.7-浅析express源码之Router模块(3)-app[METHODS]
之前的讨论都局限于use方法,所有方式的请求会被通过,这一节讨论express内部如何处理特殊请求方法。
给个流程图咯~
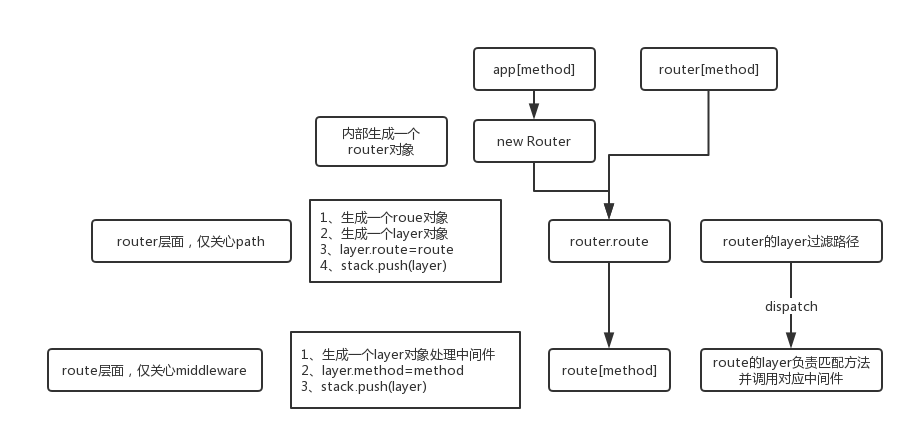
分别给出app.METHODS与router.METHODS:
// app.use methods.forEach(function(method) { // app.get、app.post... app[method] = function(path) { if (method === 'get' && arguments.length === 1) { // app.get(setting) return this.set(path); } // 这里过 this.lazyrouter(); // 生成一个route对象 var route = this._router.route(path); // 调用route的方法 route[method].apply(route, slice.call(arguments, 1)); return this; }; }); // router.use methods.concat('all').forEach(function(method) { proto[method] = function(path) { var route = this.route(path) route[method].apply(route, slice.call(arguments, 1)); return this; }; });
大体上都是一样的,唯一奇怪的是在app模块里,单独定义了app.all方法,虽然内容只是遍历METHODS数组调用对应的方法,但是这比起直接让route处理不是更优雅么(跟开发者提了这个问题,得到了答复,超开心!)……
router.route
上述的两个方法都先指向了router模块的route方法,源码如下:
proto.route = function route(path) { // new一个Route对象 var route = new Route(path); // new一个Layer对象 var layer = new Layer(path, { sensitive: this.caseSensitive, strict: this.strict, end: true }, route.dispatch.bind(route)); // 这种形式的Layer有route属性 layer.route = route; // 同样push到stack中 this.stack.push(layer); return route; };
这里接连生成了一个route对象与一个layer对象,由于只传进来了path,所以layer的中间件变成了一个route内置方法,暂时不管。
Route
这里看一眼route对象的构造函数:
function Route(path) { this.path = path; this.stack = []; debug('new %o', path) // 不同请求方式的方法集合 this.methods = {}; }
非常简单,头疼的是每个route也有一个stack。
在返回route实例后后,随即调用route对应的method,并传入中间件函数。
这里关于app[METHODS](function...)有一个问题,常规情况下app.use直接传函数相当于对所有路径都匹配该中间件,但是如果指定了请求方法后直接传函数,这个代码是无效的,虽然不会报错而且非常顺利的走完流程,但是最后返回一个无用的route对象,4月18号晚上给开发者又发了一封邮件询问这个问题,截止19号早上还没答复我。
route[method]
先不管这么多,总之先按正常流程走,route[method]源码如下:
methods.forEach(function(method) { Route.prototype[method] = function() { // 扁平化参数 var handles = flatten(slice.call(arguments)); // 遍历中间件 for (var i = 0; i < handles.length; i++) { var handle = handles[i]; // 竟然还有错误检测 if (typeof handle !== 'function') { var type = toString.call(handle); var msg = 'Route.' + method + '() requires a callback function but got a ' + type throw new Error(msg); } debug('%s %o', method, this.path); // 方法层级的Layer对象 对路径不关心 var layer = Layer('/', {}, handle); // 多的一个属性 layer.method = method; // 标记对象 this.methods[method] = true; // 这是route的stack this.stack.push(layer); } return this; }; });
这里的步骤需要稍做梳理:
1、app[method]/router[method]方法最终指向router的route方法
2、router.route会根据path生成一个route对象与一个Layer对象,将route作为一个属性挂载到layer上面,而layer对象会被push进router的stack数组
3、调用route对应的method方法,方法会遍历传入的中间件函数,每一个中间件生成一个无视路径的layer对象,并且layer有一个method属性,最后将layer对象push进route对象。
route.dispatch
总之流程大概梳理完了,接下来最后补充一下router对象上layer对象的handle函数:route.dispatch
Route.prototype.dispatch = function dispatch(req, res, done) { var idx = 0; var stack = this.stack; // 没有 if (stack.length === 0) { return done(); } // 获取请求的方法 var method = req.method.toLowerCase(); // 未注册head方式监听 head请求视为get if (method === 'head' && !this.methods['head']) { method = 'get'; } req.route = this; next(); function next(err) { if (err && err === 'route') return done(); if (err && err === 'router') return done(err); // 取出对应的中间件 var layer = stack[idx++]; if (!layer) return done(err); if (layer.method && layer.method !== method) return next(err); if (err) { layer.handle_error(err, req, res, next); } else { // 真正的处理方法 layer.handle_request(req, res, next); } } };
源码中的stack为layer数组,当有请求时,每次都会从中取出一个,然后匹配请求方式与layer.method是否一致,最后调用中间件处理请求。
完事~



