Next Permutation
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in-place, do not allocate extra memory.
Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.1,2,3 → 1,3,23,2,1 → 1,2,31,1,5 → 1,5,1
[解题思路]
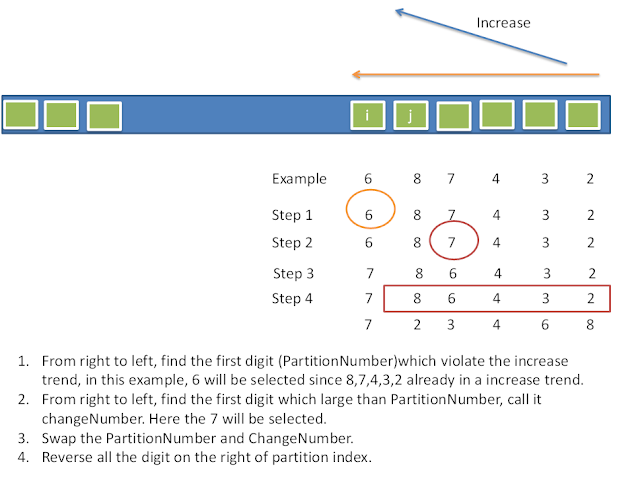
这题更像一道数学题,画了个图表示算法,如下:
1 public class Solution { 2 public void nextPermutation(int[] num) { 3 int len = num.length; 4 int pIndex = -1; 5 int changeIndex = -1; 6 for(int i = len-1; i > 0; i--){ 7 if(num[i-1] < num[i]){ 8 pIndex = i-1; 9 break; 10 } 11 } 12 13 if(pIndex == -1){ 14 reverseArray(num, 0, len-1); 15 }else{ 16 for(int i = len-1; i>= 0; i--){ 17 if(num[i] > num[pIndex]){ 18 changeIndex = i; 19 break; 20 } 21 } 22 swap(num, pIndex, changeIndex); 23 reverseArray(num, pIndex+1, len-1); 24 } 25 } 26 27 private void reverseArray(int[] num, int start, int end){ 28 while(start <= end){ 29 swap(num, start, end); 30 start++; 31 end--; 32 } 33 } 34 35 private void swap(int[] num, int a, int b){ 36 int tmp = num[a]; 37 num[a] = num[b]; 38 num[b] = tmp; 39 } 40 }
public class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] num) { // Note: The Solution object is instantiated only once and is reused by each test case. int length = num.length; int index = - 1; /* from right to left, find the first digit which violate the increase trend. /*call this digit partition number */ for(int i = length - 1; i >= 1; i--){ if(num[i] > num[i - 1]){ index = i; break; } } // if no digit violate the increase trend. reverse the digit if(index == -1){ reverseArray(num, 0, length - 1); } /* from right to left. find the first digit larger than the partition number * call this digit change number. swap it with partition number * reverse all the digit on the right of partition index */ else { int biggerIndex = findBig(num[index - 1], index, num); swap(num, biggerIndex, index - 1); reverseArray(num, index, length - 1); } } public int findBig(int sentinal, int index, int[] num){ // int bigIndex = index; // int bigValue = num[index]; // for(int i = index + 1; i < num.length; i++){ // if(num[i] > num[index - 1] && num[i] <= bigValue){ // bigValue = num[i]; // bigIndex = i; // } // } // return bigIndex; int changeIndex = 0; int changeVaule; for(int i = num.length-1;i>=0;i--){ if(num[i] > sentinal){ changeIndex = i; changeVaule = num[i]; break; } } return changeIndex; } public void reverseArray(int[] num, int start, int end){ while(start < end){ swap(num, start, end); start ++; end --; } } public void swap(int[] num, int start, int end){ int tmp = num[start]; num[start] = num[end]; num[end] = tmp; } }
ref:http://fisherlei.blogspot.com/2012/12/leetcode-next-permutation.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号