60天shell脚本计划-2/12-渐入佳境
--作者:飞翔的小胖猪
--创建时间:2021年2月1日
--修改时间:2021年2月5日
说明
每日上传更新一个shell脚本,周期为60天。如有需求的读者可根据自己实际情况选用合适的脚本,也可在评论区留言提出脚本需求,作者会尽快根据需求编写相关脚本对功能进行实现。
每篇文章包含5个脚本。
总进度:2/12
上一篇脚本链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Pigs-Will-Fly/p/14333284.html
下一篇脚本链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Pigs-Will-Fly/p/14380780.html
主要内容
21年2月1日-系统监控脚本(简易)
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
脚本说明
脚本获取Linux操作系统中内存、cpu、根目录及message日志信息,展示当前的系统的资源使用情况。 判断当前系统中是否存在僵尸进程,/var/log/message文件最后100行是否存在错误日志。
文件说明
System_health_check.sh:脚本主体程序文件
脚本主体
[root@135 6_system_check]# cat System_health_check.sh
#!/bin/bash #ip地址 ip_address=`ip a|grep -i -A2 'MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP' | grep -E -o "(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)" |grep -E -v "(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.255" |grep -E '^80|^10|^192' | head -1 ` Total_Swap=`cat /proc/meminfo |grep SwapTotal | awk '{printf ("%d\n",$2/1024)}'` #结果为一个数字,代表总的Swap值,单位为M Free_Swap=`cat /proc/meminfo |grep SwapFree | awk '{printf ("%d\n",$2/1024)}'` #结果为一个数字,代表空闲的Free值,单位为M #Mem_info=`free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $2,$3,$4,$5,$7}'` Mem_info=`free -m | awk 'BEGIN { OFS="|"};NR==2{print $2,$3,$4}'` #只要前面4个字段,total use free share Cpu_Num=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep -i process | wc -l` #获取逻辑CPU的个数 Avage_five_cpu=`uptime | sed 's/.*load average: //g' | sed 's#\,##g'|awk '{print $2}'` #采集5分钟CPU负载情况 System_start_time=`uptime | awk '{print $1}'` #得开机时间 System_uptime=`uptime |awk -F ',' '{print $1}' |sed 's#.*up##g'` #得到运行时常 #查看确认近100行日志是否有告警。 tail -100 /var/log/messages | grep -i -E 'warning|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg|err' &> /dev/null #cat /var/log/messages | grep -i -E 'warning|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg|err' &> /dev/null log_check=`echo $?` if [[ $log_check -eq 0 ]];then log_notice=waring else log_notice=no_waring fi echo "hostname | ip_address | Total_Swap | Free_Swap | total_mem| use_mem | free_mem| Cpu_Num | Avage_five_cpu | zombie | log_notice| System_start_time | System_uptime " | awk -F'|' 'BEGIN { OFS="\t"} ;{ $1=$1 ; print $0} ' > result.xls if [[ `ps -A -o stat,ppid,pid,cmd | grep -e '^[Zz]'` ]];then echo "`hostname` | $ip_address | $Total_Swap | $Free_Swap | $Mem_info | $Cpu_Num | $Avage_five_cpu | yes | $log_notice| $System_start_time | $System_uptime " | awk -F'|' 'BEGIN { OFS="\t"} ;{ $1=$1 ; print $0} ' >> result.xls else echo "`hostname` | $ip_address | $Total_Swap | $Free_Swap | $Mem_info | $Cpu_Num | $Avage_five_cpu | no | $log_notice | $System_start_time | $System_uptime " | awk -F'|' 'BEGIN { OFS="\t"} ;{ $1=$1 ; print $0} ' >> result.xls fi
结果
执行命令结果:
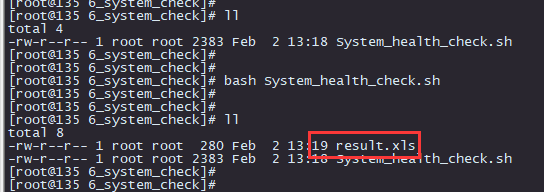
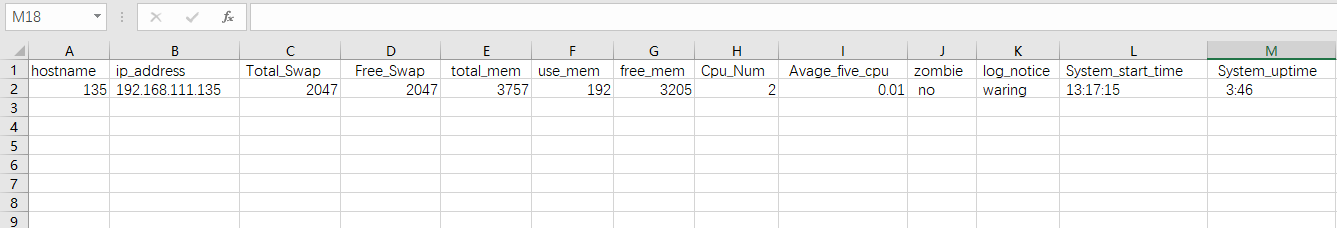
生成execl文件格式:
**************************************************************************************************************2021年2月1日脚本结束*****************************************************************************************************************
21年2月2日-一键修改ip地址
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
脚本说明
通过脚本获取当前主机的网口名和网口ip地址,再根据脚本中定义的字典获取到将要修改的新的ip地址,最后调用sed命令对网络配置文件进行修改。
使用脚本时注意由于该脚本为定制编写的在获取当前系统ip和网口名时需要更具自己环境指定。
单台设备修改IP地址时就不要采用该脚本了,单台修改时老老实实的手动修改配置文件嘛 。
文件说明
Batch_edit_add.sh:脚本主体程序文件
脚本主体
[root@135 7_edit_address]# cat Batch_edit_add.sh #!/bin/bash #修改静态路由函数 #该脚本仅仅适用于network的网络,NetworkManager不用这么麻烦。 edit_yw_ip(){ #获取主机当前接口和ip地址。 net_ip=`ifconfig | grep 192.168.111. | awk '{print $2}'` net_name=`ifconfig | egrep -B1 '192.168.111.'| grep -i ens | awk -F':' '{print $1}'` #define old_ip and new_ip dict declare -A dict_ip_b dict_ip_b=([192.168.111.4]="192.168.20.4" \ [192.168.111.1]="192.168.20.1" \ [192.168.111.2]="192.168.20.2" \ [192.168.111.135]="192.168.20.135" \ [192.168.111.3]="192.168.20.3" ) new_ip=${dict_ip_b[$net_ip]} echo "This Machine new ip and old ip info:" echo "New addres ${new_ip} , old address: $net_ip" #开始修改网络配置文件,测试时sed 不要加i参数 if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name}.bak ]; then cp -p /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name} /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name}.bak2 else cp -p /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name} /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name}.bak fi if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name}.bak ] || [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name}.bak2 ]; then sed -i "s/${net_ip}/${new_ip}/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name} sed -i "s/GATEWAY\=192.168.111.2/GATEWAY\=192.168.20.2/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${net_name} if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "重启网络服务,并修改相关静态路由,测试状态下注释掉了" #systemctl restart network else echo "network config file edit failed,not restart network progroam." fi else echo "文件备份不存在,not change network config file........." fi } #申明主函数 main(){ read -p 'Make sure you want to make network configuration changes。Please input YES(y) or NO(n): ' answer if [ $answer == y ] || [ $answer == YES ];then edit_yw_ip elif [ $answer == n ] || [ $answer == NO ];then echo "input NO or n,program will exited..................." exit 1 fi } #调用主函数 main
结果
执行前展示

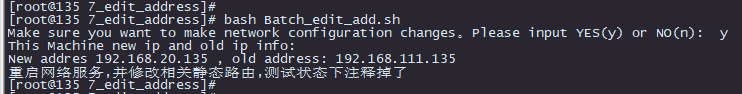
执行命令展示
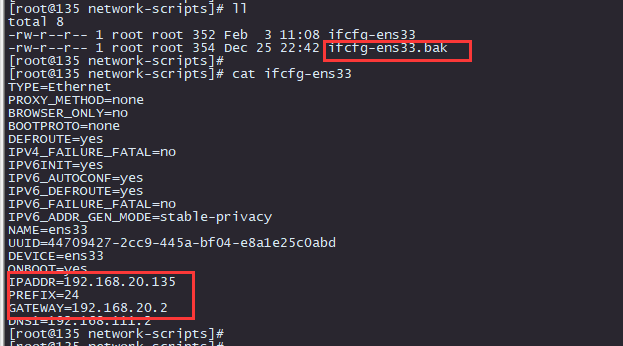
结果文件
**************************************************************************************************************2021年2月2日脚本结束*****************************************************************************************************************
21年2月3日-获取远程主机磁盘信息
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
脚本说明
获取既定主机磁盘根分区使用情况。
文件说明
System_root_mount_check.sh:脚本主体程序文件
配置文件
[root@135 8_get_remote_df]# cat machine_list.txt 192.168.111.11 root yinwan 192.168.111.12 root yinwan 192.168.111.124 root yinwan
脚本主体
[root@135 8_get_remote_df]# cat Get_remote_mount.sh #!/bin/bash generate_rsa(){ #判断是否有密钥对文件没有的化自动生成密钥对。 if [ ! -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa ];then ssh-keygen -N "" -b 4096 -t rsa -C "`hostname`" -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa &>/dev/null else echo 'rsa config file exits !! ' >> /var/log/message fi } send_file_rsa(){ #发送rsa到远程主机中,如果已经存在则可以忽略,不用执行该函数 cat machine_list.txt | while read ipaddr user passwd do echo "exec send rsa file to $ipaddr " &>/dev/null timeout 2 sshpass -p $passwd /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa $user@$ipaddr &>/dev/null done } get_remote_df(){ #远程执行命令把结果置入到临时文件中。 echo "Ipadress" >> result_ip.txt echo "Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted" >> result.txt for ipaddr in 192.168.111.11 192.168.111.12 192.168.111.124 do echo "$ipaddr" >> result_ip.txt ssh -T $ipaddr df -hP | grep -i /$ >> result.txt done paste result_ip.txt result.txt | awk 'BEGIN { OFS="\t"} ;{ $1=$1 ; print $0} ' > result.xls echo -e "Remote Machine / Info:\n`cat result.xls` " } clear_env(){ #清除执行过后的环境文件 rm -rf result_ip.txt rm -rf result.txt } #定义主函数 main(){ > result_ip.txt > result.txt generate_rsa send_file_rsa get_remote_df clear_env } #调用主函数 main
结果
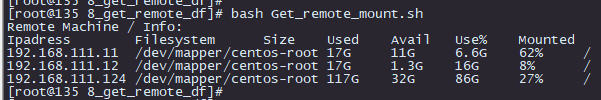
**************************************************************************************************************2021年2月3日脚本结束*****************************************************************************************************************
21年2月4日-批量修改ipmi用户脚本
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
脚本说明
通过用户之前规划的ipmi密码,写入到指定的配置文件中。脚本循环读取配置文件中的ipmi地址及用户信息等参数实现批量修改ipmi密码,用户密码修改后再测试是否能够使用新的密码连接ipmi口,如果可以连接则把能够连接的结果置入到文件中。
该脚本只作为参考,由于各厂商的产品迭代比较厉害使用脚本前还请先确认每个品牌和型号的用户id号,再根据具体情况加以修改脚本。
文件说明
machine_list.txt:物理主机ipmi表
Batch_edit_ipmi_user.sh:脚本主体程序文件
配置文件
[root@135 9_edit_ipmi_password]# cat machine_list.txt #ip_addr manufacturer user old_pass new_pass 192.168.111.3 dell root calvin calvin123456 192.168.111.4 inspur admin admin admin123456 192.168.111.5 hw root Huawei_123 Huawei_12345 192.168.111.6 ibm USERID PASSW0RD PASSW0RD12345 192.168.111.7 hp administrator hp123456 hp123456789 192.168.111.8 hw root Huawei_123 Huawei_12345 192.168.111.9 ibm USERID PASSW0RD PASSW0RD12345 192.168.111.10 hw administrator hp123456 hp123456789
脚本主体
[root@135 9_edit_ipmi_password]# cat edit_ipmi_password.sh #!/bin/bash edit_pass(){ cat machine_list.txt |while read ip_addr type user old_pass new_pass do echo $ip_addr | grep '\#' &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "注释掉了" continue fi echo "Ip Address Info: $ip_addr" case $type in 'dell') echo "this type dell" ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${old_pass} user set password 1 ${new_pass} ;; 'hw') echo "this type hw" ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${old_pass} user set password 2 ${new_pass} ;; 'inspur') echo "this type inspur" ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${old_pass} user set password 1 ${new_pass} ;; 'ibm') echo "this type ibm" ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${old_pass} user set password 2 ${new_pass} ;; 'hp') echo "this type hp" ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${old_pass} user set password 1 ${new_pass} ;; *) echo "Sorry this Model not supported for program." ;; esac done } check_new_pass_status(){ > result_eidt_pass.txt cat machine_list.txt |while read ip_addr type user old_pass new_pass do timeout 2 ipmitool -H ${ip_addr} -I lanplus -U ${user} -P ${new_pass} user list if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "${ip_addr} edit ${user} password succeed" >> result_eidt_pass.txt else echo "${ip_addr} edit ${user} password failed" >> result_eidt_pass.txt fi done } result_file_info(){ echo "######################ipmi地址修改结果统计######################" total_n=`cat result_eidt_pass.txt|wc -l` success_n=`cat result_eidt_pass.txt | grep success$|wc -l` failed_n=`cat result_eidt_pass.txt | grep failed$|wc -l` echo -e "statistics:\n待修改主机数:${total_n}\n成功修改数:${success_n}\n失败修改数:${failed_n}" echo "######################ipmi地址修改结果统计结束######################" } mian(){ edit_pass check_new_pass_status result_file_info } #IBM USERID账户id为 2 #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P old_password user set password 2 new_password #华为 root账户id为 2 #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P old_password user set password 2 new_password #浪潮 admin账户id为 1 #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P old_password user set password 1 new_password #dell root账户id为 1 #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P old_password user set password 1 new_password #hp root账户id为 2 admin账户id为 1 #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P old_password user set password 1 new_password #查看用户id #ipmitool -H 192.168.111.1 -I lanplus -U root -P password user list
**************************************************************************************************************2021年2月4日脚本结束*****************************************************************************************************************
21年2月5日-ping判断系统类型
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
脚本说明
脚本读取配置文件中的主机ip地址列表,使用ping命令截取返回ttl值根据已知的规则判断系统大致类型。
读者可以根据自己的了解在case中添加对应的行实现对更多系统的识别。
文件说明
machine.txt:配置文件
Dis_host_system.sh:脚本主体脚本
配置文件
[root@135 10_Dis_Host_Systems]# cat machine.txt 192.168.111.1 192.168.111.2 192.168.111.11 192.168.111.12 192.168.111.135 192.168.111.200 192.168.300.12
脚本主体
[root@135 10_Dis_Host_Systems]# cat Dis_host_system.sh #!/bin/bash Dis_host_system(){ > tmp_result.txt for i in `cat machine.txt` do ttl_num=`timeout 1 ping -c 1 ${i} | grep 'ttl=' | awk -F'ttl=' '{print $2}'| awk '{print $1}'` timeout 1 ping -c 1 ${i} &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then case ${ttl_num} in 64) echo "This ${i} System os Linux" >> tmp_result.txt ;; 128) echo "This ${i} System os Windows NT/2000/xp And later versions" >> tmp_result.txt ;; 32) echo "This ${i} System os Windows 98" >> tmp_result.txt ;; 255) echo "This ${i} System os UNIX/Linux" >> tmp_result.txt ;; *) echo "Sorry ${i} Unable to identify the operating system" >> tmp_result.txt ;; esac else echo "The ${i} address is unreachable or ICMP has been closed" >> tmp_result.txt fi done } statistics(){ total_num=`cat tmp_result.txt|wc -l` Linux=`cat tmp_result.txt | grep Linux|wc -l` Win=`cat tmp_result.txt | grep Windows|wc -l` Unable=`cat tmp_result.txt | grep Unable|wc -l` not_ping=`cat tmp_result.txt | grep unreachable|wc -l` echo -e "Statistics Info:\n The total number of IP addresses to be detected: ${total_num}\n Linux/Unix System num: ${Linux}\n Win System num: ${Win}\n Unable System num: ${Unable}" echo " Address unreachable or ICMP has been closed num: ${not_ping}" rm -rf tmp_result.txt } main(){ Dis_host_system statistics } main
结果
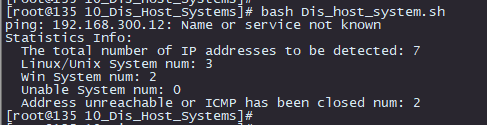
**************************************************************************************************************2021年2月5日脚本结束*****************************************************************************************************************

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号