MAC下的环境变量配置
一直没有静下心来自己了解一下环境变量,也懒得配置,真是一个不合格的程序员。今天在研究安卓sdk的时候,需要进行环境变量的配置,我用的是Mac,使用adb命令一直失败,了解到是环境变量配置问题,所以对此进行了了解和研究
环境变量的概念:
家里又各种各样的盒子,里面放着不同首饰,盒子的位置分别在不同地方。每次找东西,都要先找盒子,还不知道里面有没有想要的东西,也不知道盒子放在哪里。 于是在一个下雨天,把每一个盒子里的位置记录在大脑里,以后找什么东西,知道盒子位置,就不用一个一个线索的去先找盒子了。
path1中有一个app neckless
path2中有一个app ring
path3中有一个应用 chopsticks
path4中有一个应用 cup
其中path4和path3都有父级路径kitchen.即kitchen/path3/chopsticks 和kitchen/path4/cup
在Mac中,通过vim命令: vim ~/.bash_profile(如果不存在,要创建)打开编辑页面。进入后如果不能编辑,点击按钮i,切换到insert状态进行编辑
添加内容 export PATH=path1/neckless:$PATH 注意等号前后不能有空格. $PATH也可以放在开头。这样neckless就已经添加进环境变量了。
可以通过export PATH = $PATH:path2/ring的方式将ring添加进去。
注意chopsticks和cup的上一层有共同路径kitchen。 对此,我们可以将两者的共同路径做为一个变量: $KITCHEN_PATH=/kitchen
然后将两者添加进PATH : export PATH = $PATH:$KITCHEN_PATH/path3:$KITCHEN_PATH/path4
按下esc键,输入:wq进行保存并退出
在终端执行 source ~/.bash_profile生成环境变量
可以通过 echo $PATH来查看路径是否已经生成。如果生成,path1234就可以直接在终端上运行,而不是需要去查找路径找到app才能打开。
安卓SDK为例:
没有配置环境的前提下在终端直接执行adb或者aapt只会提示command not found. 这是因为系统在默认已经登记的路径下没有找到这两个应用。所以我们需要通过添加环境变量的方式将两个路径添加进去。
- 打开终端Terminal:键入vim ~/.bash_profile打开文件(如果文件不存在,通过touch ~/.bash_profile创建文件。):
2.键入E,此时的界面是不可编辑状态,点击键盘:i 切换到输入模式
键入下面内容:
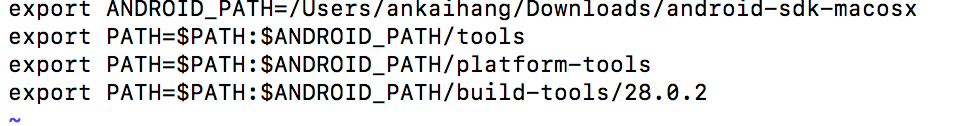
解释一下:
ANDROID_PATH是一个保存上级路径的变量,所以需要在调用时加上$。如果没有$,系统会将其默认为路径名称。
所以 $ANDROID_PATH/tools就相当于保存了路径:/Users/ankaihang/Downloads/android-sdk-macosx
如果没有$,环境变量里就只有ANDROID_PATH/tools。
因为变量的保存方式是: export PATH=$PATH:path1:path2:path3
或者: export PATH=$PATH:path1
export PATH=$PATH:path2
export PATH=$PATH:path3
如果不添加PATH变量$PATH,那么PATH就会被最新的覆盖。e.g. 在最后加上export PATH=path4. 那最后保存进去的路径就只有path4了。
3. 点击ESC退出输入模式,输入‘:wq’退出并保存
4. 在终端输入source ~/.bash_profile更新环境变量
5. 可通过 echo $PATH查看是否保存成功。
如果路径和应用所在路径一致,可以在终端直接输入adb,如果得到以下内容就说明环境变量配置成功了
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.40
Version 4797878
Installed as /Users/ankaihang/Downloads/android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools/adb
global options:
-a listen on all network interfaces, not just localhost
-d use USB device (error if multiple devices connected)
-e use TCP/IP device (error if multiple TCP/IP devices available)
-s SERIAL use device with given serial (overrides $ANDROID_SERIAL)
-t ID use device with given transport id
-H name of adb server host [default=localhost]
-P port of adb server [default=5037]
-L SOCKET listen on given socket for adb server [default=tcp:localhost:5037]
general commands:
devices [-l] list connected devices (-l for long output)
help show this help message
version show version num
networking:
connect HOST[:PORT] connect to a device via TCP/IP [default port=5555]
disconnect [HOST[:PORT]]
disconnect from given TCP/IP device [default port=5555], or all
forward --list list all forward socket connections
forward [--no-rebind] LOCAL REMOTE
forward socket connection using:
tcp:<port> (<local> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
forward --remove LOCAL remove specific forward socket connection
forward --remove-all remove all forward socket connections
ppp TTY [PARAMETER...] run PPP over USB
reverse --list list all reverse socket connections from device
reverse [--no-rebind] REMOTE LOCAL
reverse socket connection using:
tcp:<port> (<remote> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
reverse --remove REMOTE remove specific reverse socket connection
reverse --remove-all remove all reverse socket connections from device
file transfer:
push [--sync] LOCAL... REMOTE
copy local files/directories to device
--sync: only push files that are newer on the host than the device
pull [-a] REMOTE... LOCAL
copy files/dirs from device
-a: preserve file timestamp and mode
sync [all|data|odm|oem|product|system|vendor]
sync a local build from $ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT to the device (default all)
-l: list but don't copy
shell:
shell [-e ESCAPE] [-n] [-Tt] [-x] [COMMAND...]
run remote shell command (interactive shell if no command given)
-e: choose escape character, or "none"; default '~'
-n: don't read from stdin
-T: disable PTY allocation
-t: force PTY allocation
-x: disable remote exit codes and stdout/stderr separation
emu COMMAND run emulator console command
app installation:
install [-lrtsdg] [--instant] PACKAGE
install-multiple [-lrtsdpg] [--instant] PACKAGE...
push package(s) to the device and install them
-l: forward lock application
-r: replace existing application
-t: allow test packages
-s: install application on sdcard
-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only)
-p: partial application install (install-multiple only)
-g: grant all runtime permissions
--instant: cause the app to be installed as an ephemeral install app
uninstall [-k] PACKAGE
remove this app package from the device
'-k': keep the data and cache directories
backup/restore:
to show usage run "adb shell bu help"
debugging:
bugreport [PATH]
write bugreport to given PATH [default=bugreport.zip];
if PATH is a directory, the bug report is saved in that directory.
devices that don't support zipped bug reports output to stdout.
jdwp list pids of processes hosting a JDWP transport
logcat show device log (logcat --help for more)
security:
disable-verity disable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
enable-verity re-enable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
keygen FILE
generate adb public/private key; private key stored in FILE,
public key stored in FILE.pub (existing files overwritten)
scripting:
wait-for[-TRANSPORT]-STATE
wait for device to be in the given state
State: device, recovery, sideload, or bootloader
Transport: usb, local, or any [default=any]
get-state print offline | bootloader | device
get-serialno print <serial-number>
get-devpath print <device-path>
remount remount partitions read-write
reboot [bootloader|recovery|sideload|sideload-auto-reboot]
reboot the device; defaults to booting system image but
supports bootloader and recovery too. sideload reboots
into recovery and automatically starts sideload mode,
sideload-auto-reboot is the same but reboots after sideloading.
sideload OTAPACKAGE sideload the given full OTA package
root restart adbd with root permissions
unroot restart adbd without root permissions
usb restart adb server listening on USB
tcpip PORT restart adb server listening on TCP on PORT
internal debugging:
start-server ensure that there is a server running
kill-server kill the server if it is running
reconnect kick connection from host side to force reconnect
reconnect device kick connection from device side to force reconnect
reconnect offline reset offline/unauthorized devices to force reconnect
environment variables:
$ADB_TRACE
comma-separated list of debug info to log:
all,adb,sockets,packets,rwx,usb,sync,sysdeps,transport,jdwp
$ADB_VENDOR_KEYS colon-separated list of keys (files or directories)
$ANDROID_SERIAL serial number to connect to (see -s)
$ANDROID_LOG_TAGS tags to be used by logcat (see logcat --help)






