:"+ N + ";n:" + rem);
return gcd(N, rem);
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int a =gcd(1111111 , 1234567);
System.out.println(a + "");
}
-
1.1.25 使用数学归纳法证明欧几里得算法能够计算任意一对非整数p和q的最大公约数。
- 1.1.25 Use mathematical induction to prove that Euclid’s algorithm computes the greatest common divisor of any pair of nonnegative integers p and q.
答案:
欧几里德算法又称辗转相除法,是指用于计算两个正整数a,b的最大公约数。计算公式gcd(a,b) = gcd(b,a mod b)。此处递归实现。
static int euclid(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
{
return a;
}
return euclid(b, a % b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试用例(6,9)
int a=6;
int b=9;
StdOut.print(euclid(a,b));
}
-
1.1.26 将三个数字排序。假设a、b、c 和t 都是同一种原始数字类型的变量。证明以下代码能够将a、b、c 按照升序排列:
if (a > b) { t = a; a = b; b = t; }
if (a > c) { t = a; a = c; c = t; }
if (b > c) { t = b; b = c; c = t; }
答案:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=8,b=100,c=7;
int t;
if (a > b) { t = a; a = b; b = t; }
if (a > c) { t = a; a = c; c = t; }
if (b > c) { t = b; b = c; c = t; }
StdOut.println(a);
StdOut.println(b);
StdOut.println(c);
}
//输出为7 8 100
-
1.1.27 二项分布。估计用以下代码计算binomial(100, 50) 将会产生的递归调用次数:
public static double binomial(int N, int k, double p)
{
if (N == 0 && k == 0) return 1.0;
and if (N < 0 || k < 0) return 0.0;
return (1.0 - p)*binomial(N-1, k, p) + p*binomial(N-1, k-1);
}
将已经计算过的值保存在数组中并给出一个更好的实现。
-
1.1.28 删除重复元素。修改BinarySearch 类中的测试用例来删去排序之后白名单中的所有重复元素。
-
1.1.29 等值键。为BinarySearch 类添加一个静态方法rank(),它接受一个键和一个整型有序数组(可能存在重复键)作为参数并返回数组中小于该键的元素数量,以及一个类似的方法count() 来返回数组中等于该键的元素的数量。注意:如果i 和j 分别是rank(key,a) 和count(key,a)的返回值,那么a[i..i+j-1] 就是数组中所有和key 相等的元素。
-
1.1.30 数组练习。编写一段程序,创建一个N×N 的布尔数组a[][]。其中当i 和j 互质时(没有相同因子),a[i][j] 为true,否则为false。
答案:
//给数组赋值true或false
public static boolean[][] TestArrays(boolean[][] a)//
{
int N=a.length;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
if(gcd(i,j)==1)
a[i][j]=true;
else
a[i][j]=false;
}
return a;
}
//与欧几里得算法思路相似
public static int gcd(int m,int n)
{
if(m==0||n==0)
{
return 1;
}
if(m%n==0)
{
return n;
}
else
{
return gcd(n,m%n);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
boolean[][] a=new boolean[5][5];
TestArrays(a);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
for(int j=0;j<5;j++){
StdOut.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号