决策树之C4.5算法
预备知识:
- 无条件信息熵
- 条件信息熵
- 信息增益
这三个基础知识请查看我的上一篇博客 决策树之ID3算法
这篇博客主要讲 信息增益率
增益率(gain ratio):
C4.5决策树算法不直接使用信息增益来选择最优的划分属性(使样本集合的纯度提高最多的属性,或者说使样本集合的不确定度降低最多的属性),而是使用增益率来选择最优划分属性。增益率定义为:
G
a
i
n
_
r
a
t
i
o
(
D
,
a
)
=
G
a
i
n
(
D
,
a
)
I
V
(
a
)
(
1
)
Gain\_ratio(D,a) = \frac{Gain(D,a)}{IV(a)}\qquad(1)
Gain_ratio(D,a)=IV(a)Gain(D,a)(1)其中
I
V
(
a
)
=
−
∑
v
=
1
V
∣
D
v
∣
∣
D
∣
l
o
g
2
∣
D
v
∣
∣
D
∣
(
2
)
IV(a)=-\sum_{v=1}^{V}\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}log_2\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}\qquad(2)
IV(a)=−v=1∑V∣D∣∣Dv∣log2∣D∣∣Dv∣(2)
称为属性
a
a
a的固有值(intrinsic value),如果属性
a
a
a的取值越多(即V越大),则
I
V
(
a
)
IV(a)
IV(a)的值通常会越大。因此增益率对取值较少的属性有所偏好(分母越小增益率越大),C4.5算法并不是直接选择增益率最大的划分属性,而是先从候选划分属性中找出信息增益高于平均水平的属性,再从中找出增益率最高的属性
代码实现:
C4.5算法是在ID3算法基础上加以改进,所以代码基本一样,只需要修改chooseBestAttrToSplit函数中的代码,代码片段如下:
def chooseBestAttrToSplit(dataSet, DLenth):
#属性数量
attrsNum = len(dataSet[0])-1
#print(range(attrsNum))
#计算信息熵
entD = Ent(dataSet)
#计算信息增益率
bestInfoGainRatio = 0.0
bestAttr = -1
infoGainList = []
for i in range(attrsNum): #遍历每个样例的当前属性的属性值加入集合attrList
attrList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
attrsValue = set(attrList)#转化为set,可以知道有几个不同的属性
entDA = 0.0 # 初始化条件熵
for value in attrsValue:#计算条件熵
subDataSet = splitD(dataSet,value,i)#按属性值划分子集
weight = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))#计算权重
entDA += weight * Ent(subDataSet)
infoGain = entD - entDA
infoGainList.append({infoGain : i})#将当前属性计算得到的信息增益加入集合
print(infoGainList)
#求信息增益的平均值
sumInfoGain = 0
for each in infoGainList:
sumInfoGain += list(each.keys())[0]
#计算信息增益的平均值
averInfoGain = float(sumInfoGain)/len(infoGainList)
#找出比平均信息增益大的信息增益
greaterThenAverInfoGain = []
for each in infoGainList:
if list(each.keys())[0] >= averInfoGain:# 注意这里是">="号,因为信息增益可能相等
greaterThenAverInfoGain.append(each)
#从其中计算信息增益率最大的属性
for i in greaterThenAverInfoGain:
attrIndex = list(i.values())[0]#属性下标
print(attrIndex)
attrList = [sample[attrIndex] for sample in dataSet]#当前属性对应的值全部加入集合
attrsValue = set(attrList)#得到当前属性有几个不同的属性值
#初始化属性固有值
iva = 0.0
#初始化信息增益
entda = 0.0
for value in attrsValue: # 计算条件熵
subDataSet = splitD(dataSet, value, attrIndex) # 按属性值划分子集
weight1 = len(subDataSet) / float(DLenth) # 计算权重
weight = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) # 计算权重
iva -= weight1 * log(weight1,2)
entda += weight * Ent(subDataSet)
infoGain = entD - entda
#计算信息增益率
gainRatio = float(infoGain)/iva
print("gainRatio"+str(gainRatio))
#选取信息增益率最大的属性
if(gainRatio > bestInfoGainRatio):
bestInfoGainRatio = gainRatio
bestAttr = attrIndex
print("bestAttr"+str(bestAttr))
return bestAttr
完整代码如下:
- treeC45.py
from math import log
import operator
import treePlotter
dataSet = [['青绿' ,'蜷缩' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'蜷缩' ,'沉闷' ,'清晰' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'蜷缩' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['青绿' ,'蜷缩' ,'沉闷' ,'清晰' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['浅白' ,'蜷缩' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['青绿' ,'稍蜷' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'稍凹' ,'软粘' ,'好瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'稍蜷' ,'浊响' ,'稍糊' ,'稍凹' ,'软粘' ,'好瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'稍蜷' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'稍凹' ,'硬滑' ,'好瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'稍蜷' ,'沉闷' ,'稍糊' ,'稍凹' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜'],
['青绿' ,'硬挺' ,'清脆' ,'清晰' ,'平坦' ,'软粘' ,'坏瓜'],
['浅白' ,'硬挺' ,'清脆' ,'模糊' ,'平坦' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜'],
['浅白' ,'蜷缩' ,'浊响' ,'模糊' ,'平坦' ,'软粘' ,'坏瓜'],
['青绿' ,'稍蜷' ,'浊响' ,'稍糊' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜'],
['浅白' ,'稍蜷' ,'沉闷' ,'稍糊' ,'凹陷' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜'],
['乌黑' ,'稍蜷' ,'浊响' ,'清晰' ,'稍凹' ,'软粘' ,'坏瓜'],
['浅白' ,'蜷缩' ,'浊响' ,'模糊' ,'平坦' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜'],
['青绿' ,'蜷缩' ,'沉闷' ,'稍糊' ,'稍凹' ,'硬滑' ,'坏瓜']]
A = ['色泽','根蒂','敲声','纹理','脐部','触感']
def isEqual(D):# 判断所有样本是否在所有的属性上取值相同
for i in range(len(D)):#遍历样例
for j in range(i+1,len(D)):#遍历之后的样例
for k in range(len(D[i])-1):#遍历属性
if D[i][k] != D[j][k]:
return False
else:
continue
return True
def mostClass(cList):
classCount={}#计数器
for className in cList:
if className not in classCount.keys():
classCount[className] = 0
classCount[className] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
print(sortedClassCount[0][0])
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def Ent(dataSet):
sampleNum = len(dataSet)#样例总数
classCount = {}#类标签计数器
for sample in dataSet:
curLabel = sample[-1]#当前的类标签是样例的最后一列
if curLabel not in classCount.keys():
classCount[curLabel] = 0
classCount[curLabel] += 1
infoEnt = 0.0# 初始化信息熵
for key in classCount.keys():
prob = float(classCount[key])/sampleNum
infoEnt -= prob * log(prob,2)
return infoEnt
def splitD(dataSet,value,index):
retDataSet = []
for sample in dataSet: # 遍历数据集,并抽取按axis的当前value特征进划分的数据集(不包括axis列的值)
if sample[index] == value: #
reducedFeatVec = sample[:index]
reducedFeatVec.extend(sample[index + 1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
# print axis,value,reducedFeatVec
if retDataSet == []:#如果为空集返回当前集合
return dataSet
return retDataSet
def chooseBestAttrToSplit(dataSet, DLenth):
#属性数量
attrsNum = len(dataSet[0])-1
#print(range(attrsNum))
#计算信息熵
entD = Ent(dataSet)
#计算信息增益率
bestInfoGainRatio = 0.0
bestAttr = -1
infoGainList = []
for i in range(attrsNum): #遍历每个样例的当前属性的属性值加入集合attrList
attrList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
attrsValue = set(attrList)#转化为set,可以知道有几个不同的属性
entDA = 0.0 # 初始化条件熵
for value in attrsValue:#计算条件熵
subDataSet = splitD(dataSet,value,i)#按属性值划分子集
weight = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))#计算权重
entDA += weight * Ent(subDataSet)
infoGain = entD - entDA
infoGainList.append({infoGain : i})#将当前属性计算得到的信息增益加入集合
print(infoGainList)
#求信息增益的平均值
sumInfoGain = 0
for each in infoGainList:
sumInfoGain += list(each.keys())[0]
#计算信息增益的平均值
averInfoGain = float(sumInfoGain)/len(infoGainList)
#找出比平均信息增益大的信息增益
greaterThenAverInfoGain = []
for each in infoGainList:
if list(each.keys())[0] >= averInfoGain:# 注意这里是">="号,因为信息增益可能相等
greaterThenAverInfoGain.append(each)
#从其中计算信息增益率最大的属性
for i in greaterThenAverInfoGain:
attrIndex = list(i.values())[0]#属性下标
print(attrIndex)
attrList = [sample[attrIndex] for sample in dataSet]#当前属性对应的值全部加入集合
attrsValue = set(attrList)#得到当前属性有几个不同的属性值
#初始化属性固有值
iva = 0.0
#初始化信息增益
entda = 0.0
for value in attrsValue: # 计算条件熵
subDataSet = splitD(dataSet, value, attrIndex) # 按属性值划分子集
weight1 = len(subDataSet) / float(DLenth) # 计算权重
weight = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) # 计算权重
iva -= weight1 * log(weight1,2)
entda += weight * Ent(subDataSet)
infoGain = entD - entda
#计算信息增益率
gainRatio = float(infoGain)/iva
print("gainRatio"+str(gainRatio))
#选取信息增益率最大的属性
if(gainRatio > bestInfoGainRatio):
bestInfoGainRatio = gainRatio
bestAttr = attrIndex
print("bestAttr"+str(bestAttr))
return bestAttr
def treeGenerate(D,A,Dlenth):
print(D)
CnameList = [sample[-1] for sample in D]#遍历每一个样例,将每个样例的类标签组成一个集合
if CnameList.count(CnameList[0]) == len(CnameList):#当结点包含的样本全属于同一类别,无需划分,直接返回类标签
return CnameList[0]
if len(A) == 0 or isEqual(D):#如果A为空集或者所有样本在所有属性上取值相同,则无法划分,返回所含样本最多的类别
return mostClass(CnameList)
#从A中选择最优的划分属性
bestAttrIndex = chooseBestAttrToSplit(D,Dlenth) #获取最优属性下标
bestAttrName = A[bestAttrIndex]#获取最优属性名字
#使用字典存储树信息
treeDict = {bestAttrName:{}}
del(A[bestAttrIndex])# 删除已经选取的特征
attrList = [sample[bestAttrIndex] for sample in D] #获取每个样例最佳划分属性的属性值列表
attrsValue = set(attrList)
for value in attrsValue:
subA = A[:]
if len(D) == 0:#如果子集D为空集则,返回父集中样本最多的类
return mostClass(CnameList)
else:
treeDict[bestAttrName][value] = treeGenerate(splitD(D,value,bestAttrIndex),subA,Dlenth)
return treeDict
if __name__ == '__main__':
tree = treeGenerate(dataSet,A,len(dataSet))
treePlotter.createPlot(tree)
- treePlotter
# _*_ coding: UTF-8 _*_
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['KaiTi']
mpl.rcParams['font.serif'] = ['KaiTi']
"""绘决策树的函数"""
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") # 定义分支点的样式
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8") # 定义叶节点的样式
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") # 定义箭头标识样式
# 计算树的叶子节点数量
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
# 计算树的最大深度
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
# 画出节点
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', \
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va="center", ha="center", \
bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
# 标箭头上的文字
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
lens = len(txtString)
xMid = (parentPt[0] + cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 - lens * 0.002
yMid = (parentPt[1] + cntrPt[1]) / 2.0
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.x0ff + \
(1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.y0ff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.y0ff = plotTree.y0ff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.x0ff = plotTree.x0ff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], \
(plotTree.x0ff, plotTree.y0ff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.x0ff, plotTree.y0ff) \
, cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.y0ff = plotTree.y0ff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.x0ff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.y0ff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
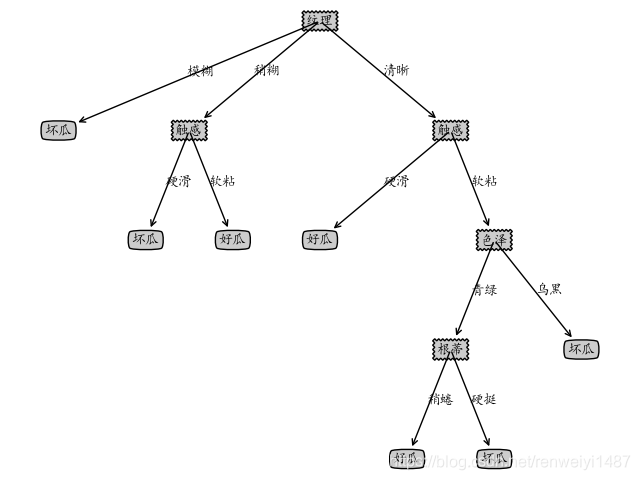
运行结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号