文本处理三剑客之 Sed ——一般编辑命令
sed简介
sed (stream editor for filtering and transforming text) 是Linux上的文本处理三剑客之一,另外两个是grep和awk.
sed又称行编辑器,每次读取并处理一行文本.
工作原理
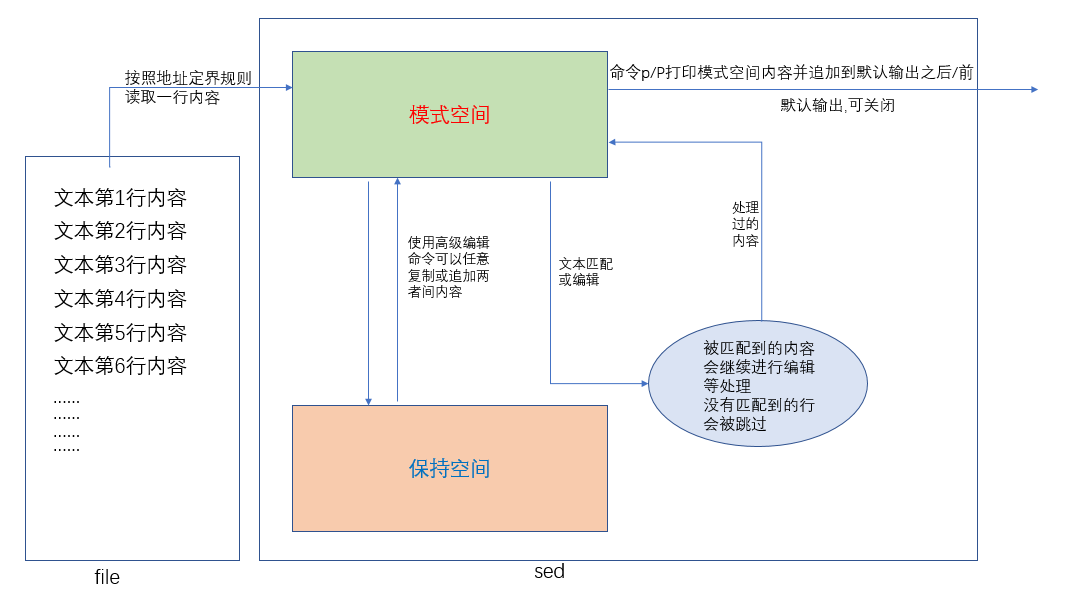
1.sed命令开始执行后
2.先从文本中读取第一行,放在模式空间 (pattern space)中
3.判断这行文本是否符合指定模式,符合则进行编辑,然后把结果输出到标准输出.
4.不符合的话默认也会输出到标准输出.除非特别指定不输出不符合的结果行.
5.继续读取下一行,以此类推.
- sed默认会对文件的每一行做处理.
- 可以指定sed仅处理匹配到的行
- 默认不对原文件进行编辑,只输出处理结果
- 在sed的高级用法中会用到sed的另一个空间:保持空间(hold space).
- 模式空间读进来的数据可以放进保持空间等待后续操作,两个空间的数据可以自由移动,互相覆盖或追加.
sed原理简图
命令格式
sed [option]... 'script' inputfile..
script:
sed处理文本所应用的脚本,如地址定界,编辑操作
sed的选项(options)
-n:不自动输出模式空间的内容到屏幕
-e script, --expression=script:实现多点编辑,
如:
# sed -e 's@^#[[:space:]]*@@' -e '/^UUID/d' /etc/fstab
-f:/PATH/SCRIPT_FILE: 从指定文件中读取编辑脚本
-r , --regexp-extended: 支持使用扩展正则表达式
-i[SUFFIX], --in-place[=SUFFIX]:对原文件进行编辑
-i.bak: 编辑原文件前会先创建一个 原文件名+.bak后缀的备份
地址定界:
(1) 不给地址:对全文进行处理
(2) 单地址:
#: 指定的行
/pattern/:被此处模式所能够匹配到的每一行
(3) 地址范围
#,#:从第#行开始到第#行结束
#,+#:从第#行开始,加#行
#,/pat1/:从第#行开始,到第一次被模式匹配的行结束
/pat1/,/pat2/:从被模式1匹配到的第一行开始,到被模式2匹配到的第一行结束;
$:最后一行
(4)步进:~
1~2:表示从1开始,步进2行,如3,5,7行即所有奇数行
2~2:表示所有偶数行
示例:
文件text内容如下:
$ cat text 1a 2b 3c 4d 5e 6f 7g 8h 9i $ sed -n '2p' /etc/issue #显示第二行 2b $ sed -n '/e$/p' text #显示e结尾的行 5e $ sed -n '4,8p' text #显示第4到第8行 4d 5e 6f 7g 8h $ sed -n '4,+3p' text #显示第4行以及后面的3行 4d 5e 6f 7g $ sed -n '/c$/,/^7/p' text #显示c结尾的行开始到7开头的行中的所有行 3c 4d 5e 6f 7g $ sed -n '5,/^7/p' text #显示第五行开始到7开头的行中的所有行 5e 6f 7g $ sed -n '2~3p' text #从第2行开始,每隔3行显示一行 2b 5e 8h $ sed -n '1~2p' text #显示奇数行 1a 3c 5e 7g 9i
常用一般编辑命令
d: 删除模式空间匹配的行,并立即进入下一轮循环
p:打印当前模式空间内容,追加到默认输出之后
a [\]text:在指定行后面追加文本,支持使用\n实现多行追加
i [\]text:在行前面插入文本
c [\]text:把匹配到的行替换为单行或多行文本
w /path/somefile: 保存模式匹配的行至指定文件
r /path/somefile:读取指定文件的文本至模式空间中匹配到的行后
=: 为模式空间中的行打印行号
!:模式空间中匹配行取反处理
示例:
$ cat /etc/passwd -n | sed '2,51d' #删除2-51行 1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash 52 apache:x:48:48:Apache:/usr/share/httpd:/sbin/nologin 53 named:x:25:25:Named:/var/named:/sbin/nologin $ sed '2~2d' text #删除偶数行,显示奇数行 1a 3c 5e 7g 9i $ df | sed -n '/^\/dev\/sd/p' #过滤出dev/sd开头的行 /dev/sda2 52403200 3932216 48470984 8% / /dev/sda5 20961280 142872 20818408 1% /app /dev/sda1 1038336 161556 876780 16% /boot $ sed '2,4a\ = = =' text #在2-4行后面分别追加自定义字符,斜线\表示之后出现的所有字符都算内容. 1a 2b = = = 3c = = = 4d = = = 5e 6f 7g 8h 9i $ sed '4i\ = = =' text #在第4行上方加入字符 1a 2b 3c = = = 4d 5e 6f 7g 8h 9i $ sed '/^6/c\6666' text #把第6行替换为6666 1a 2b 3c 4d 5e 6666 7g 8h 9i $ sed -n '/^alias/w /app/alias.txt' ~/.bashrc #把.bashrc文件中的alias开头的行保存到/app/alias.txt中
$ cat alias.txt alias rm='rm -i' alias cp='cp -i' alias mv='mv -i' $ sed '/^alias/r /etc/centos-release' ~/.bashrc #把/etc/centos-release中的内容插入到.bashrc中被模式匹配到的行之后 # .bashrc # User specific aliases and functions alias rm='rm -i' CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) alias cp='cp -i' CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) alias mv='mv -i' CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) # Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi $ sed '/^alias/=' ~/.bashrc #在匹配到的行只上添加行号 # .bashrc # User specific aliases and functions 5 alias rm='rm -i' 6 alias cp='cp -i' 7 alias mv='mv -i' # Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi $ sed -n '/^alias/!p' ~/.bashrc #显示没有被匹配到的行(结果取反) # .bashrc # User specific aliases and functions # Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi $ sed -n '/e$/!p' text #显示除了e结尾的行的所有行 1a 2b 3c 4d 6f 7g 8h 9i
查找替换:
s///,支持使用其它分隔符,如 s@@@,s### ,s___
替换标记:
g: 行内全局替换
p: 显示替换成功的行
w /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE:将替换成功的行保存至文件中
示例:
$ sed -rn 's@^[0-9]+@@p' text #删除所有数字开头行的数字 a b c d e f g h i $ sed 's@.*@#&@' text #给text文件中每一行前面加#号 #1a #2b #3c #4d #5e #6f #7g #8h #9i # 删除文件中以#号开头后跟一个空白字符的行的开头的#和空白字符 $ cat text2 this is 1 # this is 2 #this is 3 # this is 4 this is 5 $ sed 's@^#[[:space:]]@@' text2 this is 1 this is 2 #this is 3 this is 4 this is 5 # 给text2文件中不以#开头的行的行首加#号 $ cat text2 this is 1 # this is 2 #this is 3 # this is 4 this is 5 $ sed 's@^[^#].*@#&@' text2 #this is 1 # this is 2 #this is 3 # this is 4 #this is 5 $ echo /app/testdir/rootdir/motd/ | sed -r 's@(^/.*/)(.+)/?@\1@' #取目录名 /app/testdir/rootdir/ $ echo /app/testdir/rootdir/motd/ | sed -r 's@(^/.*/)(.+)/?@\2@' #取基名 motd/ $ ifconfig ens33| sed -rn 's@.*inet (.*) netmask.*@\1@p' # 取出 ifconfig ens33命令中的ipv4地址 192.168.5.137



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号