【持续更新】 | OpenCV 学习笔记
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/QingHuan/p/7365732.html,转载请注明出处
###############################################################################
OpenCV的入门书籍有很多,这里选择的是《OpenCV 3计算机视觉-Python语言实现-第二版》
所有书上的源代码:https://github.com/techfort/pycv
安装过程请查看我的另一篇博客:
http://www.cnblogs.com/QingHuan/p/7354074.html
###############################################################################
第2章 处理文件、摄像头和图形用户界面
2.1 基本I/O脚本
2.1.5 捕获摄像头的帧
下面的代码实现了捕获摄像头10秒的视频信息,并将其写入一个AVI文件中
1 import cv2 2 3 cameraCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(0) 4 fps = 30 5 size = (int(cameraCapture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), 6 int(cameraCapture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))) 7 videoWriter = cv2.VideoWriter( 8 'MyOutputVid.avi', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('I', '4', '2', '0'), 9 fps, size) 10 11 success, frame = cameraCapture.read() 12 numFrameRemaining = 10*fps - 1 13 while success and numFrameRemaining > 0: 14 videoWriter.write(frame) 15 success, frame = cameraCapture.read() 16 numFrameRemaining -= 1 17 18 cameraCapture.release()
2.1.6 在窗口显示图像
一般情况下使用imshow()来显示图片,图片会闪一下然后消失,下面代码可以是图片一直显示
1 import cv2 2 import numpy 3 4 img = cv2.imread("data/aero1.jpg") 5 cv2.imshow('Test Image', img) 6 cv2.waitKey() 7 cv2.destroyAllWindows()
虽然左上角没有关闭按钮,但是随便按一个按键,都会将其关闭
2.1.7 实时显示摄像头的内容
1 import cv2 2 import numpy 3 4 clicked = False 5 def onMouse(event, x, y, flags, param): 6 global clicked 7 if event == cv2.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON: 8 clicked = True 9 10 cameraCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(0) 11 cv2.namedWindow('MyWindow') 12 cv2.setMouseCallback('MyWindow', onMouse) 13 14 print 'Show camera feed. Click window or press any key to stop' 15 16 success, frame = cameraCapture.read() 17 while success and cv2.waitKey(1) == -1 and not clicked: 18 cv2.imshow('MyWindow', frame) 19 success, frame = cameraCapture.read() 20 21 cv2.destroyWindow('MyWindow') 22 cameraCapture.release()
setMouseCallback可以获取鼠标的输入
namedWindow()用来创建窗口
imshow()用来显示窗口
destroyWindow()用来销毁窗口
cameraCapture.release()用来释放摄像头
cv2.waitKey(1) == -1 :
参数为等待键盘触发的时间,返回值-1表示没有按键被按下
OpenCV不能处理窗口,当单击窗口的关闭按钮时,并不能将其关闭
2.3 一个小程序—— Cameo——面向对象的设计
2.3.1 使用 managers.CaptureManager 提取视频流
这里中文版讲的不太通顺,建议看看英文原版

# CaptureManager 高级I/O流接口 import cv2 import numpy import time # 初始化CaptureManager类 class CaptureManager(object): def __init__(self, capture, previewWindowManager = None, shouldMirrorPreview = False): # 更新:前面有下划线的是非公有变量,主要与当前帧的状态与文件写入操作有关 # self 类似于结构体,里面有很多变量,下面是在初始化这些变量 # 类比于C++ 中学的"类"来比较 self.previewWindowManager = previewWindowManager self.shouldMirrorPreview = shouldMirrorPreview self._capture = capture self._channel = 0 self._enteredFrame = False self._frame = None self._imageFilename = None self._videoFilename = None self._videoEncoding = None self._videoWriter = None self._startTime = None self._frameElapsed = long(0) self._fpsEstimate = None # @ 符号的解释参见:http://gohom.win/2015/10/25/pyDecorator/ @property def channel(self): return self._channel @channel.setter def channel(self, value): if self._channel != value self._channel = value self._frame = None @property def frame(self): if self._enteredFrame and self._frame is None: _, self._frame = self._capture.retrieve() return self._frame @property def isWritingImage (self): return self._imageFilename is not None @property def isWrtingVideo(self): return self._videoFilename is not None def enterFrame(self): """Capture the next frame, if any"""
暂停在书Page 30
代码暂时写到这里,因为这里根本不认真讲原理,就是简单的堆砌代码,
感觉学习不到知识,所以就不看了,跳到下一章
第3章 使用OpenCV 3 处理图像
3.2 傅立叶变换
下面是一个高通滤波器和低通滤波器的例子:注意看注释,写的很详细
import cv2 import numpy as np from scipy import ndimage # kernel defined by ourself kernel_3x3 = np.array([[-1, -1, -1], [-1, 8, -1], [-1, -1, -1]]) kernel_5x5 = np.array([[-1, -1, -1, -1, -1], [-1, 1, 2, 1, -1], [-1, 2, 4, 2, -1], [-1, 1, 2, 1, -1], [-1, -1, -1, -1, -1]]) # http://docs.opencv.org/3.1.0/d4/da8/group__imgcodecs.html # in func "imread", 0 means trans to gray image img = cv2.imread("data/lena.jpg", 0) k3 = ndimage.convolve(img, kernel_3x3) k5 = ndimage.convolve(img, kernel_5x5) """Gaussian kernel: The function convolves the source image with the specified Gaussian kernel. GaussianBlur(src, ksize, sigmaX[, dst[, sigmaY[, borderType]]]) -> dst @param ksize Gaussian kernel size. ksize.width and ksize.height can differ but they both must be . positive and odd. Or, they can be zero's and then they are computed from sigma. @param sigmaX Gaussian kernel standard deviation in X direction.""" # here is a per-defined Gaussian Blur and the # kernel is set to 11x11, start in X axis direction # Attention: GaussianBlur is a low pass filter but the above two are high pass filters # after minus with the origin image, finally equivalent to a high pass filter blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (11, 11), 0) g_hpf = img - blurred cv2.imshow("3x3", k3) cv2.imshow("5x5", k5) cv2.imshow("g_hpf", g_hpf) cv2.waitKey() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
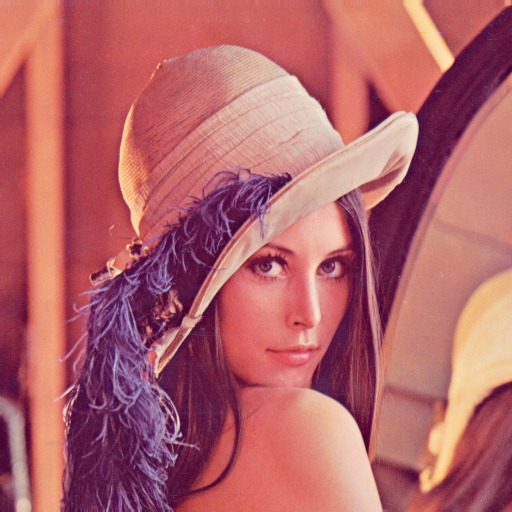
可以看一下处理效果:
原图:

高通滤波器:
3x3 kernel:

5x5 kernel:
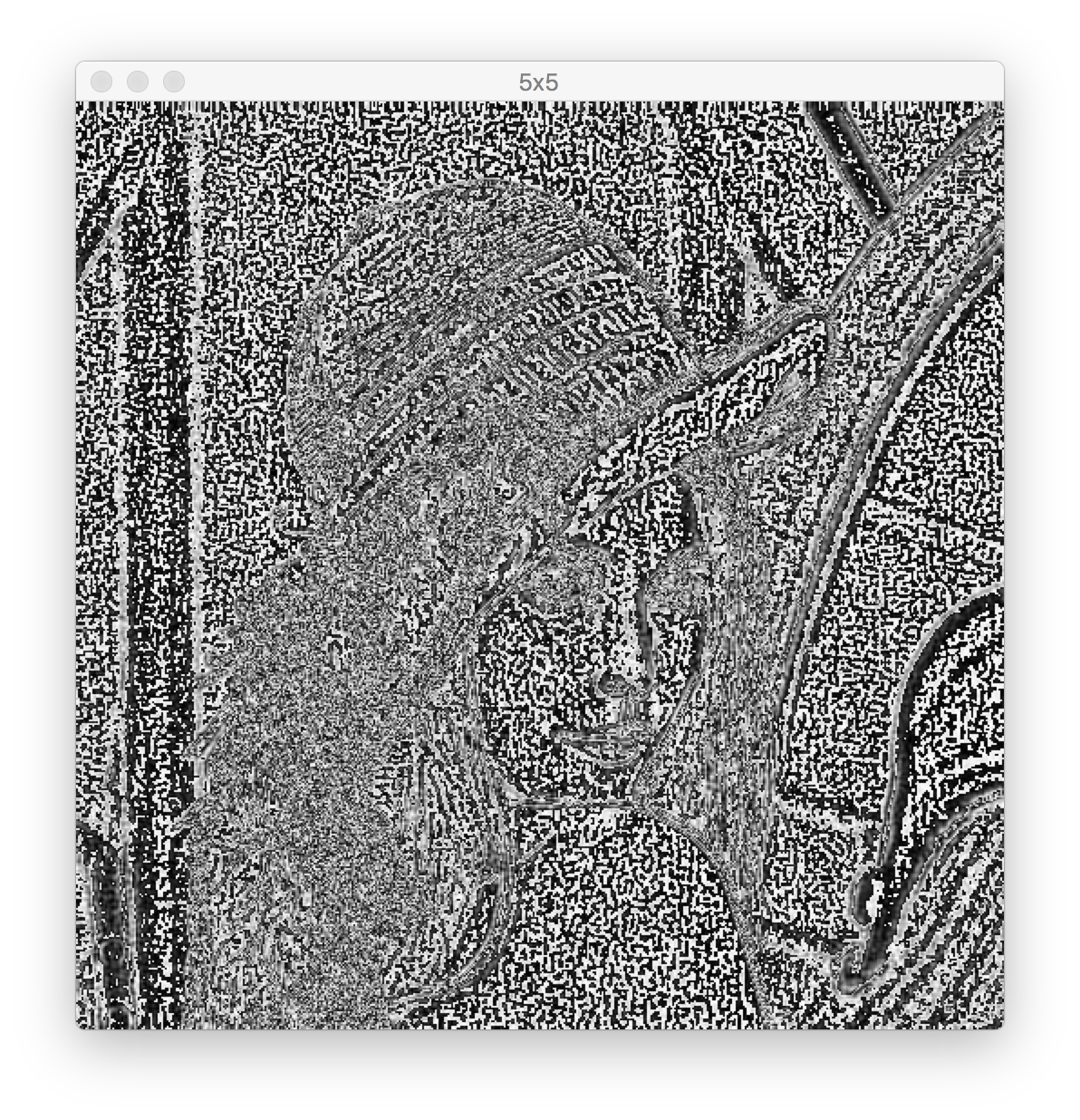

用低通滤波器处理后的图片,与原图相减,得到高通滤波器的效果:(原理待查)

可以发现第三张图的效果最好
中间都跳过去了,书上讲的不好,所以只是大概看了一遍没有敲代码
读完这本书一定要换一本再补充一下
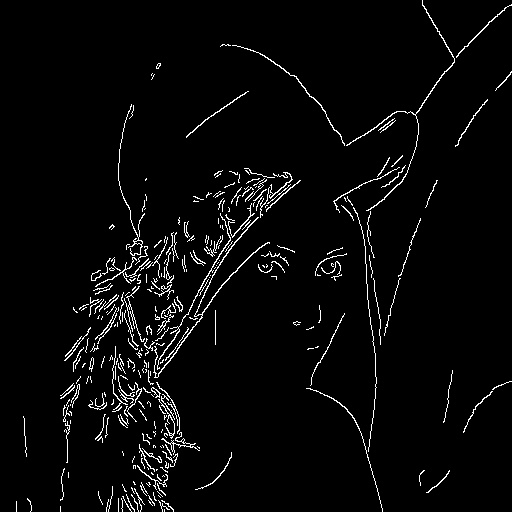
3.7 Canny 边缘检测
Canny函数可以非常方便的识别出边缘,
例子如下:
import cv2 import numpy as np import filters from scipy import ndimage img = cv2.imread("data/lena.jpg", 0) cv2.imwrite("lena_edge.jpg", cv2.Canny(img, 200, 300)) cv2.imshow("lena", cv2.imread("lena_edge.jpg")) cv2.waitKey() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
lena_edge.jpg:

3.8 简单的轮廓检测
首先创建了一个黑色图像,然后在中间放了一个白色方块。然后对方块寻找轮廓并把轮廓标注出来
(其实没有看懂代码)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -* import cv2 import numpy as np import filters from scipy import ndimage # dark, blank image img = np.zeros((200, 200), dtype=np.uint8) # assign the middle square white img[50:150, 50:150] = 255 # 二值化 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, 0) image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) color = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) img = cv2.drawContours(color, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.imshow("contours", color) cv2.waitKey() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果:

3.9 找到一个图形的边界框、最小矩形区域和最小闭圆的轮廓
# -*- coding: utf-8 -* import cv2 import numpy as np img = cv2.pyrDown(cv2.imread("pycv-master/chapter3/hammer.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)) ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(cv2.cvtColor(img.copy(), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) , 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) image, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) for c in contours: # find bounding box coordinates x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 画一个正方形 cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2) # 画最贴近的正方形,有一定的旋转 # find minimum area rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c) # calculate coordinates of the minimum area rectangle box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) # normalize coordinates to integers box = np.int0(box) # draw contours cv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0,0, 255), 3) # 画一个圆正好包裹住 # calculate center and radius of minimum enclosing circle (x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c) # cast to integers center = (int(x),int(y)) radius = int(radius) # draw the circle img = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0,255,0),2) cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 1) cv2.imshow("contours", img) cv2.waitKey() cv2.destroyAllWindows() cv2.imwrite("hammer_contours.jpg", img)
结果:





