软件篇-04-OMPL和FCL用于SLAM轨迹规划
使用OMPL内置的infoRRTstar算法模块和FCL碰撞检测库实现当前点和目标点的轨迹规划,
因为我们的SLAM底盘轨迹是二维的,这样说可能不太准确,你可以说它的轨迹在给定小的区域内是二维的,因为野外/室外的地面有坡度和沟壑,所以我们要做的是二维RRT。
有关RRT的论文维基百科已经列的很全了:
核心思想就是利用快速随机搜索树从当前点出发,迭代生出树枝,利用FCL检测树枝生长的方向是否有障碍物,有的话最后生成的路径将不会包括该路径,所以最后连接当前点和目标点的轨迹是collisionless的。至于轨迹是不是最优,infoRRTstar已经对传统RRT算法做了优化,轨迹规划的效果很大的取决于用户在API中对轨迹生成时间的限制,只要时间足够长,两点之间没有障碍物的话得出来的都是一条直线。这个“足够长的时间”具体是多长,又取决于设置的rrtRange步长和两点之间的距离,我们可以根据系统对实时性的要求具体设置。
-
效果图
下面的白色坐标系是我写的上位机里的二维俯视图,用的是qcustomplot,不错,推荐一下。点云是在真实环境中采的。
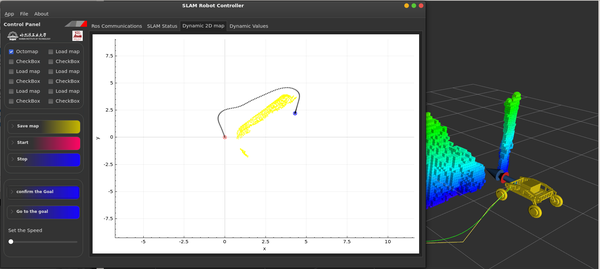
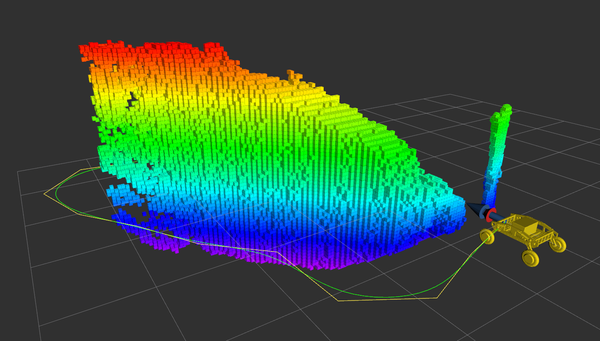
黄色点就是环境,红点为当前点,蓝色为目标点 RVIZ中的OctoMap
-
将pointcloud点云转化为OctoMap,用于碰撞检测
我这里加了个 "groundHeightMax" 是为了滤去地面的一部分点云,防止其影响轨迹规划,"carTF_zed2.pose.position.z"是涉及到相对位置。使用八叉树地图减小内存占用。
"std::shared_ptr" 智能指针是C++ 11的东西,如果编译出错的注意了。"tree_obj" 就是FCL检测是否碰撞的环境对象,另一个对象就是我们的SLAM底盘了。
// turn the pcl cloud to fcl::CollisionGeometry after octree // updtae the octomap octomap::OcTree* treeOctomapPtr = new octomap::OcTree( 0.05 );
for(auto p:pclCloud->points) {
if(p.z > groundHeightMax + carTF_zed2.pose.position.z) treeOctomapPtr->updateNode
( octomap::point3d(p.x, p.y, p.z), true );
}
treeOctomapPtr->updateInnerOccupancy();
fcl::OcTree<float>* tree = new fcl::OcTree<float>(std::shared_ptr<const octomap::OcTree>(treeOctomapPtr));
tree_obj = std::shared_ptr<fcl::CollisionGeometry<float>>(tree);
-
设置OMPL轨迹规划限制空间
"bounds_hmin" 和 "bounds_hmax"设置世界坐标系的高度范围,也应该是相对于底盘的高度空间。
// set the bounds for the R^3 part of SE(3)
ompl::base::RealVectorBounds bounds(3);
// set X-Y-Z dimensions bound
bounds.setLow(0,bounds_lmin);
bounds.setHigh(0,bounds_lmax);
bounds.setLow(1,bounds_wmin);
bounds.setHigh(1,bounds_wmax);
bounds.setLow(2,bounds_hmin);
bounds.setHigh(2,bounds_hmax);
-
使用FCL检测当前状态是否碰撞
bool Navigation::isStateValid(const ompl::base::State *state)
{
// cast the abstract state type to the type we expect const ompl::base::SE3StateSpace::StateType *se3state = state->as<ompl::base::SE3StateSpace::StateType>();
// extract the first component of the state and cast it to what we expect const ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *pos = se3state->as<ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>(0); // extract the second component of the state and cast it to what we expect const ompl::base::SO3StateSpace::StateType *rot = se3state->as<ompl::base::SO3StateSpace::StateType>(1); fcl::CollisionObject<float> treeObj((tree_obj)); fcl::CollisionObject<float> slamCarObject(slamCar); // check validity of state defined by pos & rot fcl::Vector3f translation(pos->values[0],pos->values[1],pos->values[2]); fcl::Quaternionf rotation(rot->w, rot->x, rot->y, rot->z); slamCarObject.setTransform(rotation, translation); fcl::CollisionRequest<float>requestType(1,false,1,false); fcl::CollisionResult<float> collisionResult; fcl::collide(&slamCarObject,&treeObj, requestType, collisionResult);return(!collisionResult.isCollision());} 在下面的代码将FCL和OMPL相联系,这里的 "std::placeholders::_1"是一个占位符。 si = ompl::base::SpaceInformationPtr(new ompl::base::SpaceInformation(space));
si->setStateValidityChecker(std::bind(&Navigation::isStateValid, this, std::placeholders::_1 ));
-
一切设置好后就可以开始计算路径了
这个"rrtSolutionTimeLimit" 就是我在上文中说到的时间限制。这里我另外加了个异常处理。
ompl::base::PlannerStatus solved;
try
{
solved = plan->solve(rrtSolutionTimeLimit);
}
catch(ompl::Exception e)
{
ROS_WARN("Error occourred: %s", e.what());
}
然后获取路径,这里的SE3和SO3分别是特殊欧式群和特殊正交群,说的直白一点在这里代表的就是齐次变换和旋转矩阵。下面的是优化的路径,优化后轨迹会更加平滑,当然点也会更多。
ompl::geometric::PathSimplifier* pathBSpline = new ompl::geometric::PathSimplifier(si);
path_smooth = new ompl::geometric::PathGeometric(dynamic_cast<const ompl::geometric::PathGeometric&>(*pdef->getSolutionPath()));
pathBSpline->smoothBSpline(*path_smooth,3);
// ROS_INFO("Smoothed Path:"); // path_smooth->print(std::cout); smooth_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); smooth_msg.header.frame_id = "map"; for (std::size_t idx = 0; idx < path_smooth->getStateCount (); idx++) { // cast the abstract state type to the type we expect const ompl::base::SE3StateSpace::StateType *se3state = path_smooth->getState(idx)->as<ompl::base::SE3StateSpace::StateType>(); // extract the first component of the state and cast it to what we expect const ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *pos = se3state->as<ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>(0); // extract the second component of the state and cast it to what we expect const ompl::base::SO3StateSpace::StateType *rot = se3state->as<ompl::base::SO3StateSpace::StateType>(1); geometry_msgs::PoseStamped point; point.pose.position.x = pos->values[0]; point.pose.position.y = pos->values[1]; point.pose.position.z = pos->values[2]; point.pose.orientation.x = rot->x; point.pose.orientation.y = rot->y; point.pose.orientation.z = rot->z; point.pose.orientation.w = rot->w; smooth_msg.poses.push_back(point);}








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?