校内 第一届ACM校赛——热身赛
我很好奇,如果是第一届校赛的话,谁是出题人呢是༼ つ ◕_◕ ༽つ
A

-
TAG:签到题
我都不屑于说为什么它签到,因为它太签到是(づ ̄ 3 ̄)づ
A.cpp
#include<cstdio>
int n,a,b;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--){
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("%d\n",a+b);
}
return 0;
}
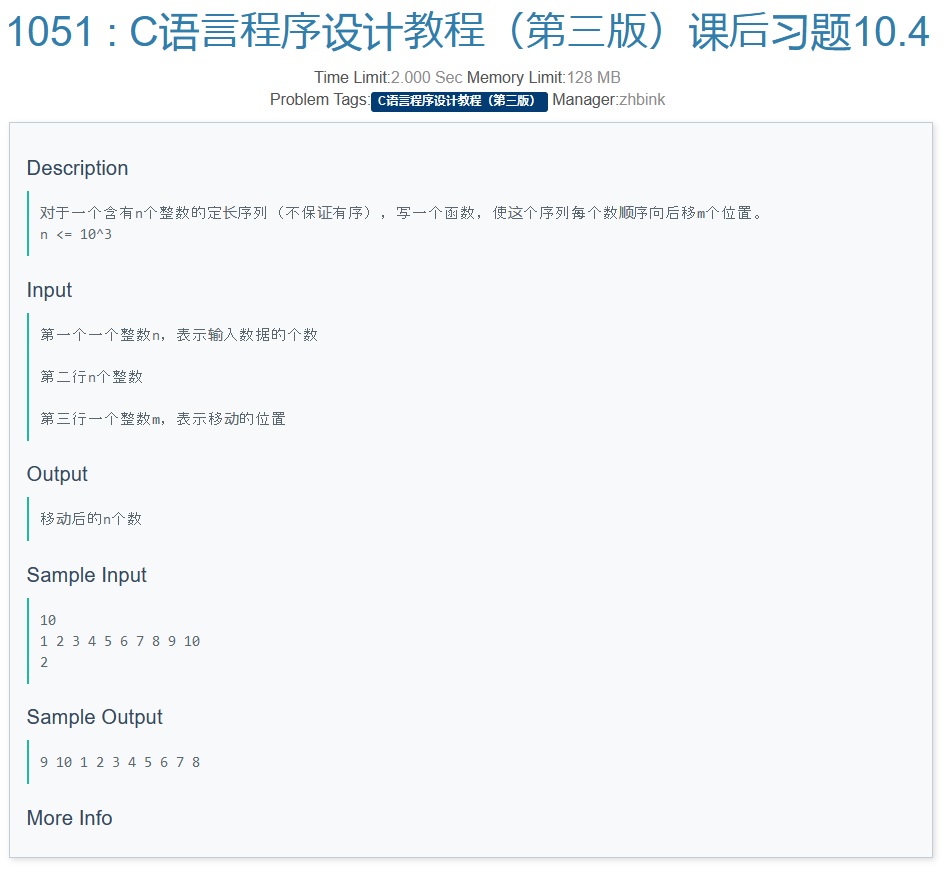
B
-
PZ's solution:
1. 初步设想利用 取模运算\(\%\) 来达到位置推移;
2.由于取模运算的特点,我们 以0代替1 为位置起点;
3.对于后\(i-m+1\)个数,可以直接套用 \(i_{new}=(i-m) \% n\)
4.对于前\(m-1\)个数,由于\((i-m) \leq 0\),我们要加上\(n\)防止其出现负数,即 \(i_{new}=(n+i-m) \% n\),而此公式对3.也适用
-
TAG:签到题
B.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[1005],b[1005],n,m;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) printf("%d ",a[(n+i-m)%n]);
return 0;
}
C

-
TAG:模拟;签到题
这题,只要照着模拟就好了,注意 独立 的定义即可ㄟ( ▔, ▔ )ㄏ
C.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s;
int T,n;
bool check(char x){
if('0'<=x&&x<='9') return 0;
if('a'<=x&&x<='z') return 0;
if('A'<=x&&x<='Z') return 0;
return 1;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&T); getline(cin,s);
while(T--){
getline(cin,s);
n=s.size();
cout<<s<<endl;
s=" "+s;
printf("AI: ");
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(check(s[i-1]) &&
s[i]=='c' && s[i+1]=='a' && s[i+2]=='n' &&
s[i+3]==' '&&
s[i+4]=='y' && s[i+5]=='o' && s[i+6]=='u' &&
check(s[i+7])){
printf("I can ");
i+=7;
} else
if(check(s[i-1]) &&
s[i]=='c' && s[i+1]=='o' && s[i+2]=='u' && s[i+3]=='l' && s[i+4]=='d' &&
s[i+5]==' ' &&
s[i+6]=='y' && s[i+7]=='o' && s[i+8]=='u' &&
check(s[i+9])){
printf("I could ");
i+=9;
} else
if(check(s[i-1]) &&
s[i]=='I' &&
check(s[i+1])){
printf("you ");
i+=1;
} else
if(check(s[i-1]) &&
s[i]=='m' && s[i+1]=='e' &&
check(s[i+2])){
printf("you ");
i+=2;
} else printf("%c",s[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
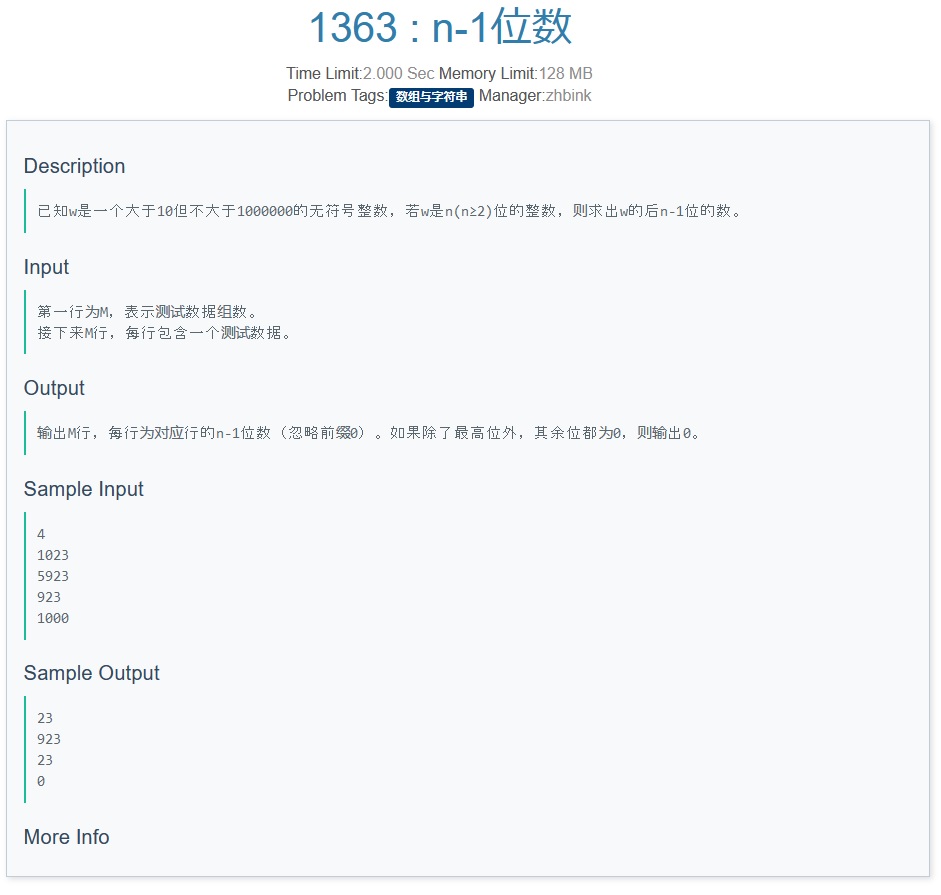
D
-
TAG:签到题
我只能说 懂的都懂,不懂的自然不懂( ͡• ͜ʖ ͡• )
D.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int M,n,res,cnt;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&M);
while(M--){
scanf("%d",&n);
res=0; cnt=1;
while(n>10){
res=(n%10)*cnt+res;
n/=10;
cnt*=10;
}
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return 0;
}
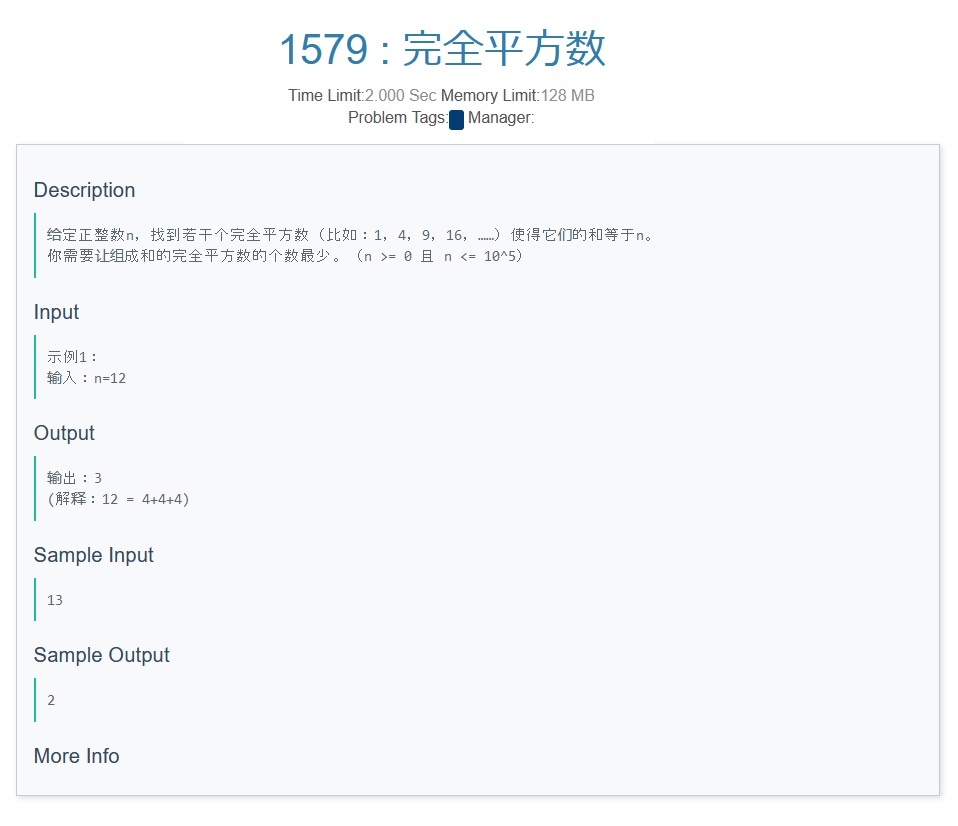
E
-
PZ's solution:
1.考虑动态规划,用类似背包的思想,设\(f[i]\)为 \(n==i\)时的答案 ;
2.类似完全背包,由于求个数最少,有状态转移方程 $ f[i]=min(f[i],f[i-j*j]+1)$
3.通过取 \(min\) 来体现求个数最少的情况,可以让后继 完全平方数更大的答案 覆盖 原来的答案,体现动态规划的作用
-
TAG:背包;多重背包;动态规划
E.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,f[100005];
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof(f));
f[0]=0;
//初始化非法状态 与 合法状态
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j*j<=i;++j)
f[i]=min(f[i],f[i-j*j]+1);
printf("%d",f[n]);
return 0;
}
F

-
PZ's solution:
1.考虑到答案最多不会超过\(5\)位数,可以使用搜索;
2.我们从每个点出发,向四周延伸,直到凑成\(5\)位数,中途所有数用 \(vis[x]\) 记录下来即可
3.搜索遍历结束后,遍历 \(vis[x]\) 数组寻找答案即可
-
TAG:搜索;签到题
F.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,a[55][55];
bool vis[1000000];
void dfs(int x,int y,int res,int cnt){
if(cnt>5) return;
vis[res]=1;
if(x+1<=n) dfs(x+1,y,res*10+a[x+1][y],cnt+1);
if(y+1<=n) dfs(x,y+1,res*10+a[x][y+1],cnt+1);
if(x-1>=1) dfs(x-1,y,res*10+a[x-1][y],cnt+1);
if(y-1>=1) dfs(x,y-1,res*10+a[x][y-1],cnt+1);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]),vis[a[i][j]]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
dfs(i,j,a[i][j],1);
for(int i=1;i<=99999;++i)
if(!vis[i]){
printf("%d",i);
return 0;
}
}
G

-
PZ's solution:
1.由于\(x,y(x=y+1)\)为两个相邻自然数,
由辗转相除法 \(gcd(x,y)=gcd(y,x \% y)\) ,\(x \% y=1\) 即 $ gcd(x,y)=gcd(y,1) \equiv 1;$
2.注意 \(n==1\) 的情况需要特判,因为 一个数时 没有数与其互质
-
TAG:数论;GCD最大公约数;结论题
G.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
string n;
int main(){
cin>>n;
if(n=="1") n="0";
cout<<n;
return 0;
}
吐槽
1.总共7道题,有5道签到题是(っ °Д °;)っ,热身赛不愧是热身赛!
2.最后一道题果然恶意坑人!
3.这次的热身赛题目全是从OJ上扒下来的,但第二届热身赛,是从第一届正赛中扒的题是(ノへ ̄、)
彩蛋.正赛的F题、G题的图片名称是反的,大家注意到了吗?这其实是个小失误,至于为啥会这样,大家可以猜一猜是( ̄▽ ̄)"


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号