文件操作
文件:
python文件,word文件,音频文件,图片文件
.py
.docx
.xlsx
.pptx
.mp4
.png
文件的作用:
数据持久化:利用文件来保存软件运行过程中的数据,并且可以通过对文件中的数据进行读写
文件中常用的操作:
1.打开文件
file = open("url","w",encoding="utf-8")
r:只读
w:写入,文件名存在,重新创建覆盖后写入;文件名不存在,创建后写入
a:追加写入,文件名存在,在文件内容最后进行写入操作;文件名不存在,创建后写入
2.读/写
写入文件
write("写入内容")
读取文件
read():一次性读取所有的,并且存储数据类型为str
readline():只能读取一行数据,并且存储数据类型为str
readlines():一下读取所有的行,并且存储数据类型为list列表
3.关闭文件
file.close()
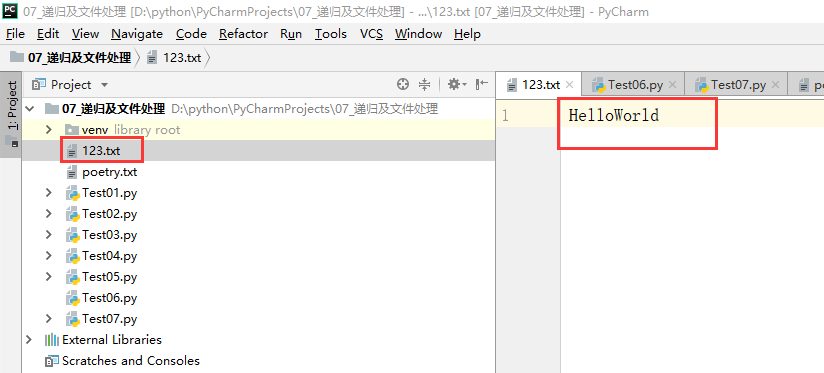
实例1:
将"HelloWorld"写入到指定的文件中123.txt
# 1.打开文件 # 编码方式默认为cp936(GBK) 手动指定为utf-8 file = open("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/07_递归及文件处理/123.txt","w",encoding="utf-8") # 2.读/写 file.write("HelloWorld") # 3.关闭文件 file.close()
实例2:
将你最喜欢的一首古诗写入指定的文件,注意换行
# 创建一个写入函数,将古诗写入指定文件poetry.txt def write_poetry(): # 1.打开文件 file = open("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/07_递归及文件处理/poetry.txt","a",encoding="utf-8") for i in range(1,5): content = input("请输入第%d行古诗:"%i) # 2.读/写 file.write(content+"\n") # 文件刷新操作 file.flush() print("古诗写入成功!") # 3.关闭文件的时候,默认刷新 file.close() # 调用写入函数 write_poetry()
# 文件的读取操作 # 1.第一种read()读取方式,一次性读取所有的,并且存储数据类型为str def read_poetry(): # 1.打开文件 file = open("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/07_递归及文件处理/poetry.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") # 2.读取文件 if file.readable(): # 判断文件是否可读 content = file.read() print(content) print("数据类型:",type(content)) # 3.关闭文件 file.close() read_poetry()

# 文件的读取操作 # 2.第二种readline()读取方式,只能读取一行数据,并且存储数据类型为str def read_poetry_2(): # 1.打开文件 file = open("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/07_递归及文件处理/poetry.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") # 2.读取文件 if file.readable(): # 判断文件是否可读 content = file.readline() # 这一步是为了将,每一行古诗后面的换行去掉 content = content[:-1] while content != "": print(content) print("数据类型:",type(content)) content = file.readline() content = content[:-1] # 3.关闭文件 file.close() read_poetry_2()

# 文件的读取操作 # 3.第三种readlines(),一下读取所有的行,并且存储数据类型为list列表 def read_poetry_3(): # 1.打开文件 file = open("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/07_递归及文件处理/poetry.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") # 2.读取文件 if file.readable(): # 判断文件是否可读 content = file.readlines() print(content) print("数据类型:",type(content)) # 3.关闭文件 file.close() read_poetry_3()

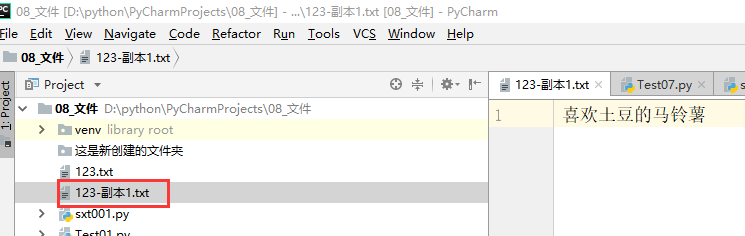
实例3
复制目标文件123.txt,在当前文件目录下创建一个副本123-副本.txt
""" 切片 字符串[start:end:step] 切片操作: 包括start,不包括end """ # 复制目标文件,文件为srcFile(表示文件的完整路径/绝对路径) # D:/python/PyCharmProjects/08_文件/123.txt def copy_file(srcFile): # 1.打开目标文件 file = open(srcFile,"r",encoding="utf-8") # 2.读取文件内容 content = file.read() # 3.写入新文件 # 创建新的文件,并对名字进行处理:原文件名-副本.txt # 3_1 在文件名中,从右往左找到"/"的位置,并提取"123.txt index = srcFile.rindex("/") file_name = srcFile[index+1::] # 3_2 在file_name中,从右往左找到"."的位置,并分离出"123"和".txt" index_1 = file_name.index(".") name_1 = file_name[0:index_1] name_2 = file_name[index_1::] # 新的文件名字 new_file_name = name_1 + "-副本" + name_2 new_file_path = srcFile[:index+1] + new_file_name new_file = open(new_file_path,"w",encoding="utf-8") # 将读取到的内容,写入到新文件中 new_file.write(content) # 4.关闭文件 file.close() new_file.close() copy_file("D:/python/PyCharmProjects/08_文件/123.txt")