skynet源码分析之sproto解析和构建
skynet提供一套与客户端通讯的协议sproto,设计简单,有利于lua使用,参考官方wiki https://github.com/cloudwu/skynet/wiki/Sproto。本篇介绍组装".sproto"文件以及sproto构建流程。之后,会另写一篇介绍sproto的使用方法。
1. 组装.sproto文件流程
以下面简单的test.sproto文件为例介绍.sproto文件组装流程:
-- test.sproto .Person { name 0 : string id 1 : integer email 2 : string .PhoneNumber { number 0 : string type 1 : integer } phone 3 : *PhoneNumber } .AddresBook { person 0 : *Person } proto1 1001 { request { p 0 : integer } response { ret 0 : *Person } }
通过sparser.parse api组装.sproto文件,参数text即test.sproto文件的内容:
1 -- lualib/sprotoparser.lua 2 function sparser.parse(text, name) 3 local r = parser(text, name or "=text") 4 dump(r) 5 local data = encodeall(r) 6 sparser.dump(data) 7 return data 8 end
第3-4行,通过lpeg库将.sproto文件分析转化成一个lua表,部分结果如下,包含protocol和type两大类。protocol里包含所有的协议,每个协议有request,response,tag三个key;type里包含所有的类型,每个类型有1个或多个域(field),每个field里包含name,tag,typename等信息。
1 "protocol" = { 2 "proto1" = { 3 "request" = "proto1.request" 4 "response" = "proto1.response" 5 "tag" = 1001 6 } 7 } 8 "type" = { 9 "AddresBook" = { 10 1 = { 11 "array" = true 12 "name" = "person" 13 "tag" = 0 14 "typename" = "Person" 15 } 16 } 17 "Person" = { 18 1 = { 19 "name" = "name" 20 "tag" = 0 21 "typename" = "string" 22 } 23 ...
第5-6行,把lua表按特定格式组装成二进制数据后,结果如下(每一行16个字节):
1 02 00 00 00 00 00 65 01 - 00 00 32 00 00 00 02 00 2 00 00 00 00 0A 00 00 00 - 41 64 64 72 65 73 42 6F 3 6F 6B 1A 00 00 00 16 00 - 00 00 05 00 00 00 01 00 4 04 00 02 00 04 00 06 00 - 00 00 70 65 72 73 6F 6E 5 6E 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 - 00 00 06 00 00 00 50 65 6 72 73 6F 6E 5A 00 00 00 - 12 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 7 06 00 01 00 02 00 04 00 - 00 00 6E 61 6D 65 10 00 8 00 00 04 00 00 00 02 00 - 01 00 04 00 02 00 00 00 9 69 64 13 00 00 00 04 00 - 00 00 06 00 01 00 06 00 10 05 00 00 00 65 6D 61 69 - 6C 15 00 00 00 05 00 00 11 00 01 00 06 00 08 00 04 - 00 05 00 00 00 70 68 6F 12 6E 65 4E 00 00 00 02 00 - 00 00 00 00 12 00 00 00 13 50 65 72 73 6F 6E 2E 50 - 68 6F 6E 65 4E 75 6D 62 14 65 72 2E 00 00 00 14 00 - 00 00 04 00 00 00 06 00 15 01 00 02 00 06 00 00 00 - 6E 75 6D 62 65 72 12 00 16 00 00 04 00 00 00 02 00 - 01 00 04 00 04 00 00 00 17 74 79 70 65 2F 00 00 00 - 02 00 00 00 00 00 0E 00 18 00 00 70 72 6F 74 6F 31 - 2E 72 65 71 75 65 73 74 19 13 00 00 00 0F 00 00 00 - 04 00 00 00 02 00 01 00 20 02 00 01 00 00 00 70 34 - 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 21 00 0F 00 00 00 70 72 6F - 74 6F 31 2E 72 65 73 70 22 6F 6E 73 65 17 00 00 00 - 13 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 23 01 00 04 00 02 00 04 00 - 03 00 00 00 72 65 74 18 24 00 00 00 14 00 00 00 04 - 00 00 00 D4 07 08 00 0A 25 00 06 00 00 00 70 72 6F - 74 6F 31
通过这个结果(下面称为result)反推sproto组装流程:
第2-4行,按“<s4”格式打包字符串,即字符串长度占4个字节,按小端格式打包在头部,再加上字符串内容。
第14-22行,result前6个字节分别是"\2\0\0\0\0\0",接下来分别是type的组装结果(tt)和protocol的组装结果(tp)。result7-10个字节是65 01 00 00,为type组装后的长度357(6*2^4+5+1*2^16)。 result从368个字节开始是protocol的组装结果,368-371个字节是18 00 00 00,表示protocol的组装结果有24个字节(1*2^4+8),即最后24个字节。
1 -- lualib/sprotoparser.lua 2 function packbytes(str) 3 return string.pack("<s4",str) 4 end 5 6 local function encodeall(r) 7 return packgroup(r.type, r.protocol) 8 end 9 10 local function packgroup(t,p) 11 ... 12 tt = packbytes(table.concat(tt)) 13 tp = packbytes(table.concat(tp)) 14 result = { 15 "\2\0", -- 2fields 16 "\0\0", -- type array (id = 0, ref = 0) 17 "\0\0", -- protocol array (id = 1, ref =1) 18 19 tt, 20 tp, 21 } 22 return table.concat(result) 23 end
type组装结果共有357个字节(11-367):按字典升序遍历所有type,依次调用packtype进行组装。
第一个type是“AddresBook”:result11-14个字节是32 00 00 00,表示“AddresBook”组装结果有50个字节(3*2^4+2)(第21行),因为有1个field,result15-20个字节是02 00 00 00 00 00(第13-15行),紧接着是第16行packbytes("AddresBook"),长度是10,结果是 0A 00 00 00 41(A) 64(d) 64(d) 72(r) 65(e) 73(s) 42(B) 6F(o) 6F(o) 6B(k),即result的21-34个字节。接下来第35-38的四个字节1A 00 00 00,是"AddresBook"的所有field组装后长度26(1*2^4+10)。
1 -- lualib/sprotoparser.lua 2 local function packtype(name, t, alltypes) -- 组装每一个type 3 ... 4 local data 5 if #fields == 0 then 6 data = { 7 "\1\0", -- 1 fields 8 "\0\0", -- name (id = 0, ref = 0) 9 packbytes(name), 10 } 11 else 12 data = { 13 "\2\0", -- 2 fields 14 "\0\0", -- name (tag = 0, ref = 0) 15 "\0\0", -- field[] (tag = 1, ref = 1) 16 packbytes(name), 17 packbytes(table.concat(fields)), 18 } 19 end 20 21 return packbytes(table.concat(data)) 22 end
field组装流程,result第39-42的4个字节16 00 00 00,是第一个field的组装结果长度22(1*2^4+6),即result的43-64个字节。由AddresBook的数据可知,组装流程是:
第8行, 05 00
第13行,00 00
第23行,01 00
第24行,04 00, f.type=1
第25行,02 00, f.tag=0
第28行,04 00
第33行,06 00 00 00 70(p) 65(e) 72(r) 73(s) 6F(o) 6E(n),name="person"。正好对应result的43-64个字节。
"AddresBook" = { 1 = { "array" = true "name" = "person" "tag" = 0 "typename" = "Person" } }
1 -- lualib/sprotoparser.lua 2 local function packfield(f) -- 组装每一个field 3 local strtbl = {} 4 if f.array then 5 if f.key then 6 table.insert(strtbl, "\6\0") -- 6 fields 7 else 8 table.insert(strtbl, "\5\0") -- 5 fields 9 end 10 else 11 table.insert(strtbl, "\4\0") -- 4 fields 12 end 13 table.insert(strtbl, "\0\0") -- name (tag = 0, ref an object) 14 if f.buildin then 15 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.buildin)) -- buildin (tag = 1) 16 if f.extra then 17 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.extra)) -- f.buildin can be integer or string 18 else 19 table.insert(strtbl, "\1\0") -- skip (tag = 2) 20 end 21 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.tag)) -- tag (tag = 3) 22 else 23 table.insert(strtbl, "\1\0") -- skip (tag = 1) 24 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.type)) -- type (tag = 2) 25 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.tag)) -- tag (tag = 3) 26 end 27 if f.array then 28 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(1)) -- array = true (tag = 4) 29 end 30 if f.key then 31 table.insert(strtbl, packvalue(f.key)) -- key tag (tag = 5) 32 end 33 table.insert(strtbl, packbytes(f.name)) -- external object (name) 34 return packbytes(table.concat(strtbl)) 35 end
接下来,依次组装其他type,组装完type,然后调用packproto组装每一个proto。result372-375四个字节14 00 00 00,表示"proto1"组装后的长度20(1*2^4+4)。
"proto1" = {
"request" = "proto1.request"
"response" = "proto1.response"
"tag" = 1001
}
组装流程如下:
第10-12行, 04 00 00 00 D4 07
第18行,08 00 (alltypes[p.request].id=3)
第24行,0A 00 (alltypes[p.response].id=4)
第35行,name="proto1",长度是6,打包后是 06 00 00 00 70(p) 72(r) 6F(o) 74(t) 6F(0) 31(1)。正好对应result的最后20个字节。
-- lualib/sprotoparser.lua
1 local function packproto(name, p, alltypes) -- 组装每一个proto 2 if p.request then 3 local request = alltypes[p.request] 4 if request == nil then 5 error(string.format("Protocol %s request type %s not found", name, p.request)) 6 end 7 request = request.id 8 end 9 local tmp = { 10 "\4\0", -- 4 fields 11 "\0\0", -- name (id=0, ref=0) 12 packvalue(p.tag), -- tag (tag=1) 13 } 14 if p.request == nil and p.response == nil and p.confirm == nil then 15 tmp[1] = "\2\0" -- only two fields 16 else 17 if p.request then 18 table.insert(tmp, packvalue(alltypes[p.request].id)) -- request typename (tag=2) 19 else 20 table.insert(tmp, "\1\0")-- skip this field (request)
21 22 end 23 if p.response then 24 table.insert(tmp, packvalue(alltypes[p.response].id)) -- request typename (tag=3) 25 elseif p.confirm then 26 tmp[1] = "\5\0" -- add confirm field 27 table.insert(tmp, "\1\0") 28 -- skip this field (response) 29 table.insert(tmp, packvalue(1)) -- confirm = true 30 else 31 tmp[1] = "\3\0" -- only three fields 32 end 33 end 34 35 table.insert(tmp, packbytes(name)) 36 37 return packbytes(table.concat(tmp)) 38 end
小结:组装.sproto文件流程如下:
(1). 用lpeg库解析.sproto文件内容,把信息保存在一个lua表里
(2). 依次组装所有types,对每一个type先组装名称,再组装它的fields
(3). 依次组装所有protos
最后组装出的二进制块是由N个type和N个proto组成,每个type又包含name和N个field,每个field包含name、buildin、type、tag、array等信息;每个proto包含name、tag、request、response等信息。不论是field,type还是proto,都会加一些字节前缀,用来表示接下来字节的信息。格式如下: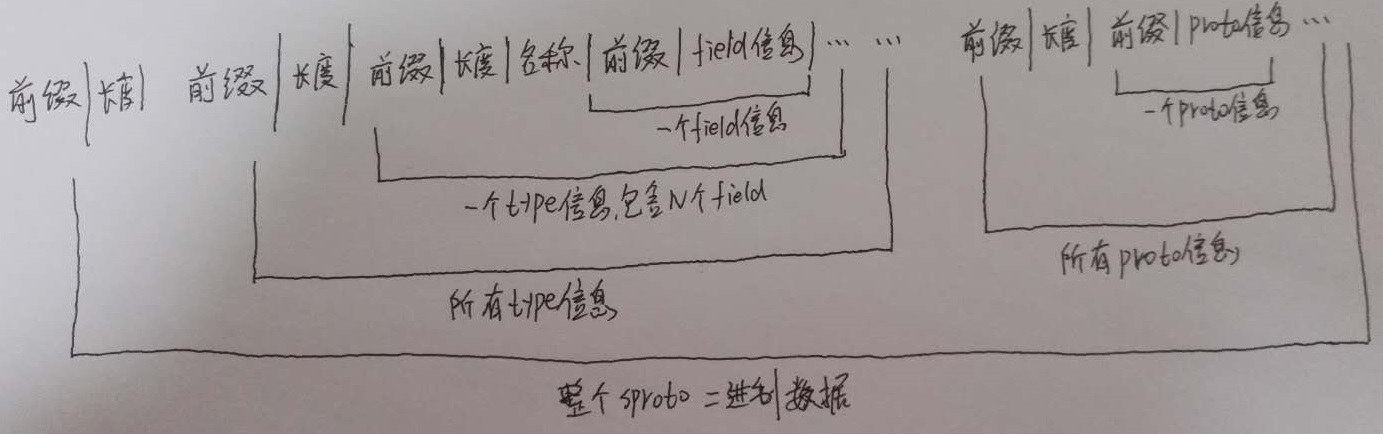
2. sproto构建流程
当把.sproto文件组装成二进制块后,sproto构建就是解析这个二进制块。了解了组装过程后,解析过程就是把组装过程倒过来,最后把解析结果保存在c结构里。通过lua层newproto,最终会调用到create_from_bundle 这个api来构建sproto,三个参数:s构建后的sproto保存在这个结构里,stream组装的二进制数据块,sz长度。
第19行,struct_field api计算前缀,不同的前缀接下来的数据含义不同
第23行,count_array api计算数目,比如计算types的总数,计算protos的总数,每个type中fields的总数
第26-29行,保存types总数s->type_n
第31-34行,保存protos总数s->protocol_n
第38-43行,通过import_type api构建每一个type的数据,保存在s->type这个数组里
第44-49行,通过import_protocol api构建每一个proto的数据,保存在s->proto这个数组里
1 // lualib/sproto/sproto.c 2 struct sproto * 3 sproto_create(const void * proto, size_t sz) { 4 ... 5 if (create_from_bundle(s, proto, sz) == NULL) { 6 pool_release(&s->memory); 7 return NULL; 8 } 9 return s; 10 } 11 12 static struct sproto * 13 create_from_bundle(struct sproto *s, const uint8_t* stream, size_t sz) { 14 ... 15 int fn = struct_field(stream, sz); 16 int i; 17 ... 18 for (i=0;i<fn;i++) { 19 int value = toword(stream + i*SIZEOF_FIELD); 20 int n; 21 if (value != 0) 22 return NULL; 23 n = count_array(content); 24 if (n<0) 25 return NULL; 26 if (i == 0) { 27 typedata = content+SIZEOF_LENGTH; 28 s->type_n = n; 29 s->type = pool_alloc(&s->memory, n * sizeof(*s->type)); 30 } else { 31 protocoldata = content+SIZEOF_LENGTH; 32 s->protocol_n = n; 33 s->proto = pool_alloc(&s->memory, n * sizeof(*s->proto)); 34 } 35 content += todword(content) + SIZEOF_LENGTH; 36 } 37 38 for (i=0;i<s->type_n;i++) { 39 typedata = import_type(s, &s->type[i], typedata); 40 if (typedata == NULL) { 41 return NULL; 42 } 43 } 44 for (i=0;i<s->protocol_n;i++) { 45 protocoldata = import_protocol(s, &s->proto[i], protocoldata); 46 if (protocoldata == NULL) { 47 return NULL; 48 } 49 } 50 51 return s; 52 }
sproto数据结构如下:
// lualib/sproto/sproto.c struct sproto { // 整个sproto结构 struct pool memory; int type_n; // types总数 int protocol_n; // proto总数 struct sproto_type * type; // N个type信息 struct protocol * proto; // N个proto信息 }; struct sproto_type { // 单个type结构 const char * name; // 名称 int n; // fields实际个数 int base; //如果tag是连续的,为最小的tag,否则是-1 int maxn; //fields实际个数+最小的tag+不连续的tag个数,比如tag依次是1,3,5,则maxn=3+1+2=6 struct field *f; // N个field信息 }; struct field { // 单个field结构 int tag; //唯一的tag int type; // 类型,可以是内置的integer,string,boolean,也可以是自定义的type,也可以是数组 const char * name; // 名称 struct sproto_type * st; //如果是自定义的类型,st指向这个类型 int key; int extra; }; struct protocol { //单个proto结构 const char *name; //名称 int tag; //唯一的tag int confirm; // confirm == 1 where response nil struct sproto_type * p[2]; //request,response的类型 };
通过sproto_dump api,打印出构建后的sproto的信息如下:
=== 5 types === AddresBook 1 0 1 person (0) *Person Person 4 0 4 name (0) string id (1) integer email (2) string phone (3) *Person.PhoneNumber Person.PhoneNumber 2 0 2 number (0) string type (1) integer proto1.request 1 0 1 p (0) integer proto1.response 1 0 1 ret (0) *Person === 1 protocol === proto1 (1001) request:proto1.request response:proto1.response
构建成功后,调用saveproto将sproto保存在全局数组G_sproto中,供所有lua VM加载(loadproto)使用。
这就是sproto的解析和构建流程。接下来会写一篇文章介绍sproto如何使用。




