涉及知识点:
solution:
- 我们根据题,知道1号节点是根节点,并且所有工业城市的人都要到一号节点来,所以根据贪心思维我们能确定一号节点一定是旅游城市
- \(那么其他节点呢?\)
- \(我们通过审题发现该题是一个树形结构,那么不难通过反证证明越靠近根节点的节点,会贡献出更多\)
- \(现在我们知道,该找哪些点是旅游节点之后,如何计算最大和呢?\)
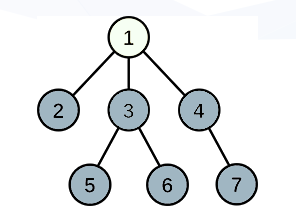
- \(我们通过上面的图来举例\)
- \(当只有一个根节点是旅游城市的时候,其最大和是6\)
- \(在往上添加一个旅游城市节点3,我们发现此时的最大和为6 + 2 -1\)
- \(换成4 呢,6 + 1 - 1\)
- 通过上面的举例,我们会发现随着一个节点变为旅游节点,那个时刻的最大和会跟着变为之前的最大和-(该节点的祖先节点-该节点的子节点)
std:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N =1e6+10;
LL e[N*2],h[N*2], ne[N*2],idx;
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx]= b, ne[idx] = h[a],h[a]=idx++ ;
}
LL n,m,k;
LL fa[N], son[N], num[N];
bool st[N]={0};
int dfs(int root,int cnt ){
// cout<<"?"<<" ";
st[root]=1 ;
int sum =0 ;
for(int i=h[root];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){
int j =e[i];
if(st[j])continue ;
int s =dfs(j,cnt+1);
sum+=s;
}
fa[root] =cnt;
son[root]= sum;
num[root] =fa[root]-son[root];
//cout<<cnt-sum<<" "<<root<<endl;
return sum+1;
}
int main(){
cin >>n >> m;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int a,b;cin >>a >>b ;
add(a,b ) ;add(b,a);
}
// cout<<"?"<<endl;
dfs(1,0);
sort(num+1, num+1+n);
// for(int i=1 ;i<=n;i++)cout<<num[i]<<" ";cout<<endl;
LL sum =0 ;
for(int i=n;i>=max(1LL,n-m+1);i--) sum+=num[i];
cout<<sum<<endl;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号