剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
示例 1:
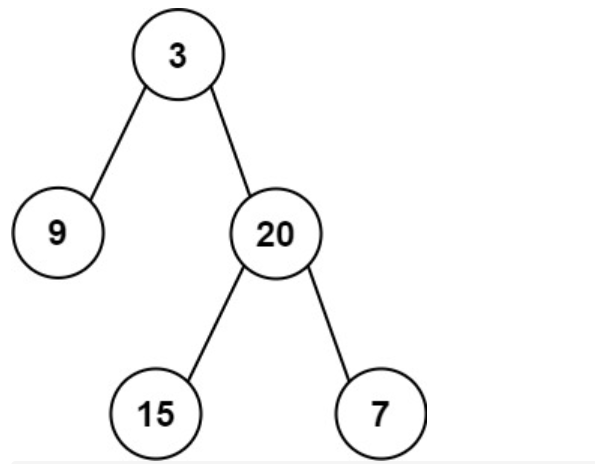
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
限制:
- 0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
解题思路:
做这道题,最好先理解一下前序遍历和中序遍历的基本概念。
前序遍历性质: 节点按照 [ 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ] 排序。
中序遍历性质: 节点按照 [ 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ] 排序。
以题目示例为例:
前序遍历划分 [ 3 | 9 | 20 15 7 ]
中序遍历划分 [ 9 | 3 | 15 20 7 ]
然后再根据k神的代码写出解题思路:
-
递推参数:根节点在前序遍历的索引root,子树在中序遍历的左边界left和右边界right
-
终止条件:当left>right时,代表越过节点,返回null
-
递推:
- 建立根节点node:节点值为preorder[root]
- 再划分左右子树,查找根节点在中序遍历下面的索引id
- 最后构建左右子树开启左右子树的递归
这个时候,最难理解的来了,就是理解左右子树的索引
| 根节点索引 | 中序遍历左边界 | 中序遍历右边界 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 左子树 | root + 1 | left | id - 1 |
| 右子树 | root + id - left + 1 | id + 1 | right |
像右子树的根节点索引是最让人昏的,但只要理解到其实就是右子树根节点=(中序根节点坐标-中序左边界)+先序根节点坐标+1,其中括号内=左子树长度。当然最重要的还是要知道,这里面的 left 和 i 还有 right 都是用来给 inorder 中序遍历处理边界的,不要直接用来给 preorder 确定根节点!!!
- 返回值:回溯返回node,作为上一层递归的左右节点
k神代码如下:
class Solution {
int[] preorder;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++)
dic.put(inorder[i], i);
return recur(0, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
TreeNode recur(int root, int left, int right) {
if(left > right) return null; // 递归终止
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(preorder[root]); // 建立根节点
int i = dic.get(preorder[root]); // 划分根节点、左子树、右子树
node.left = recur(root + 1, left, i - 1); // 开启左子树递归
//右子树的根的索引为先序中的 当前根位置 + 左子树的数量 + 1
node.right = recur(root + i - left + 1, i + 1, right); // 开启右子树递归
return node; // 回溯返回根节点
}
}
注释详细版本:
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//标记中序遍历
int[] preorder;//保留的先序遍历,方便递归时依据索引查看先序遍历的值
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
//将中序遍历的值及索引放在map中,方便递归时获取左子树与右子树的数量及其根的索引
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
//三个索引分别为
//当前根的的索引
//递归树的左边界,即数组左边界
//递归树的右边界,即数组右边界
return recur(0,0,inorder.length-1);
}
TreeNode recur(int pre_root, int in_left, int in_right){
if(in_left > in_right) return null;// 相等的话就是自己
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pre_root]);//获取root节点
int idx = map.get(preorder[pre_root]);//获取在中序遍历中根节点所在索引,以方便获取左子树的数量
//左子树的根的索引为先序中的根节点+1
//递归左子树的左边界为原来的中序in_left
//递归左子树的右边界为中序中的根节点索引-1
root.left = recur(pre_root+1, in_left, idx-1);
//右子树的根的索引为先序中的 当前根位置 + 左子树的数量 + 1
//递归右子树的左边界为中序中当前根节点+1
//递归右子树的右边界为中序中原来右子树的边界
root.right = recur(pre_root + (idx - in_left) + 1, idx+1, in_right);
return root;
}
}
参考链接:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号