28-集合(进阶版)

1. 单列集合:一次添加一个元素(Collection接口)
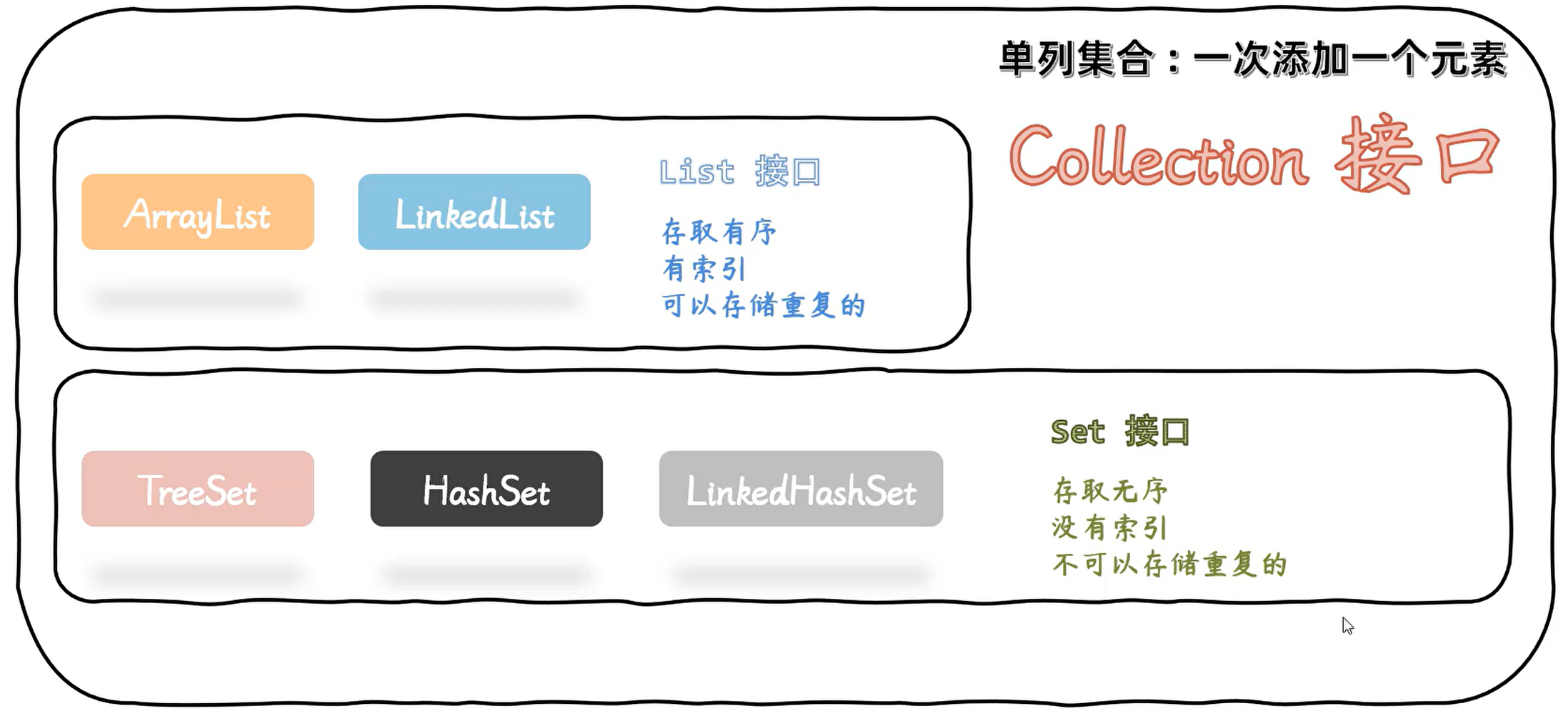
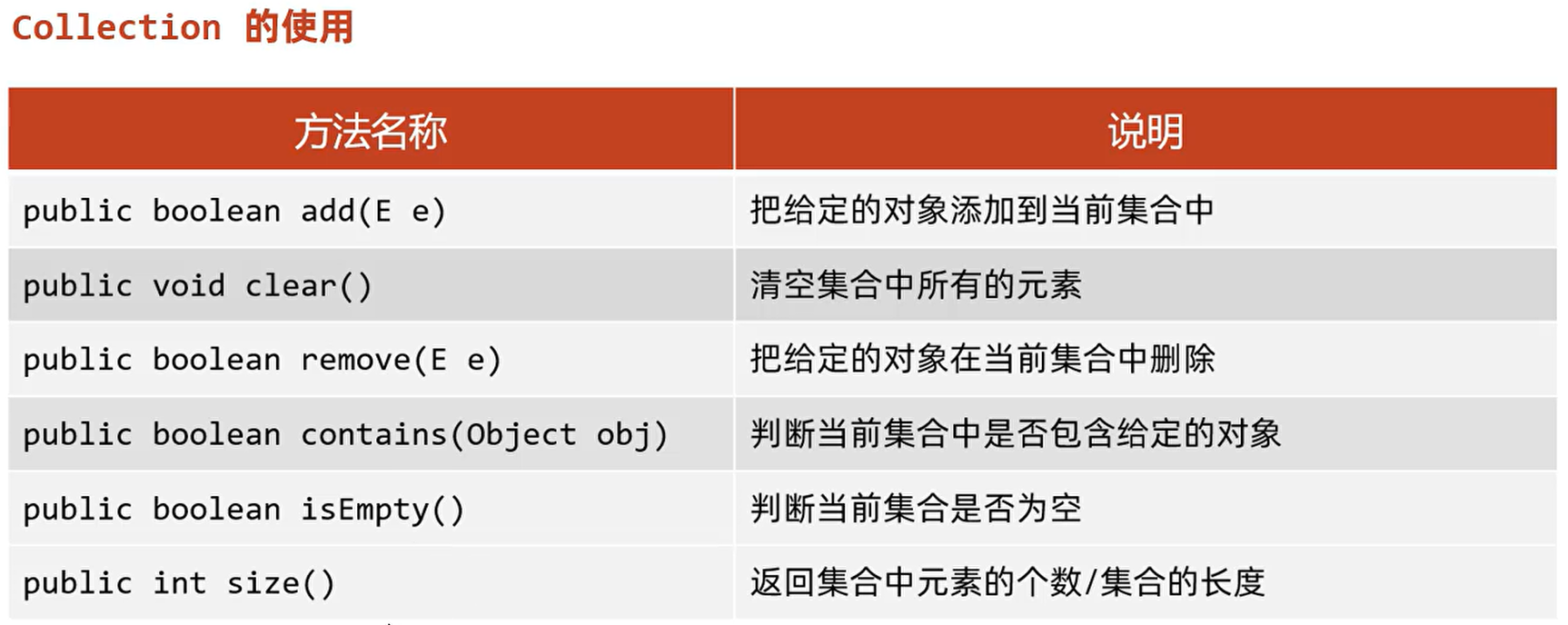
注意:这里的Collection接口,指的是List 和 Set接口所共有的方法
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; public class CollectionTest1 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 使用多态的形式创建集合对象,调用集合中的共有方法:接口的引用指向实现类的对象 // 左边是编译类型,右边是运行类型(左边的编译类型决定调用哪些属性和方法,右边的运行类型决定具体实现哪些内容) Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>(); // public boolean add(E e):把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 c.add("张三"); c.add("李四"); System.out.println(c); // public boolean remove(E e):把给定的对象在当前集合中删除 c.remove("李四"); System.out.println(c); // public void clear():清空集合中所有的元素 c.clear(); System.out.println(c); // public boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空(这里只是判断集合中是否有元素,无法判断集合是否为null) System.out.println(c.isEmpty()); // public boolean contains(E e):判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象 c.add("张三"); c.add("李四"); System.out.println(c.contains("张三")); // public int size():返回集合中元素的个数 System.out.println(c.size()); } }
集合的通用遍历方式:迭代器、for循环、foreach方法
Student类
package domain; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Student(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
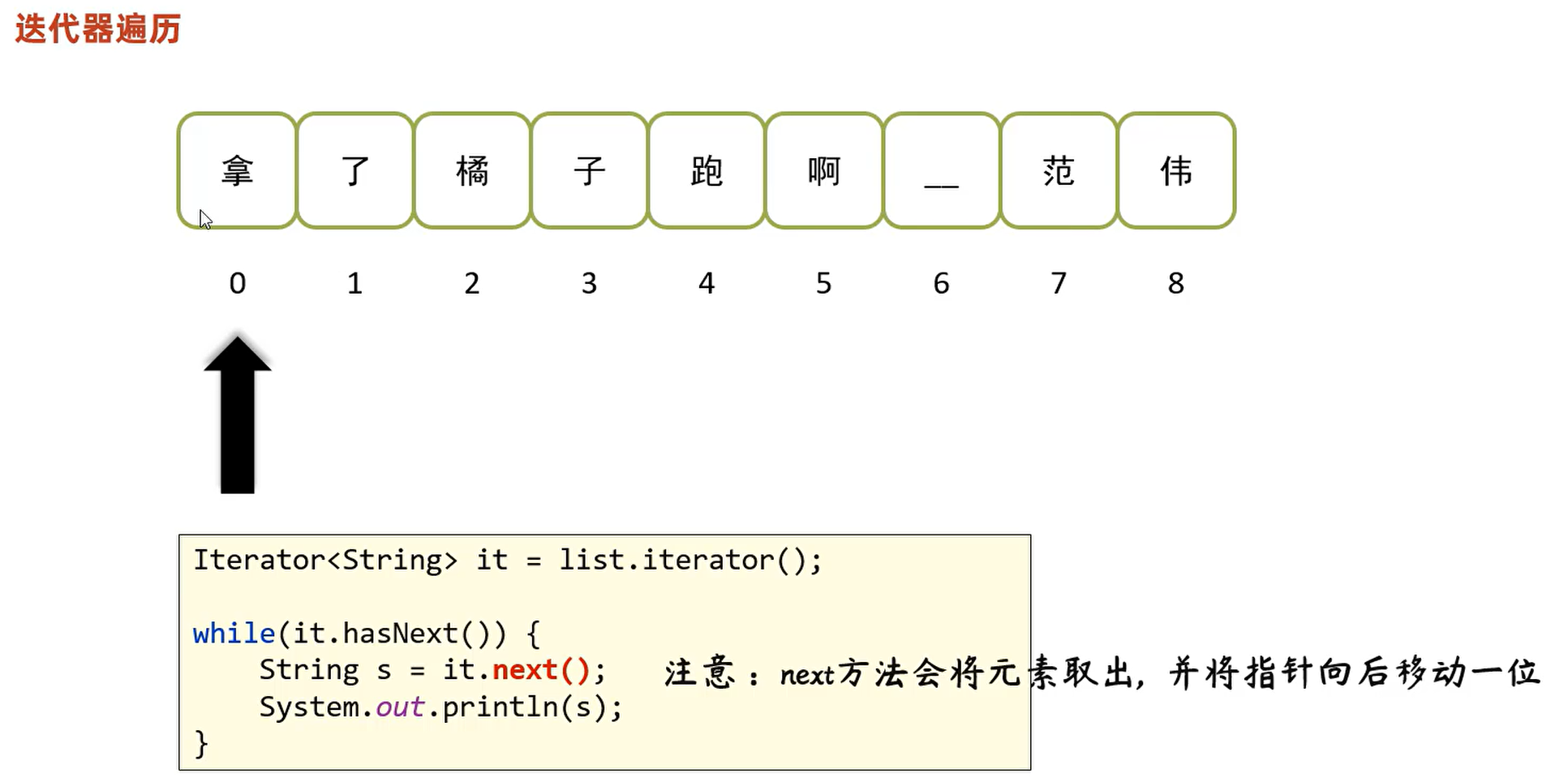

package collection; import domain.Student; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; public class CollectionTest2 { public static void main(String[] args){ Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<>(); c.add(new Student("张三", 23)); c.add(new Student("李四", 24)); c.add(new Student("王五", 25)); // 1.迭代器遍历 System.out.println("=================迭代器遍历=================="); // Iterator<E> iterator():获取遍历集合的迭代器对象 Iterator<Student> it = c.iterator(); // boolean hasNext():判断集合中是否还有下一个元素 while(it.hasNext()){ // E next():获取集合中的下一个元素 Student s = it.next(); System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); } } }

package collection; import domain.Student; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; public class CollectionTest3 { public static void main(String[] args){ Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<>(); c.add(new Student("张三", 23)); c.add(new Student("李四", 24)); c.add(new Student("王五", 25)); // 2.增强for循环遍历 System.out.println("=================增强for循环遍历=================="); for(Student stu:c){ System.out.println(stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge()); } } }

package collection; import domain.Student; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; public class CollectionTest4 { public static void main(String[] args){ Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<>(); c.add(new Student("张三", 23)); c.add(new Student("李四", 24)); c.add(new Student("王五", 25)); // 3.foreach循环遍历 System.out.println("=================foreach循环遍历=================="); c.forEach(stu -> System.out.println(stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge())); } }

扩展:在List集合中 添加另一个集合时,一般常用两种方法
boolean add(E e) : 将 list 作为一个元素添加到集合中
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) : 把 list 中的所有元素添加到集合中
package list; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ListDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args){ List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // public void add(int index, E element):在此集合中的指定位置插入指定的元素 list.add("张三"); list.add(1,"李四"); list.add(2,"王五"); System.out.println(list); // public E remove(int index):删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素 list.remove(1); System.out.println(list); // public E set(int index, E element):修改指定索引处的元素,返回被修改的元素 list.set(1,"马铃薯"); System.out.println(list); // public E get(int index):返回指定索引处的元素 System.out.println(list.get(1)); } }

List集合的通用遍历方式:迭代器、for循环、foreach方法、普通for循环、ListIterator(List集合特有的迭代器)
package list; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.ListIterator; public class ListDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args){ List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("张三"); list.add("李四"); list.add("王五"); // 1.迭代器遍历 // Iterator<E> iterator():获取遍历集合的迭代器对象 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); System.out.println("=================迭代器遍历=================="); // boolean hasNext():判断集合中是否还有下一个元素 // E next():获取集合中的下一个元素 while(it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); System.out.println(s); } // 2.增强for循环遍历 System.out.println("=================增强for循环遍历=================="); for(String s:list){ System.out.println(s); } // 3.普通for循环遍历 System.out.println("=================普通for循环遍历=================="); for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){ System.out.println(list.get(i)); } // 4.forEach遍历 System.out.println("=================forEach遍历=================="); list.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s)); // 5.ListIterator遍历(List集合特有的遍历方式) // ListIterator<E> listIterator():获取列表迭代器对象 // ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index):获取列表迭代器对象,从指定的索引开始 ListIterator<String> list2 = list.listIterator(); System.out.println("=================ListIterator正序遍历=================="); // boolean hasNext():判断是否有下一个元素 // E next():获取下一个元素 while(list2.hasNext()){ String s = list2.next(); System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("=================ListIterator逆序遍历=================="); // boolean hasPrevious():判断是否有上一个元素 // E previous():获取上一个元素 while(list2.hasPrevious()){ String s = list2.previous(); System.out.println(s); } } }
这里需要注意:使用迭代器遍历集合的过程中,调用了集合对象的添加,删除方法,会触发并发修改异常ConcurrentModificationException

package list; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.ListIterator; public class ListDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args){ List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("张三"); list.add("李四"); list.add("王五"); System.out.println("初始化的集合:" + list); // ListIterator遍历(List集合特有的遍历方式) // 使用迭代器遍历集合时,不可以使用"集合对象"的方法操作集合中的元素,否则会发生并发修改异常(ConcurrentModificationException) // 但可以使用"迭代器对象",在遍历的过程中实现添加或删除方法 ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); if(s.equals("李四")){ // list.add("马铃薯"); 报错,使用迭代器遍历集合时,不可以使用"集合对象"的方法操作集合中的元素 it.add("马铃薯"); } if(s.equals("王五")){ // list.remove("王五"); 报错,使用迭代器遍历集合时,不可以使用"集合对象"的方法操作集合中的元素 it.remove(); } } System.out.println("修改后的集合:" + list); } }




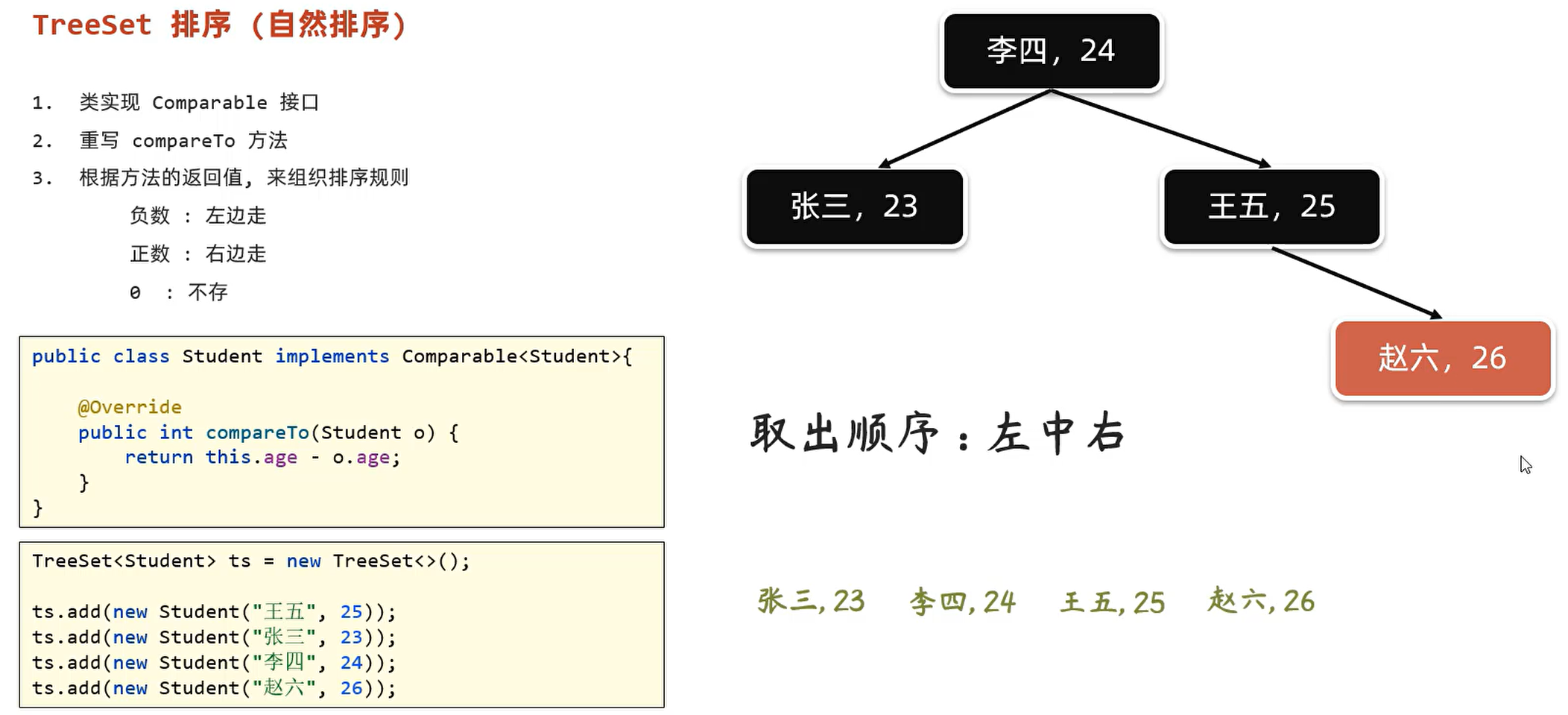

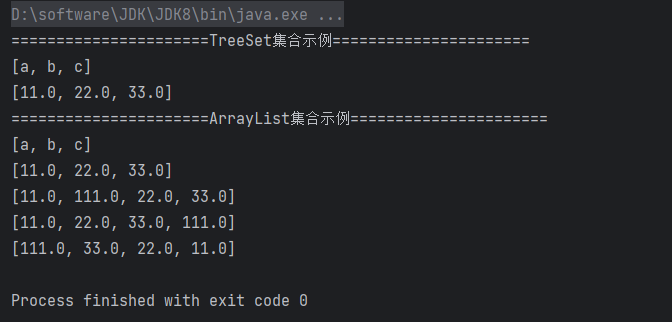
package set; /* * TreeSet集合: * 1. TreeSet集合底层是一个TreeMap(二叉树结构)数据结构 * 2. TreeSet集合是一个有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的 * 3. TreeSet集合是一个不重复的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的 * * TreeSet集合的特点:排序和不重复 * * */ import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.TreeSet; public class TreeSetDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("======================TreeSet集合示例======================"); TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(); ts.add("a"); ts.add("c"); ts.add("b"); ts.add("b"); // 不重复,只会存储一个"b"元素 System.out.println(ts); // [a, b, c] 排序,不重复 TreeSet<Double> ts2 = new TreeSet<>(); ts2.add(11.0); ts2.add(33.0); ts2.add(22.0); System.out.println(ts2); // [11.0, 22.0, 33.0] 排序,不重复 System.out.println("======================ArrayList集合示例======================"); // 以上两个例子,都是String和Double类型的,这两个类型都是包装类,都实现了Comparable接口,所以可以排序 // ArrayList集合进行排序 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("a"); list.add("c"); list.add("b"); list.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2)); // [a, b, c] System.out.println(list); List<Double> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); list2.add(11.0); list2.add(33.0); list2.add(22.0); list2.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2)); // [11.0, 22.0, 33.0] System.out.println(list2); // 特殊情况,但比较常见:String和Double类型的集合,但是集合中的元素是字符串类型的数字 List<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>(); list3.add("11.0"); list3.add("33.0"); list3.add("22.0"); list3.add("111.0"); // 不进行数据类型转换,直接比较会出问题 list3.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2)); System.out.println(list3); // [11.0, 111.0, 22.0, 33.0] 有问题,因为是字符串,所以比较的是字符串的大小,而不是数字的大小 // 先进行数据类型转换,再进行比较 // 从小到大排序 list3.sort((o1, o2) -> (int)(Float.parseFloat(o1) - Float.parseFloat(o2))); System.out.println(list3); // [11.0, 22.0, 33.0, 111.0] // 从大到小排序 Collections.reverse(list3); System.out.println(list3); // [111.0, 33.0, 22.0, 11.0] } }

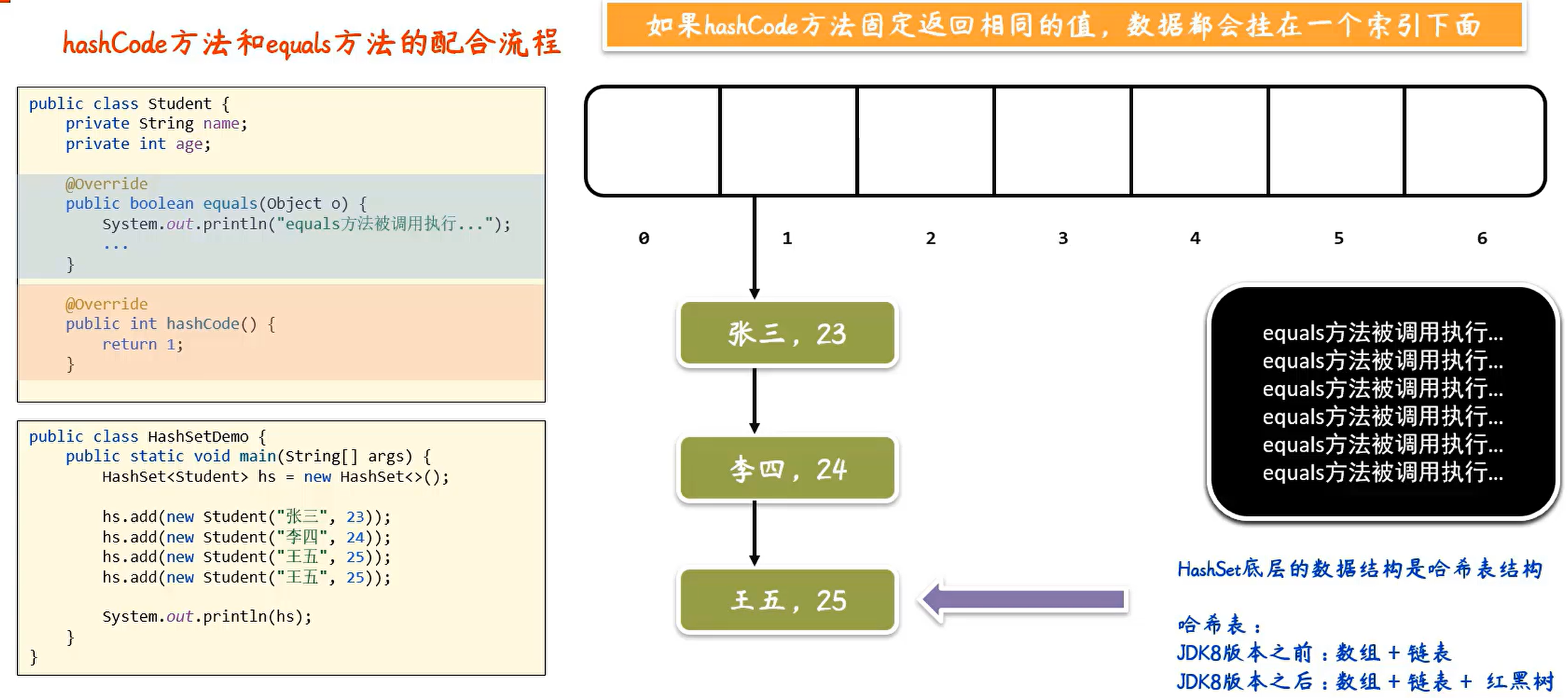
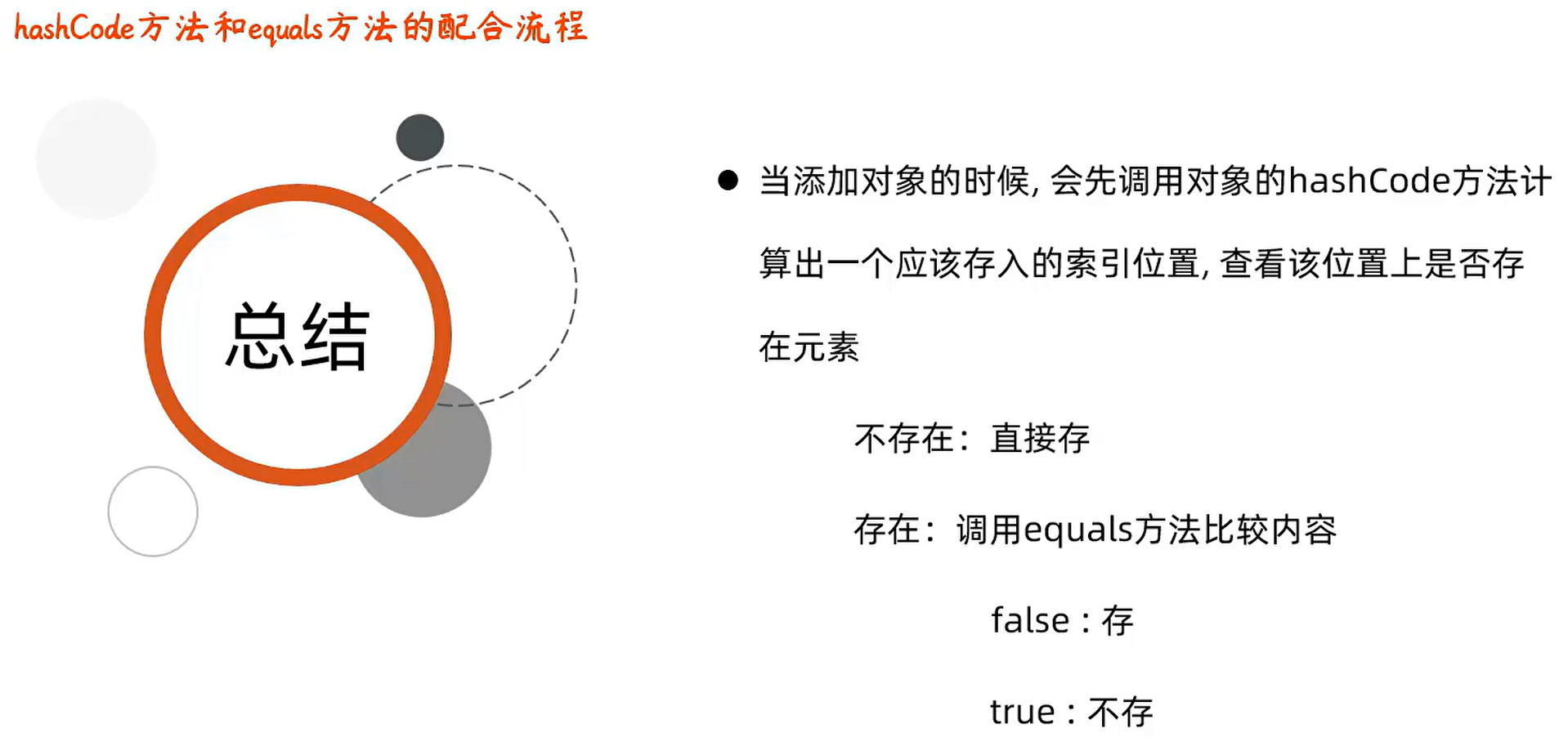



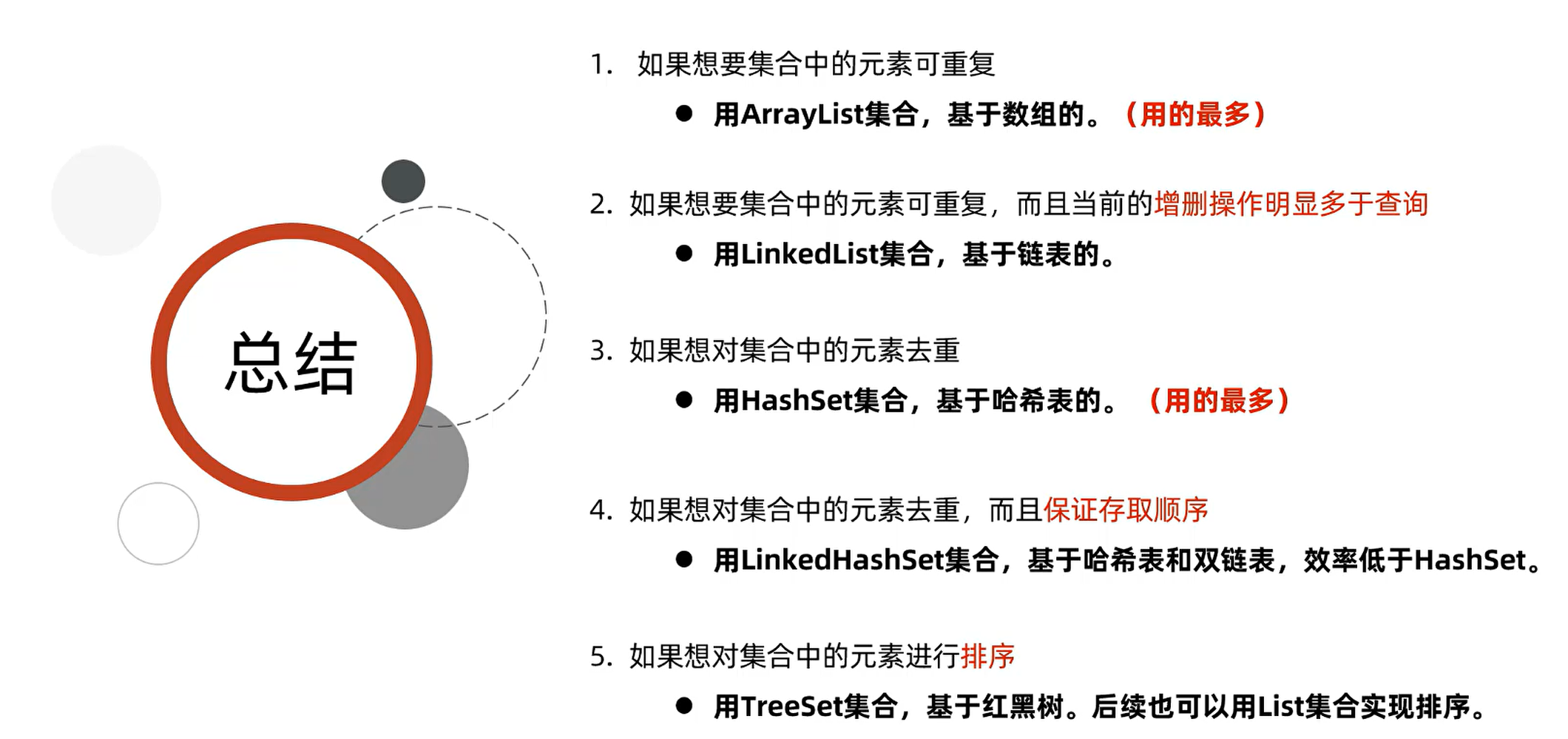
扩展小知识:可变参数

package args; public class ArgsDemo { public static void main(String[] args){ // 调用方法,计算两个整数的和 int sum1 = getSum(10, 20); System.out.println(sum1); // 调用方法,计算三个整数的和 int sum2 = getSum(10, 20, 30); System.out.println(sum2); // 调用方法,计算任意个整数的和 int sum3 = getSum(10, 20, 30, 40, 50); System.out.println(sum3); } // 计算两个整数的和 public static int getSum(int a, int b){ return a + b; } // 计算三个整数的和 public static int getSum(int a, int b, int c){ return a + b + c; } // 可变参数,可以接收任意个整数,计算整数的和 public static int getSum(int... nums){ int sum = 0; for(int num : nums){ sum += num; } return sum; } }
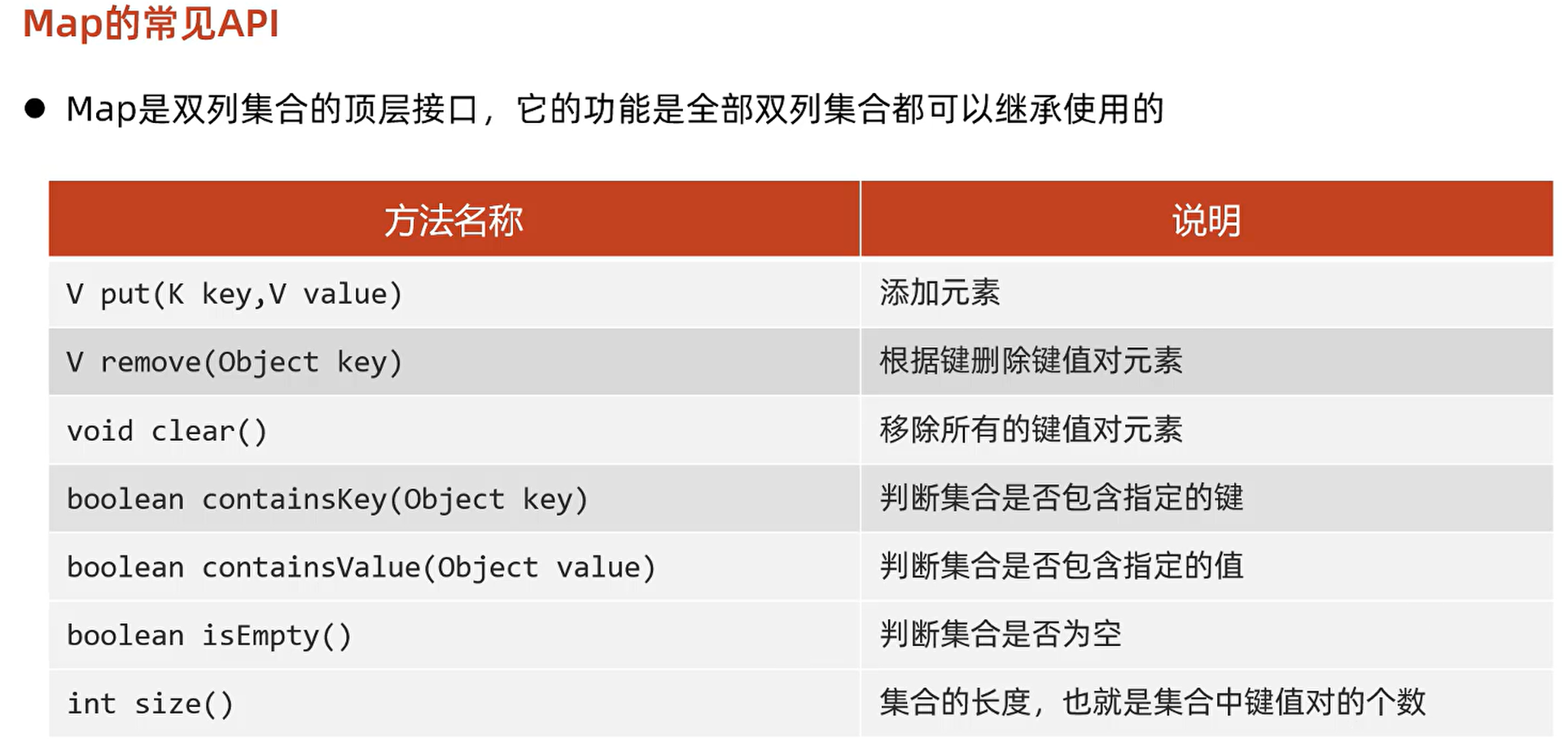
2. Collections 集合工具类
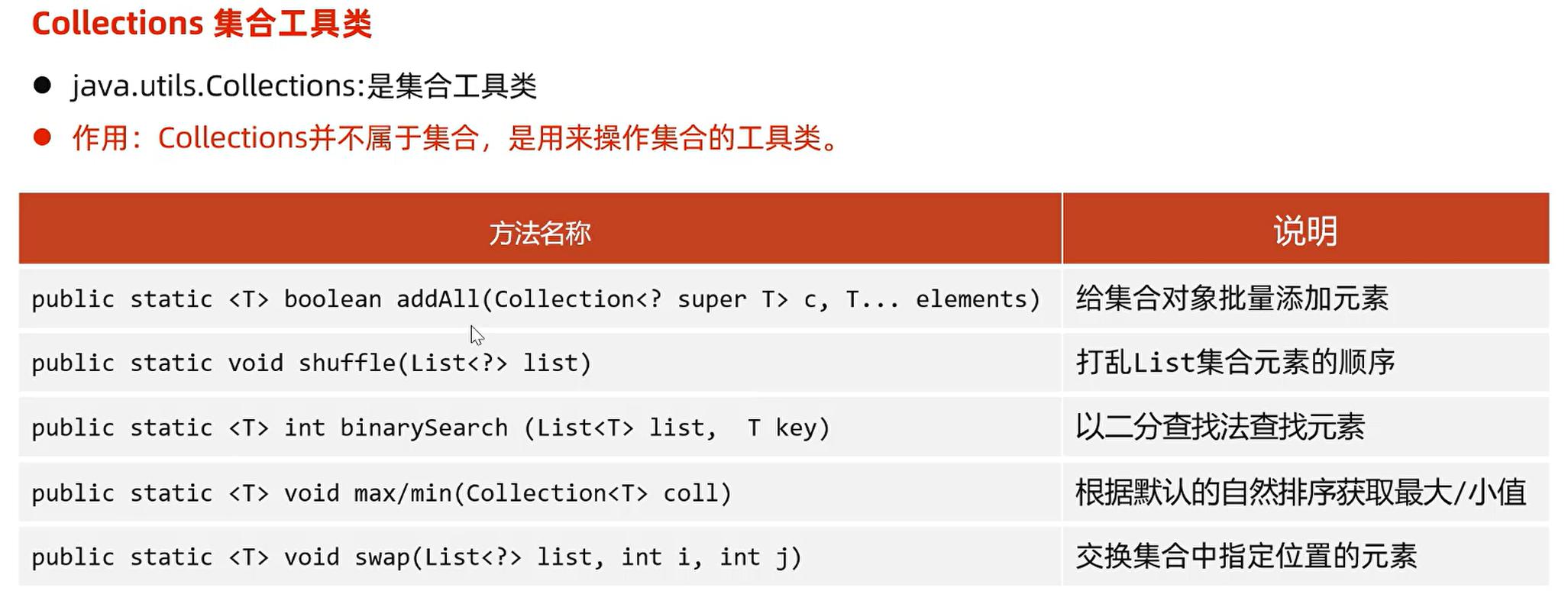
扩展:Collections集合工具类,其它比较常用的方法
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list):将集合中元素按照默认规则排序
public static void reverse(List<?> list):反转集合中元素的顺序
package collections; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; public class CollectionsDemo { public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<T> c, T... elements):给集合对象批量添加元素 Collections.addAll(list, "a", "b", "c"); System.out.println(list); // [a, b, c] // public static void shuffle(List<?> list):打乱集合中元素的顺序 Collections.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list); // [b, a, c] // public static <T> void sort(List<T> list):将集合中元素按照默认规则排序 Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list); // [a, b, c] // public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list, T key):二分查找 // 注意:使用二分查找的集合,必须是有序的 int index = Collections.binarySearch(list, "b"); System.out.println(index); // 1 // public static <T> T max(Collection<?> coll):返回集合中的最大元素 String max = Collections.max(list); System.out.println(max); // c // public static <T> T min(Collection<?> coll):返回集合中的最小元素 String min = Collections.min(list); System.out.println(min); // a // public static void reverse(List<?> list):反转集合中元素的顺序 Collections.reverse(list); System.out.println(list); // [c, b, a] } }
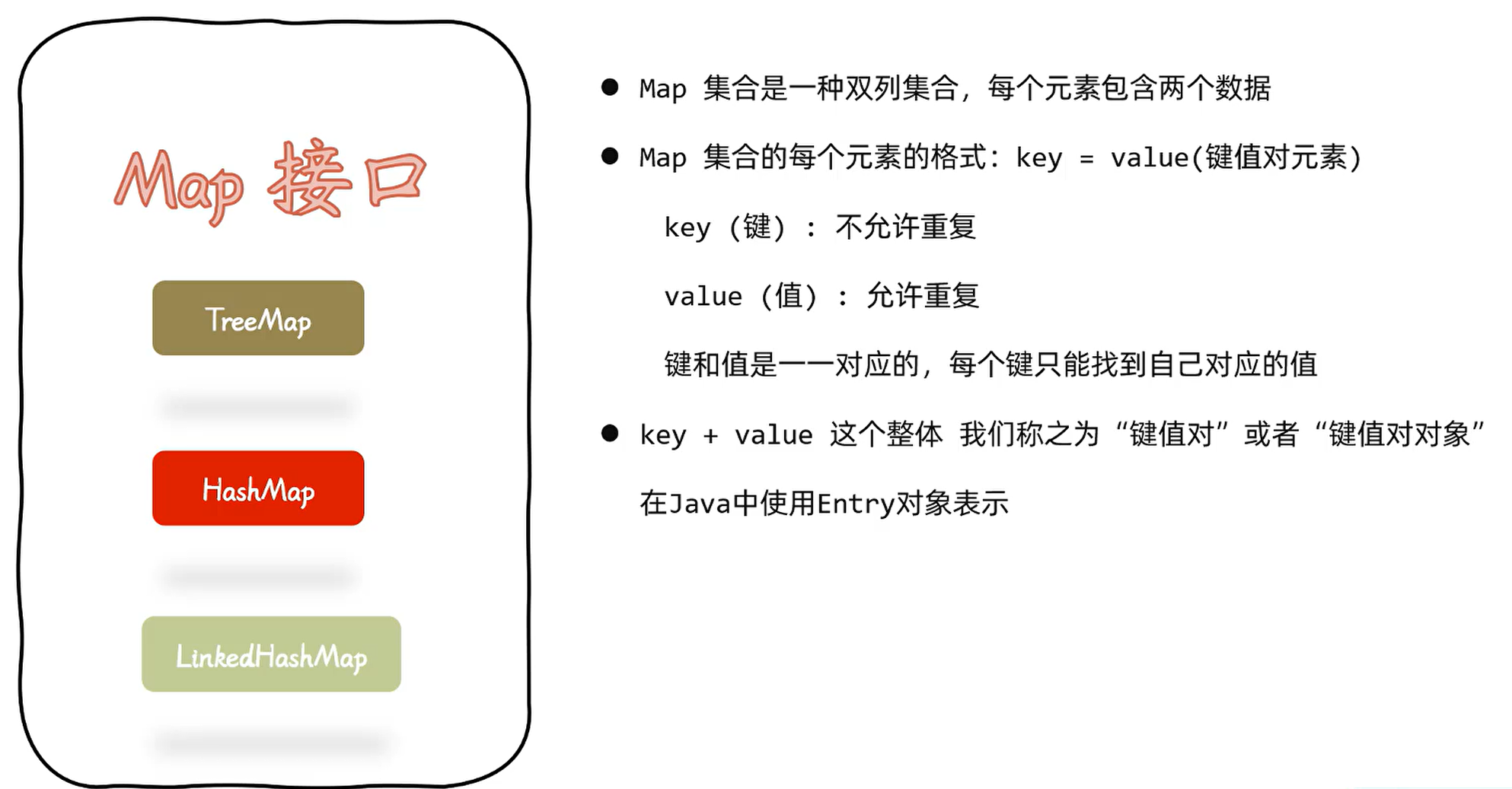
3. 双列集合:一次添加两个元素(Map接口)
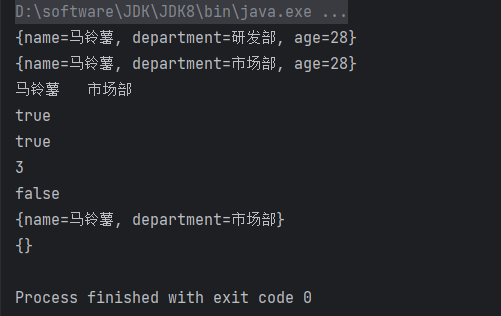
package map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MapDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args){ Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); // public V put(K key, V value):添加元素/修改元素 map.put("name", "马铃薯"); map.put("age", "28"); map.put("department", "研发部"); System.out.println(map); // {name=马铃薯, department=研发部, age=28} 这里需要注意,HashMap是无序的 // 当添加元素的时候,如果添加的 键key 已经存在,那么就会使用 新的值value 替换掉 原有的值value,然后返回 原有的值value map.put("department", "市场部"); System.out.println(map); // {name=马铃薯, department=市场部, age=28} // public V get(Object key):根据指定的键,获取对应的值 System.out.println(map.get("name") + "\t" + map.get("department")); // 马铃薯 市场部 // public boolean containsKey(Object key):判断集合中是否包含指定的键 System.out.println(map.containsKey("name")); // true // public boolean containsValue(Object value):判断集合中是否包含指定的值 System.out.println(map.containsValue("市场部")); // true // public int size():返回集合中键值对的个数 System.out.println(map.size()); // 3 // public boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空 System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); // false // public V remove(Object key):根据指定的键,删除对应的键值对元素 map.remove("age"); System.out.println(map); // {name=马铃薯, department=市场部} // public void clear():清空集合中所有的键值对元素 map.clear(); System.out.println(map); // {} } }




Map集合的遍历:键找值、键值对对象获取键和值、foreach方法遍历


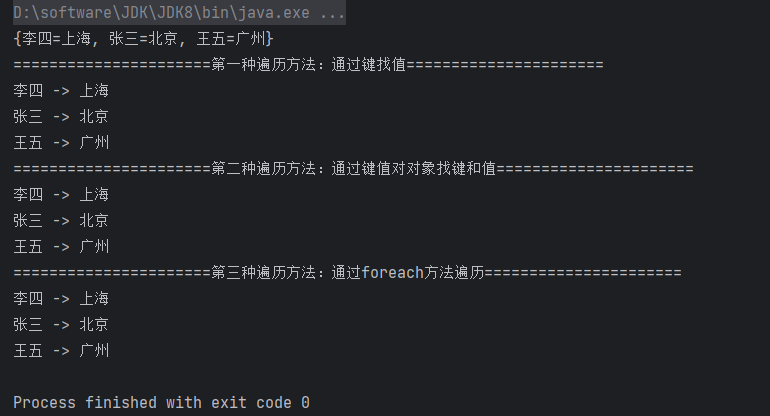
package map; import domain.Student; import java.util.HashMap; public class MapDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args){ HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("张三", "北京"); map.put("李四", "上海"); map.put("王五", "广州"); System.out.println(map); // {王五=广州, 张三=北京, 李四=上海} // 1.第一种遍历方法:通过键找值 // public get(Object key):根据指定的键,获取对应的值 // public Set<K> keySet():获取集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中 System.out.println("======================第一种遍历方法:通过键找值======================"); for (String key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key + " -> " + map.get(key)); } // 2.第二种遍历方法:通过键值对对象找键和值 // public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():获取集合中所有的键值对对象的集合,存储到Set集合中 System.out.println("======================第二种遍历方法:通过键值对对象找键和值======================"); for (HashMap.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " -> " + entry.getValue()); } // 3.第三种遍历方法:通过foreach方法遍历 System.out.println("======================第三种遍历方法:通过foreach方法遍历======================"); map.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " -> " + v)); } }

package map; import java.util.*; public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args){ HashMap<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); // public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection <T> c, T... elements):给集合对象批量添加元素 Collections.addAll(list1, "南京市", "扬州市", "苏州市", "无锡市", "常州市"); ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list2, "武汉市", "孝感市", "十堰市", "宜昌市", "鄂州市"); ArrayList<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list3, "成都市", "绵阳市", "自贡市", "攀枝花市", "泸州市"); map.put("江苏省", list1); map.put("湖北省", list2); map.put("四川省", list3); // 遍历 for(Map.Entry<String,List<String>> entry : map.entrySet()){ // 键:省份名称 String province = entry.getKey(); // 值:多个市区名称 List<String> list = entry.getValue(); String city = ""; for(int i = 0; i < list.size() -1; i++){ city += list.get(i) + ", "; } city += list.get(list.size() - 1); System.out.println(province + " = " + city); } } }


