1.4 浅谈Spring-Spring AOP的谎言
前言
最近又开始看源码了,虽然Spring AOP早就看过了,但是有的时候还是记得不熟,虽然Spring AOP已经被人分析了千万遍了,但仍然无法逃出我的魔爪...
这里我个人觉得有一个有歧义的点,这就像标题的那样,Spring AOP的谎言——AOP其实是一套解决方案,意思就是说它只是一个概念上的东西。实际在Spring处理的过程中,关于Spring对AOP的处理其实
就是DI(依赖注入),所以从现象上升到本质,此篇文章就是在探讨AOP的作用和依赖注入时Spring如何识别被AOP标记的Bean。
Spring AOP
什么是AOP?
我们通常叫它面向切面编程。但是似乎这种说法太官方了,不太容易理解。
我们可以这样来解释它,在我们开发的过程中,总有一些与我们主业务逻辑关系不大的代码会散落在代码中的各个地方,难以维护。
AOP就是把这些横切性问题与主业务分离,统一进行管理。从而起到解耦的目的
Spring AOP基本使用
AOP的增强类型
AOP的增强类型其实就是我们配置xml文件时的 advice,不知道为什么叫AOP增强(大多数人认可的方式)
我个人理解为 AOP建议我们使用的地方,分为以下5种
前置增强 (org.springframework.aop.BeforeAdvice) 表示在目标方法执行前来实施增强(用在目标方法执行之前)
后置增强 (org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice) 表示在目标方法执行后来实施增强(用在目标方法执行之后)
环绕增强 (org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor) 表示在目标方法执行前后同时实施增强(用在目标方法执行之中)
异常抛出增强 (org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice) 表示在目标方法抛出异常后来实施增强(用在目标方法抛出异常)
引介增强 (org.springframework.aop.introductioninterceptor) 表示在目标类中添加一些新的方法和属性
AOP的用途
Spring AOP的用途有很多,最常用的应该就是记录 日志了。上面我们说到了Spring aop会把横切性问题与主业务分离,统一进行管理。
那么这么横切性问题即会出先在业务之前,又会出现在业务之后,甚至存在于整个业务之中。所以,它有什么用,我们大可发挥自己的想象空间。如:做权限管理
在用户执行主业务(登录)之前,先做认证授权操作。做缓存,在执行业务之前(查询数据库),先去nosql里面查。还有很多用法,只不过
看我们怎么用罢了。
使用范例
这里,我们就简单的演示一下aop的作用,就记录一下目标方法执行时间
1.引入AOP的dependency
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency>
2.创建UserService
package com.example.originaltest.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @Auther: Anthony * @Date: 2019/5/6 18:21 * @Description: */ public interface UserService { void login(); }
3.创建具体实现
package com.example.originaltest.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @Auther: Anthony * @Date: 2019/5/6 18:21 * @Description: */ @Service("userService") public class UserServiceImpl{ public void login() { System.out.println("UserServiceImpl login"); } }
4.创建AOP切面
package com.example.originaltest.springaop; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class UserAspect { @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.originaltest.service.*.*(..))") private void pointcut(){ } @Around("com.example.originaltest.springaop.UserAspect.pointcut()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object process = null; try{ process = joinPoint.proceed(); }catch (Throwable throwable) { throwable.printStackTrace(); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("消耗时间:"+(end-current)); return process; } @Before("com.example.originaltest.springaop.UserAspect.pointcut()") public void before(){ System.out.println("before"); } @After("com.example.originaltest.springaop.UserAspect.pointcut()") public void after(){ System.out.println("After"); } }
这里有几个概念,需要提一下:
1.@Aspect:切面 其实就是前面说的与主业务无关的部分,这些部分的整体就是一个切面。也有这样理解,这些与主业务无关的代码被剥离了出来,自成体系,形成切面
2.@Pointcut:切入点 可以理解为从哪些业务里被剥离出来,既然是从那些业务里被剥离出来的,自然也作用于那些业务。可以认为是作用的地方
3.@Around,@Before,@After: 这些就是前面说的增强,也即作用在目标方法的什么位置。这里还有几个增强没有展示。
5.创建启动类
package com.example.originaltest; import com.example.originaltest.service.UserService; import com.example.originaltest.service.UserServiceImpl; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; /** * @Auther: Anthony * @Date: 2019/5/6 18:22 * @Description: */ @EnableAspectJAutoProxy @ComponentScan("com.example.originaltest.*") public class SpringAnnotationApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringAnnotationApplication.class); UserService userService = (UserService) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("userService"); // UserServiceImpl userService = (UserServiceImpl) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("userService"); userService.login(); } }
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 这里是自动代理注解,可以理解为开启AOP功能,这里注释了一段代码,先埋个伏笔。
6.执行结果

AOP的几个增强都发挥了作用。
源码分析
在分析过程中,能截图我就截图,截图不了的我就以代码代替。
1.IOC容器的初始化,这在之前IOC那篇文章里已经提到过.具体就不细讲了。

2.来看一下refresh方法
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // 实例化所有非延迟的单例bean. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
3.进入标红的方法 finishBeanFactoryInitialization
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Initialize conversion service for this context. if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } // Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor // (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before: // at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values. if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal)); } // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
在该方法中,是对bean工厂的初始化,标红的方法 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons() 是对单例bean的初始化
4.进入标红方法 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()
@Override public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); } // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean; boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName); } } } else { getBean(beanName); } } }
这里beanName获取到的就是IOC容器中所有的BeanDefinition的name,isFactoryBean来判断是否是工厂bean,本次例子是单例,故只用看else处的getBean方法
5.标红方法getBean(beanName)
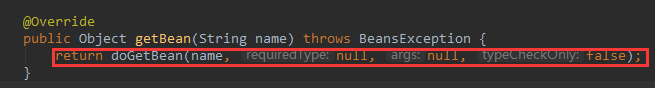
进入 AbstractBeanFactory 的getBean方法。
6.进入标红方法@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean; // 从缓存中取出bean,beanName就是我们的'userService',这里相当于第一次创建,缓存里不会有内容,所以sharedInstance = null Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) { return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean( nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly); } else if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else if (requiredType != null) { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } else { return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup); } } //这里的typeCheckOnly就是getBean传过来的 false,markBeanAsCreated方法是开始创建bean的标志 if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } try { final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // 当前bean的依赖会保存在dependsOn数组中 String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dep : dependsOn) { if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); } registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); try { getBean(dep); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex); } } } // 创建bean实例 if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//使用拉姆达表达式来创建bean sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } }
这里的 markBeanAsCreated 是将当前的beanName添加到一个map中,该map里都是已经创建的bean,添加完成之后就开始创建的逻辑
再看拉姆达表达式的那一块儿的 getSingleton方法
7.getSingleton
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
//从singletonObjects中获取, Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) { throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName, "Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " + "(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)"); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } beforeSingletonCreation(beanName); boolean newSingleton = false; boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null); if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>(); } try { singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); newSingleton = true; } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { // Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime -> // if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state. singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { throw ex; } } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) { ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException); } } throw ex; } finally { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = null; } afterSingletonCreation(beanName); } if (newSingleton) { addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject); } } return singletonObject; } }
看着里标红的几个地方 newSingleton一开始为false,bean创建完成后置为true,然后在finally方法里,根据newSingleton将beanName添加到单例缓存中。
最后就是看看他是如何创建这个单例的了,就是 singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();这里会回到6中标蓝色的方法里。createBean(beanName, mbd, args)
我们来看这个方法
8.createBean(beanName, mbd, args)
@Override protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); } RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd; // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and // clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class // which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition. Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) { mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd); mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass); } // Prepare method overrides. try { mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides(); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex); } try { // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); if (bean != null) { return bean; } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex); } try { Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); } return beanInstance; } catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) { // A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already, // or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry. throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex); } }
真正执行创建的doCreateBean方法
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance(); Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass(); if (beanType != NullBean.class) { mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; } // 允许后处理器修改合并的bean定义. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
这里要提一下beanWrapper 这个类是bean的包裹接口,它有具体的实现,主要是给bean去注入属性的。
这里我们重点关注两个方法
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //使用属性值填充给定BeanWrapper中的bean实例 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
我们依次来看这两个方法
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
//这里判断注入bean的方式,当然我们是通过注解来注入的,显然这两种方式都不是
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
//因为我们是注解的方式,所以会有后置处理器
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
//通过后置处理器来装配一些属性
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
//装配属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
然后就是
initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
这里我们看一下 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization 这是在初始化之后应用后置处理器的操作
@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
我们需要关注的后置处理器为:

执行 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
wrapIfNecessary 方法:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // 如果有advice就创建Proxy Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法
@Override @Nullable protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
找到所有符合条件的自动代理advice,如果存在就返回一个数组,不存在就返回 DO_NOT_PROXY

往回看 wrapIfNecessary 方法中,浅蓝色标记的部分,
如果返回的不是DO_NOT_PROXY(null),那么就创建一个代理返回这个代理
如果返回的是DO_NOT_PROXY(null)那么就直接返回这个bean。
是否返回DO_NOT_PROXY取决于是否配置了advice,也即是否配置了AOP,所以这里就跟一般的bean区分开了,
如果配置了aop的bean就会返回代理,没有配置AOP就会返回该bean
那现在我们需要讨论的只有两个问题
1.返回的到底是什么? 这个在上面标记的 findEligibleAdvisors 中
2.如果不是DO_NOT_PROXY,那么代理如何创建? 这个在 wrapIfNecessary 的 createProxy中
我们先看第一个
findEligibleAdvisors
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
findCandidateAdvisors 这里是找出所有的aop增强
@Override protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() { // 在当前容器中找符合条件的advisors List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors(); // 为beanFactory中所有的AspectJ切面创建advisors if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) { advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); } return advisors; }
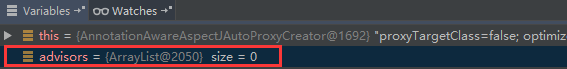
显然,这个切面的advice还没有创建,所以当前容器中没有
后面就是创建advisors buildAspectJAdvisors()
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() { List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null) { //... } if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String aspectName : aspectNames) { List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName); if (cachedAdvisors != null) { advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors); } else { MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName); advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)); } } return advisors; }
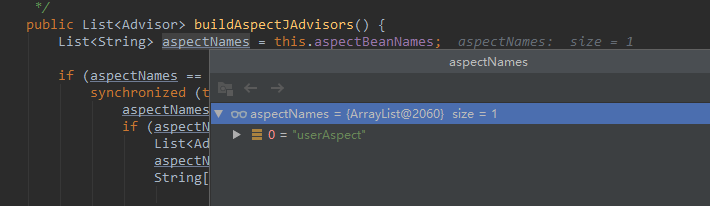
这里我们获取到的aspectName即是我们创建的切面 userAspect
看上面浅蓝色的部分
在advisorCache中取出所有的 Advisor
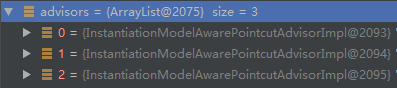

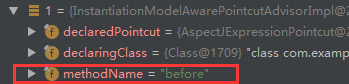
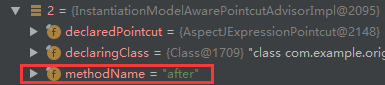
对应的就是我们取出的三个,findEligibleAdvisors 方法中的 extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors)
该方法会添加一个包含ExposeInvocationInterceptor的增强器到增强器列表头部。该拦截器将会是第一个被应用的,调用它时会将MethodInvocation放置到ThreadLocal结构中,供其他@Aspect注解对应的增强器使用。它的作用其实就是为了让通过@Aspect注解加入的增强器可以访问到MethodInvocation对象
接着上面说,既然增强器有了,那么就会创建一个代理
我们回到 wrapIfNecessary 方法 只看代理这部分
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { //...// Create proxy if we have advice. Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } }
直接跟到底
@Override public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
如果目标是接口,则用jdk动态代理创建,否则用Cglib来创建代理。


