[USACO 2012 Feb G]Cow Coupons----贪心&带悔(看完稳AC)
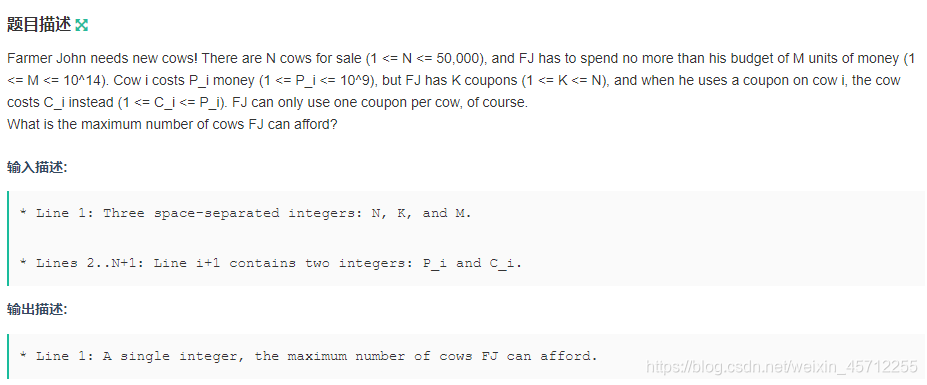
输入:
4 1 7
3 2
2 2
8 1
4 3
输出:
3
提示:
FJ has 4 cows, 1 coupon, and a budget of 7.FJ uses the coupon on cow 3 and buys cows 1, 2, and 3, for a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6.
意思是有n头牛,现在有k张优惠券以及m元,每头牛有一个原始价格和折扣价格,问最多能买多少牛
一开始的方法很简单,由于题目里面说了折扣价格一定比原始价格便宜,所以说首先按照折扣价格从小大大进行排序,将前k个牛的花费看作是折扣之后的价格,而将后面的花费看作是原始价格,然后重新将价值从小到大进行排序,尽可能的多选
然后交了一发之后ac
其实是错的
Wrong_code:
ll n, m, k;
struct node {
int p, c;
int flag;
int val;
} a[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.c < b.c;
}
bool cmp2(node a, node b) {
return a.val < b.val;
}
int main() {
n = read, k = read, m = read;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i].p = read, a[i].c = read;
a[i].flag = 0;
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i <= k)
a[i].val = a[i].c;
else
a[i].val = a[i].p;
}
ll sum = 0;
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += a[i].val;
if(sum > m){
printf("%d\n",i-1);
return 0;
}
}
cout << n <<endl;
return 0;
}
/**
**/
没想到这个错误的代码在牛课上竟然ac
码完这个代码之后,突然被同学hack了
给了一组样例:
2 1 5
3 1
1000 2
应该是2才是,可惜我的结果是1
像这样的数据点有的是,在牛客后台也有很多错误的代码
比如向上面的这个样例,我们应该还要维护一个大根堆,将选择的优惠差值放在里面,考虑是不是可以将用过券的牛不用了,反悔掉,然后用到另一头牛上
然后写了一手交了亿发:
还是错误代码:
ll n, m, k;
struct node {
ll p, c;
} a[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.c < b.c;
}
bool cmp2(node a, node b) {
return a.p < b.p;
}
priority_queue<ll> que;
int main() {
n = read, k = read, m = read;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i].p = read, a[i].c = read;
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += a[i].c;
if(sum > m) {
printf("%d\n",i-1);
return 0;
}
que.push(a[i].p - a[i].c);
}
//
if(k == n) {
printf("%lld\n",n);
return 0;
}
sort(a + 1 + k, a + 1 + n, cmp2);
for (int i = k + 1; i <= n; i++) {
ll sub = a[i].p - a[i].c;
if(sub > que.top()) {
sum += que.top();
que.pop();
que.push(sub);
sum += a[i].c;
} else sum += a[i].p;
if(sum > m) {
printf("%d\n",i-1);
return 0;
}
}
cout << n <<endl;
return 0;
}
然后想了个错误数据:
3 2 6
2 1
1000 3
5 1
结果应该是3才是,可惜我得出2
方案是优惠购买后两个,花费4,原始价格购买第一个,花费为6
对于上面的错误代码我们可以看到:
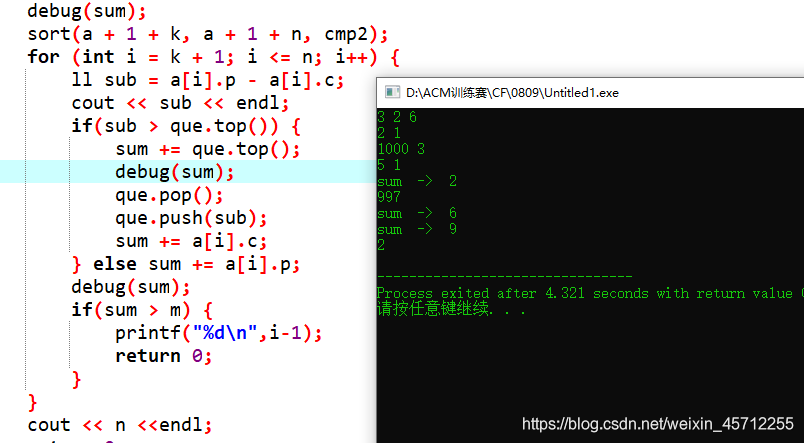
开始花费为2,买了两个折扣后为1的,然后进入之后,第三个物品可以优惠997,然后将优惠4的取消使用优惠券,加上差值之后变成了6,然后又买了折扣价值为3的物品,此时相当于给2 1物品以及1000 3物品使用了优惠券,其实是应该对1000 3和5 1使用优惠券
所以说这个代码是错的!!!而且很多晚上的代码都用了这种方法
在看博客的时候一定要审慎的看待这些代码,要有批判的眼光去学习
正确思路
首先我们将n头牛按照折扣价值从小到大进行排序
然后选折扣价值里面最小的k个进行求和,如果连折扣后的最小的k个都买不了的话,直接判断下进行输出i-1,在处理值的过程中加和记录sum,并且将优惠的价格放到小根堆里进行维护(que)
然后我们考虑剩下的n-k头牛是否可以替换掉已经用券的k头牛中的一部分
2 1 5
3 1
1000 2
比如在这个样例中,我们开始选择的是折扣价格为1的这头牛
然后将剩下的n-k头牛的原始价格和折扣价格分别放到小根堆里进行维护queP,queC
每次选取的时候,如果说优惠的最小的价格 + 当前优惠的价格甚至小于未进行优惠的最小价格,那么说明就可以替换掉
这时候就要把之前在前k头牛里面的折扣弥补回来 sum += que.top()
弥补之后,还要附上当前折扣之后的价格queC.top()
然后记得pop&&push相应的价值
具体代码如下:
AC_code:
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
ll n, m, k;
struct node {
ll p, c;
} a[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.c < b.c;
}
bool vis[maxn];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > que;
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII> >queP,queC;
int main() {
n = read, k = read, m = read;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i].p = read, a[i].c = read;
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += a[i].c;
if(sum > m) {
printf("%d\n",i-1);
return 0;
}
que.push(a[i].p - a[i].c);
}
for(int i=k+1; i<=n; i++) {
queP.push({a[i].p,i});
queC.push({a[i].c,i});
}
// debug(sum);
for(int i=k+1; i<=n; i++) {
while(vis[queC.top().second]) queC.pop();
while(vis[queP.top().second]) queP.pop();
int p1 = queC.top().second;
int p2 = queP.top().second;
int t1 = queC.top().first;
int t2 = queP.top().first;
t1 += que.top();
// debug(p1);
// debug(p2);
// debug(t1);
// debug(t2);
if(t1 < t2) {
sum += t1;
queC.pop();
que.pop();
que.push(a[p1].p - a[p1].c);
vis[p1] = 1;
} else {
sum += t2;
queP.pop();
vis[p2] = 1;
}
// cout << sum <<endl;
if(sum > m) {
printf("%d\n",i-1);
return 0;
}
}
cout << n <<endl;
return 0;
}
/**
3 2 6
2 1
1000 3
5 1
4 2 8
1001 4
1001 4
4 4
4 4
**/
洛谷牛客很多代码都是错的,错误代码都能AC,稍感无语



