05 串 | 数据结构与算法
1. 串
1. 串的定义
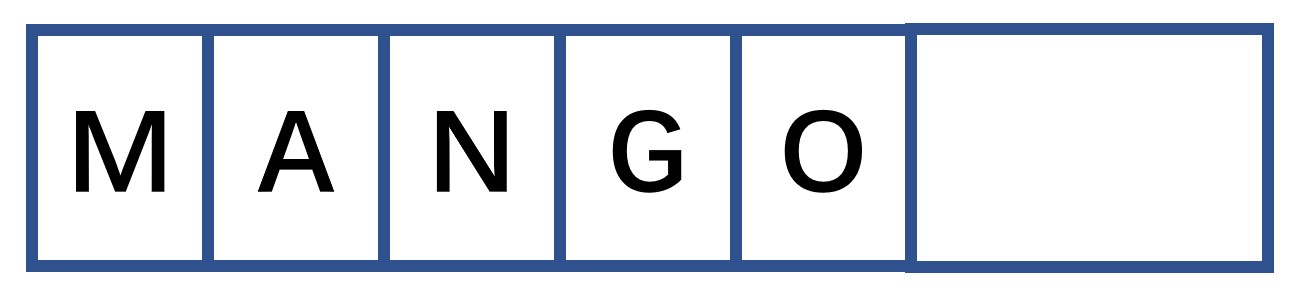
- 串:零个或多个 字符 组成的 有限 序列
- 串的长度:串中字符的个数
- 空串:长度为 0 的串
"" - 非空串:
String = "c1c2c3...cn"- 串名:
String - 定界符:
" " - 数据元素:字符
ci
- 串名:
- 主串:包含子串的串
- 子串:串中任意个 连续 的字符组成的子序列
- 子串的位置:子串中的第一个字符在主串中的序号
- 串相同:串长度相同并且各个对应的字符也相同
2. 串的存储设计
- 顺序串:采用连续设计存储的字符序列
- 链接串:采用链接存储设计来存储串。串的链式存储结构和线性表的串的链式存储结构类似,采用单链表来存储串,结点的构成是:
data域:存放字符,data域可存放的字符个数称为结点的大小;next域:存放指向下一结点的指针。
若每个结点仅存放一个字符,则结点的指针域就非常多,造成系统空间浪费,为节省存储空间,考虑串结构的特殊性,使每个结点存放若干个字符,这种结构称为块链结构。
2. 串的模式匹配 /
1. 串的匹配
- 目标串:主串
- 模式串:子串
- 匹配:在目标串当中找到子串的位置
2.
-
算法出发点:利用前面已经匹配的结果,进行 无回溯 的匹配
-
next[]表示将模式串向右滑动尽可能远的一段距离 -
next[]的本质:找到模式串中 最长的相同前缀和后缀 -
算法:
- 计算
next[]数组
- 匹配
- 计算
-
改进的
- 对于下面这种情况:有多个相同的连续字符,显然如果匹配不成功可以直接跳过这一大段连续的相同字符,因此对于新的
nextval[],我们有- 如果当前模式串位置的字符和目标串位置的字符 不相同,那么
nextval[index] = next[index] - 如果当前模式串位置的字符和目标串位置的字符 相同,那么
nextval[index] = nextval[next[index]]
- 如果当前模式串位置的字符和目标串位置的字符 不相同,那么
- 例子
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 pattern a a a b b a b c c a a a a next-1 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 nextval-1 -1 -1 2 0 -1 1 0 0 -1 -1 -1 3 - 算法
- 对于下面这种情况:有多个相同的连续字符,显然如果匹配不成功可以直接跳过这一大段连续的相同字符,因此对于新的
__EOF__
本文作者:RadiumGalaxy
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/RadiumGalaxy/p/16800358.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/RadiumGalaxy/p/16800358.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!
标签:
Courses

 串以及串的匹配
串以及串的匹配


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署