.13-浅析webpack源码之WatcherManager模块
从模块流可以看出,这个NodeWatchFileSystem模块非常深,这里暂时不会深入到chokidar模块,有点太偏离本系列文章了,从WatcherManager开始讲解。
流程如图:
源码非常简单,包括一个工厂函数与两个原型方法,整理如下:
var path = require("path"); class WatcherManager { constructor() { // 监视容器 this.directoryWatchers = {}; }; getDirectoryWatcher(directory, options) { var DirectoryWatcher = require("./DirectoryWatcher"); options = options || {}; // 目录路径拼接参数 这个有够厉害的 // 假设directory为lib options不传 拼接后为'lib {}' var key = directory + " " + JSON.stringify(options); if (!this.directoryWatchers[key]) { // 根据监视路径生成一个DirectoryWatcher实例 this.directoryWatchers[key] = new DirectoryWatcher(directory, options); // 监听监视关闭事件 this.directoryWatchers[key].on("closed", function() { delete this.directoryWatchers[key]; }.bind(this)); } // 返回对应的实体类 return this.directoryWatchers[key]; }; // 路径 参数 开始事件 watchFile(p, options, startTime) { // 返回目录名作为根目录 // lib/newFile.js => lib var directory = path.dirname(p); // 生成实例并调用watch方法 // 由于上面返回的是实体类 这里可以进行链式调用 return this.getDirectoryWatcher(directory, options).watch(p, startTime); }; watchDirectory(directory, options, startTime) { return this.getDirectoryWatcher(directory, options).watch(directory, startTime); }; } module.exports = new WatcherManager();
包含一个容器类和三个实例方法,每一次调用watchFile或watchDirectory方法时会在容器中添加一个目录监视信息,在关闭监视事会删除对应的信息。
主流方法还是引用的DirectoryWatcher模块,从构造函数开始详细看源码:
function DirectoryWatcher(directoryPath, options) { // 继承EventEmitter EventEmitter.call(this); // 获取配置 this.options = options; // 根目录 this.path = directoryPath; // 根目录下的文件信息 this.files = Object.create(null); // 根目录下的文件夹信息 this.directories = Object.create(null); // 目录下的文件所有监听器容器 this.watchers = Object.create(null); // 初始化监视器 跳过 this.watcher = chokidar.watch(directoryPath, { /*options*/ }); // 事件监听 this.watcher.on("add", this.onFileAdded.bind(this)); this.watcher.on("addDir", this.onDirectoryAdded.bind(this)); this.watcher.on("change", this.onChange.bind(this)); this.watcher.on("unlink", this.onFileUnlinked.bind(this)); this.watcher.on("unlinkDir", this.onDirectoryUnlinked.bind(this)); this.watcher.on("error", this.onWatcherError.bind(this)); // 初次扫描标记 this.initialScan = true; // 对整个文件夹进行监视 仅在传入监视路径为文件夹时置true this.nestedWatching = false; this.initialScanRemoved = []; // 初始化扫描 this.doInitialScan(); // 记录watchers中监听器数量 this.refs = 0; }
这里可以分为几块内容:
1、继承nodejs的事件模块
2、获取传进来的路径与配置参数
3、根据参数初始化一个watcher对象,并对文件操作做事件监听
4、初始化扫描
watcher对象的生成过程暂时不考虑,太深入会偏离主线任务。
初始化扫描
在构造函数中会对传进来的路径进行扫描,源码如下:
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.doInitialScan = function doInitialScan() { // 读取根目录 fs.readdir(this.path, function(err, items) { // 即使报错仍然置initialScan标记为false if (err) { this.initialScan = false; return; } // items为到根目录下所有文件的文件名组成的数组 // 同时包含文件与文件夹 async.forEach(items, function(item, callback) { // 将路径与文件名进行拼接获取完整路径 var itemPath = path.join(this.path, item); // 获取文件信息 fs.stat(itemPath, function(err2, stat) { // 该方法仅支持初次扫描 if (!this.initialScan) return; if (err2) { callback(); return; } // 处理文件 if (stat.isFile()) { if (!this.files[itemPath]) this.setFileTime(itemPath, +stat.mtime, true); } // 处理文件夹 else if (stat.isDirectory()) { if (!this.directories[itemPath]) this.setDirectory(itemPath, true, true); } callback(); }.bind(this)); }.bind(this), function() { // 回调函数中处理标记initialScan标记 this.initialScan = false; this.initialScanRemoved = null; }.bind(this)); }.bind(this)); };
代码十分易懂,基本上都是fs模块的方法,主要分为以下几步:
1、读取指定根目录下所有文件
2、将文件名与当前路径进行拼接获取完整路径,然后尝试获取文件信息
3、分别处理文件与文件夹
这里的流程可以用一个案例测试,首先目录如图:
a.js是执行JS文件,lib是用来测试的文件夹,包含几个js文件和一个空文件夹。
测试代码如下:
// a.js const fs = require('fs'); const async = require('async'); const path = require('path'); // 读取文件夹 fs.readdir('./lib', (err, items) => { // 这里没有传路径 所以用process.cwd()模拟 // 这里需要拼接一下路径 const absPath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'lib'); // items => ['DirectoryWatcher.js','fileDirectory',...,'watchpack.js'] async.forEach(items, (item, callback) => { // 第一个元素拼接后为d:\workspace\doc\lib\DirectoryWatcher.js const itemPath = path.join(absPath, item); fs.stat(itemPath, (err2, stat) => { // 处理文件 if (stat.isFile()) { console.log('Find file,the name is: ' + item); } // 处理文件夹 else if (stat.isDirectory()) { console.log('Find directory,the name is: ' + item); } }); }); });
执行JS文件后输出如图:

可以看到,通过该方法可以区别开文件与文件夹,然后分类处理。
下面看两种处理方法。
setFileTime
// this.setFileTime(itemPath, +stat.mtime, true); // itemPath => 路径 // +stat.mtime => 修改时间 // 是否初始化 => true DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setFileTime = function setFileTime(filePath, mtime, initial, type) { // 获取当前时间 var now = Date.now(); var old = this.files[filePath]; // 初始化取文件修改时间与当前时间的较小值 // 否则files = {path:[now,mtime]} // 键为文件路径 值为数组 包含当前时间与上一次修改时间 this.files[filePath] = [initial ? Math.min(now, mtime) : now, mtime]; // 这里的FS_ACCURACY是假设操作可能的运行时间 // 尝试通过加一点点来更精确修改时间 if (mtime) mtime = mtime + FS_ACCURACY; if (!old) { if (mtime) { if (this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)]) { /**/ } } } else if (!initial && mtime && type !== "add") { /**/ } else if (!initial && !mtime) { /**/ } // 初始化不会有watchers if (this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { /**/ } };
从名字也能看出这个方法的作用就是设置时间,在初始化的情况下,会在files容器中注册,键为文件路径,值为当前时间与修改时间。
由于watchers对象此时为null,所以后面的代码并不会进入,后面再讨论。
setDirectory
// this.setDirectory(itemPath, true, true); DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setDirectory = function setDirectory(directoryPath, exist, initial, type) { if (directoryPath === this.path) { if (!initial && this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { /**/ } } else { var old = this.directories[directoryPath]; // 初次扫描 if (!old) { if (exist) { // 默认为false if (this.nestedWatching) { this.createNestedWatcher(directoryPath); } else { // 根目录在监听器容器中的值默认设置为true this.directories[directoryPath] = true; } if (!initial && this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { /**/ } } } else { /**/ } } };
在初始化的扫描中,根目录下所有的文件夹也会在对应的容器中注册一个键,值为true。
其余代码在初始化并不会执行,后面再讲。
在经过doInitialScan初始化之后,files、directories容器会被填充进对应的键值对,存储文件与文件夹的路径信息。
watch
无论是watchFile还是watchDirectory都在初始化后直接调用了watch方法对具体文件进行了监视,这里分析该处源码:
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.watch = function watch(filePath, startTime) { // 将路径小写 // 第一次监视指定路径会初始化一个空数组 this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)] = this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)] || []; // 记数 this.refs++; // 生成一个内部辅助类 var watcher = new Watcher(this, filePath, startTime); // 监听closed事件 watcher.on("closed", function() { // 删除对应的watcher var idx = this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].indexOf(watcher); this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].splice(idx, 1); // 当对应watcher数组为空时直接删除该键 if (this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].length === 0) { delete this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)]; // 如果触发了文件夹的closed事件 关闭文件夹的监视 if (this.path === filePath) this.setNestedWatching(false); } // 当watchers为空时调用类的close方法 if (--this.refs <= 0) this.close(); }.bind(this)); // 加进去 this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].push(watcher); var data; // 当监视文件路径为一个文件夹时 // 文件夹的修改时间应该为内部文件中修改时间最新的 if (filePath === this.path) { this.setNestedWatching(true); data = false; // 取出所有文件的时间信息中最新的 Object.keys(this.files).forEach(function(file) { var d = this.files[file]; if (!data) data = d; else data = [Math.max(data[0], d[0]), Math.max(data[1], d[1])]; }, this); } // 取对应文件信息 else { data = this.files[filePath]; } // node中的异步函数 process.nextTick(function() { if (data) { // 相等说明是初始化阶段 修正时间 var ts = data[0] === data[1] ? data[0] + FS_ACCURACY : data[0]; if (ts >= startTime) watcher.emit("change", data[1]); } // 监视的文件路径之前被移除过 else if (this.initialScan && this.initialScanRemoved.indexOf(filePath) >= 0) { watcher.emit("remove"); } }.bind(this)); return watcher; }; class Watcher { constructor() { EventEmitter.call(this); this.directoryWatcher = directoryWatcher; this.path = filePath; this.startTime = startTime && +startTime; this.data = 0; }; // 也不知道检测啥的 checkStartTime(mtime, initial) { if (typeof this.startTime !== "number") return !initial; var startTime = this.startTime; return startTime <= mtime; }; // 此方法触发closed事件 close() { this.emit("closed"); }; }
内部的Watcher对象负责对应路径文件的操作事件响应。
watch有两种情形,一种是普通的文件监视,一种是对文件夹的监视。
如果是普通的文件监视,直接生成一个Watcher监听器,然后将该监听器加入已有目录监视容器对应的watchers容器中。
如果是传入的是文件夹,会对根目录下所有的文件夹再次调用watchDirectory收集目录信息,代码如下:
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setNestedWatching = function(flag) { if (this.nestedWatching !== !!flag) { this.nestedWatching = !!flag; if (this.nestedWatching) { Object.keys(this.directories).forEach(function(directory) { // 对根目录下所有文件夹路径调用该方法 this.createNestedWatcher(directory); }, this); } else { // 关闭文件夹监视 Object.keys(this.directories).forEach(function(directory) { this.directories[directory].close(); this.directories[directory] = true; }, this); } } }; DirectoryWatcher.prototype.createNestedWatcher = function(directoryPath) { // 文件夹信息容器的值设为一个DirectoryWatcher实例 // startTime设为1 this.directories[directoryPath] = watcherManager.watchDirectory(directoryPath, this.options, 1); // 实例监听change事件 this.directories[directoryPath].on("change", function(filePath, mtime, type) { // 文件夹改变时触发对应的监听器 if (this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)].forEach(function(w) { if (w.checkStartTime(mtime, false)) { w.emit("change", filePath, mtime, type); } }); } }.bind(this)); };
fs.watch
下面开始讲解文件操时作触发的事件处理,其中包括文件与文件夹的操作。
先简要介绍下nodejs原生的watch系统,官方文档:https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v8.x/docs/api/fs.html#fs_fs_watch_filename_options_listener。
通过引入nodejs中的fs模块,通过调用fs.watch方法可以对文件进行监视,具体的api如下:
const fs = reqire('fs');
fs.watch(filename /*文件名*/ , options /*配置参数 可忽略*/ , listener /*监听器*/ )
这里的filename可以是文件,也可以是一个目录。
options有三个可选参数:
persistent:文件如果在被监视,进程是否应该继续进行,默认为true
recursive:是否监视所有子目录,默认为false
encoding:指定传给监听器文件名的字符编码,默认为'uft-8'
监听器则是一个函数,有两个参数,分别为事件类型与对应的文件名。
这里用了小案例来进行演示,代码如下:
const fs = require('fs');
fs.watch('./lib', ((event, filename) => {
console.log('event type is: ' + event);
console.log('the relative filename is: ' + filename);
}));
目录结构可参考上图,执行node指令后终端会被挂起,等待变化。
此时新建一个文件,如图:
在新建成功的时候,会发现监听器被触发,打印信息如图: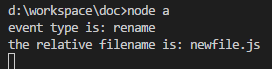
修改文件内容,打印信息如图:
根据官方文档,事件只有rename与change两种,无论是添加、删除、重命名都会触发rename事件,而修改文件内容会触发change事件。
所以很明显,框架内部对事件类型进行了细粒度更大的划分,将rename分解为增加文件/文件夹,删除文件/文件夹四种情况。
实现的原理根据上面的代码也很容易想到,可以根据文件名与files、directories容器中的键做比对,区分文件与文件夹,根据修改时间,区分是新建还是删除。
下面可以看构造函数中对特殊文件操作的监听器。
add
// 增加文件时触发的事件 this.watcher.on("add", this.onFileAdded.bind(this)); DirectoryWatcher.prototype.onFileAdded = function onFileAdded(filePath, stat) { // filePath => 文件路径 // stat => fs.stat(...) // 检测文件是否在监视目录中 if (filePath.indexOf(this.path) !== 0) return; if (/[\\\/]/.test(filePath.substr(this.path.length + 1))) return; // 设置文件修改时间信息 this.setFileTime(filePath, +stat.mtime, false, "add"); };
可以看出,进行简单的文件合法性检测后,还是进入了setFileTime函数,不过这一次的init标记为false,并且有对应的eventType。
这一次setFileTime的流程如下:
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setFileTime = function setFileTime(filePath, mtime, initial, type) { var now = Date.now(); // 初始化的值会被获取 var old = this.files[filePath]; // initial是false 所以值为[now,mtime] this.files[filePath] = [initial ? Math.min(now, mtime) : now, mtime]; // ... };
一句话概括就是,add情况下,只会在files容器中注册该文件的信息。
addDir => 在directories容器中注册该文件夹
change
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.onChange = function onChange(filePath, stat) { // ... // 会根据mtime值修改FS_ACCURACY ensureFsAccuracy(mtime); // 仍然进入此函数 this.setFileTime(filePath, mtime, false, "change"); }; function ensureFsAccuracy(mtime) { if (!mtime) return; // 当mtime为小数时才会跳过 if (FS_ACCURACY > 1 && mtime % 1 !== 0) FS_ACCURACY = 1; // 0-9或非10的倍数 else if (FS_ACCURACY > 10 && mtime % 10 !== 0) FS_ACCURACY = 10; // 0-99或非100倍数 else if (FS_ACCURACY > 100 && mtime % 100 !== 0) FS_ACCURACY = 100; else if (FS_ACCURACY > 1000 && mtime % 1000 !== 0) FS_ACCURACY = 1000; else if (FS_ACCURACY > 2000 && mtime % 2000 !== 0) FS_ACCURACY = 2000; } DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setFileTime = function setFileTime(filePath, mtime, initial, type) { // ... if (!old) { /*...*/ } // change else if (!initial && mtime && type !== "add") { if (this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)]) { this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].forEach(function(w) { w.emit("change", mtime, type); }); } } // remove else if (!initial && !mtime) { /*...*/ } // 如果监视了根目录 if (this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)].forEach(function(w) { // 根目录触发change事件 if (!initial || w.checkStartTime(mtime, initial)) { w.emit("change", filePath, mtime, initial ? "initial" : type); } }); } };
这里有一个ensureFsAccuracy函数,这里默认的FS_ACCURACY为10000,而mtime一般都是很大的整数,所以这个函数的作用有待研究。
可以看到change事件除了设置文件的时间信息,同时也对watchers中每个监听器触发了change事件。
最后,如果根目录设置了监视,由于监视文件在根目录中,所以根目录必定也发生了改变,所以根目录的所有监视器也会同时触发change事件。
unlink
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.onFileUnlinked = function onFileUnlinked(filePath) { // ... // 注意第二个参数mtime为null this.setFileTime(filePath, null, false, "unlink"); // 记录被删除的文件路径 if (this.initialScan) { this.initialScanRemoved.push(filePath); } }; DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setFileTime = function setFileTime(filePath, mtime, initial, type) { // ... if (!old) { /**/ } // 触发remove事件 else if (!initial && mtime && type !== "add") { if (this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)]) { this.watchers[withoutCase(filePath)].forEach(function(w) { w.emit("change", mtime, type); }); } } else if (!initial && !mtime) { /**/ } if (this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { /**/ } };
当删除文件时,传入的mtime会置null,所以会对所有的watcher触发remove。
另外,这里被删除的文件路径会被记录到initialScan中。
unlinkDir
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.onDirectoryUnlinked = function onDirectoryUnlinked(directoryPath) { // ... // 这里调用文件夹的删除 this.setDirectory(directoryPath, false, false, "unlink"); if (this.initialScan) { this.initialScanRemoved.push(directoryPath); } }; DirectoryWatcher.prototype.setDirectory = function setDirectory(directoryPath, exist, initial, type) { if (directoryPath === this.path) { /**/ } // 删除文件夹 else { var old = this.directories[directoryPath]; if (!old) { /**/ } else { if (!exist) { if (this.nestedWatching) this.directories[directoryPath].close(); // 删除容器中的文件夹信息 delete this.directories[directoryPath]; if (!initial && this.watchers[withoutCase(this.path)]) { /*...*/ } } } } };
在nestedWatching参数为false的情况下,这里是直接从文件夹信息容器中删除对应信息,否则会调用watcher对应的close方法。
error
DirectoryWatcher.prototype.onWatcherError = function onWatcherError( /* err */ ) {};
源码中,这个事件监听器并没有任何内容,需要自定义。
由于这节内容比较多,这里做一个简单的内容总结,也帮助自己复习:
watcherManager模块
1、有一个directoryWatchers容器保存已监视目录信息
2、getDirectoryWatcher方法会根据监视路径与options参数生成容器键,如果存在对应的值直接返回,否则新建一个DirectoryWatcher实体类注册到容器中,并监听closed事件,触发时自动删除该键
3、WatchFile、WatchDirectory分别处理文件、文件夹的监视,会同时调用getDirectoryWatcher方法与返回实体类的watch方法
4、在WatchFile中,监视文件所在的文件夹会作为根目录传入实例化的参数中,且只会监视根目录的该文件
5、若传入文件夹,则该文件夹目录下所有文件夹会被嵌套调用watchDirectory并将数据传入directories容器中,键为路径,值为一个新的DirectoryWatcher对象
DirectoryWatcher模块
1、包含多个容器,分别为:
files:保存根目录下所有文件信息
directories:保存根目录下所有文件夹信息
initialScanRemoved:记录已被删除的文件或文件夹路径
watchers:指定目录下监听器容器,其中键为监视文件的路径,值为监听器
2、内部细分了原生nodejs的rename、change事件,分别为add、addDir、change、unlink、unlinkDir
3、触发了对应路径文件的事件,会依次触发watchers中对应路径数组中所有监听器
完结!



