数据结构入门
1. 两数之和

解法1
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { //使用暴力搜索做,复杂度(O(n^2)) 只想到暴力搜,思维和做题方法和掌握的东西都还是不够啊 vector<int> res; int len = nums.size(); for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){ for(int j = i; j < len; j++){ if(i != j && (nums[i] + nums[j] == target)){ res.push_back(i); res.push_back(j); return res; } } } return res; } };
解法2
使用哈希表。
//JAVA class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { //使用哈希表 Map<Integer, Integer>map=new HashMap<>();//建立元素值和元素位置之间的映射 map.put(nums[0],0);//记录第一个元素和其下标0 for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){ int matchNum = target - nums[i];//寻找nums[i]对应的值 if(map.containsKey(matchNum)){ int idx1 = i; int idx2 = map.get(matchNum); return new int[] {idx1, idx2}; }else{ map.put(nums[i], i); } } return null; } }
//C++
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { //使用哈希表 vector<int> res; map<int, int> pairs; pairs.insert({nums[0], 0});//记录第一个元素和其下标0 for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){ int matchNum = target - nums[i];//寻找nums[i]对应的值 for (auto itr = pairs.find(matchNum); itr != pairs.end(); itr++) { res.push_back(i); res.push_back(itr->second); return res; } pairs.insert({nums[i], i}); } return res; } };
c++中map使用参考:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/map-associative-containers-the-c-standard-template-library-stl/
2. 合并两个有序数组

class Solution { public: void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) nums1[m+i] = nums2[i]; sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()); } };
3. 两个数组的交集

方法一,使用hash表 即map 第一轮循环统计nums1元素出现次数,第二轮与nums2对比找到交集元素,并更新出现的次数
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { //使用hash表 vector<int> res; map<int, int> m; //先把nums1 中的所有元素加入到hash表中 for (auto i : nums1){ m[i]++;//此时所有的element为key i 的计数次数 } for (auto i : nums2){ if (m[i]>0)//如果在m中找到2中的元素i { res.push_back(i); //把找此时到的这个加入到输出中 m[i]--;//由于nums2中的某个元素计数可能比nums1多,所以就要更新m中的 element } } return res; }
速度还行,就是消耗内存比较大.
方法二,双指针 暴力搜 速度慢,内存消耗小一点
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { //排序 双指针 暴力搜 速度慢很多,内存消耗小一点 不用存所有的元素在新的内存中 sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()); sort(nums2.begin(), nums2.end()); int idx1 = 0, idx2 = 0; vector<int> ans; while (idx1 < nums1.size() && idx2 < nums2.size()) { int n1 = nums1[idx1], n2 = nums2[idx2]; if (n1 == n2) { ans.push_back(n1); idx1 ++; idx2 ++; } else if (n1 < n2){ idx1 ++; } else { idx2 ++; } } return ans; }
4. 买卖股票最佳时机

使用暴力搜不行的,当数据量大的时候,很可能会花费大量的时间,这样看起来就不是很经济。
双循环暴力搜(不是好方法)
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) { //回忆起返回数组中连续元素最大和 int res = 0; for(int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++){ for(int j = i; j < prices.size(); j++){ if(prices[j]-prices[i] > res){ res = prices[j]-prices[i]; } } } return res; }
动态规划(dynamic programming)
- DP状态方程: 第i天的收益 = max(第i-1天的收益+第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格,第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格)
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) { //解题思路 DP动态规划,dynamic programming int len=prices.size(), dp[len], ret=0; dp[0]=0; for(int i = 1; i<len; i++){ //动态规划状态转移方程 dp[i]=max(dp[i-1] + prices[i] - prices[i-1], prices[i] - prices[i-1]); ret = max(ret, dp[i]);//c++中取多个数中最大值没有直接接口但是两个数取大小还是有接口呀 max() min() } return ret; }
- DP状态方程: 前i天的最大收益 = max(前i-1天的最大收益,第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格)
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) { //解题思路 DP动态规划,dynamic programming //前i天的最大收益 = max{前i-1天的最大收益,第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格} int len=prices.size(), ret=0; if(len<=1) return 0; int min_ago_iminus1 = prices[0]; for(int i = 1; i<len; i++){ //动态规划状态转移方程 min_ago_iminus1=min(prices[i],min_ago_iminus1); ret = max(ret, prices[i]-min_ago_iminus1); } return ret;
关于动态规划,hxd说过:(size的扩展get到了吗?)

5. 存在重复元素
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) { return set<int>(nums.begin(), nums.end()).size() != nums.size(); }
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) { int n = nums.size(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());//从小到大 int j = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { j = i - 1; if (nums[i] - nums[j] == 0) { return true; } } return false; //一行代码实现 简单,but消耗时间多一些些 }
6. 最大子序和
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) { /* * 给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。 * 输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] * 输出:6 * 解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。 * 复杂度要为 O(n) 遍历两次复杂度肯定达不到 */ if (nums.size() == 0) return NULL; int res = INT_MIN; int f_n = -1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { f_n = max(nums[i], f_n + nums[i]); //关键在于 连续 每次计算一个值 同返回的最大值比较即可 res = max(f_n, res); } return res; }
7. 重塑矩阵

我的思路:先打散,在动态创建vector重新赋值
vector<vector<int>> matrixReshape(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int r, int c) { if(mat.size()*mat[0].size() != r*c){ return mat; } vector<int> temp; for(int i = 0; i < mat.size(); i++){ for(int j = 0; j< mat[0].size(); j++){ temp.push_back(mat[i][j]); } } vector<vector<int>> ret; int sub = 0; for(int i = 0; i < r; i++){ vector<int> single; for(int j = 0; j< c; j++){ single.push_back(temp[sub]); sub++; } ret.push_back(single); } return ret; }
可以尝试根据需求固定创建二维矩阵的方法:
vector<vector<int>> matrixReshape(vector<vector<int>>& nums, int r, int c) { int m = nums.size(); int n = nums[0].size(); if (m * n != r * c) return nums; vector<vector<int>> ret(r, vector<int>(c)); for (int i = 0; i < m * n; i++) { ret[i / c][i % c] = nums[i / n][i % n]; } return ret; }
重新赋值语句:
ret[i / c][i % c] = nums[i / n][i % n]
8. 杨辉三角
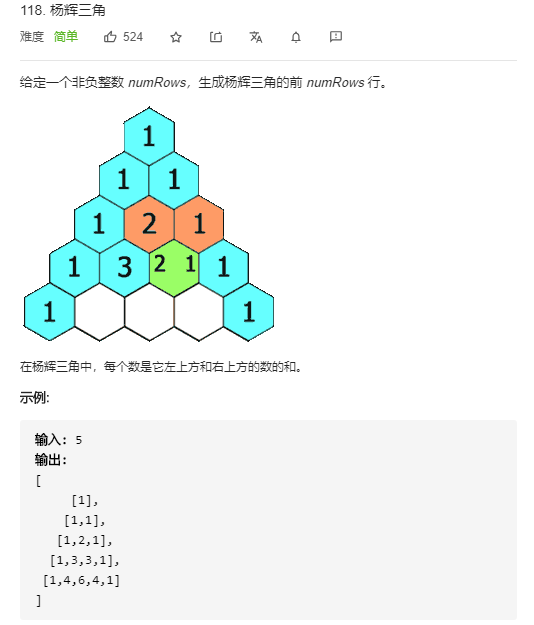
最重要的是每个数是由它左上方和右上方的数的和,这个怎么表达出来:
temp[j] = ret[i-1][j-1] + ret[i-1][j]
vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) { vector<vector<int>> ret; for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++){ //创建中间vector,全初始化1再做修改 vector<int> temp(i+1, 1); for(int j = 1; j <= i-1; j++){ temp[j] = ret[i-1][j-1] + ret[i-1][j]; } ret.push_back(temp); } return ret; }
9. 有效的数独

方法一:用空间换时间,内存消耗较大
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { //使用count就可以记录刚生成的vector有没有重复 中间完成判断,而不是等生成后再判断 vector<unordered_set<char>> rows(9); vector<unordered_set<char>> cols(9); vector<unordered_set<char>> boxes(9); for(int i=0; i<9; i++){ for(int j=0; j<9; j++){ int num = board[i][j]; if(num!='.'){ int boxes_i = (i/3)*3 + j/3; if(rows[i].count(num) || cols[j].count(num) || boxes[boxes_i].count(num)) return false; rows[i].insert(num); cols[j].insert(num); boxes[boxes_i].insert(num); } } } return true; }
方法二: 位运算
其中一维数组的每个元素表示一行或一列或一个子数独的值,因为int为32位,数独每行列数独都是9个数,可以用二进制0、1进行存储到一个元素中,通过这种方式压缩空间
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { vector<int> row(9,0); vector<int> line(9,0); vector<int> son(9,0); for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ for(int j=0;j<9;j++){ if(board[i][j]=='.') continue; int k=(i/3)*3+j/3; int val=1<<(board[i][j]-'1'); if(row[i]&val||line[j]&val||son[k]&val) return false; row[i]|=val; line[j]|=val; son[k]|=val; } } return true; }
10. 矩阵置零
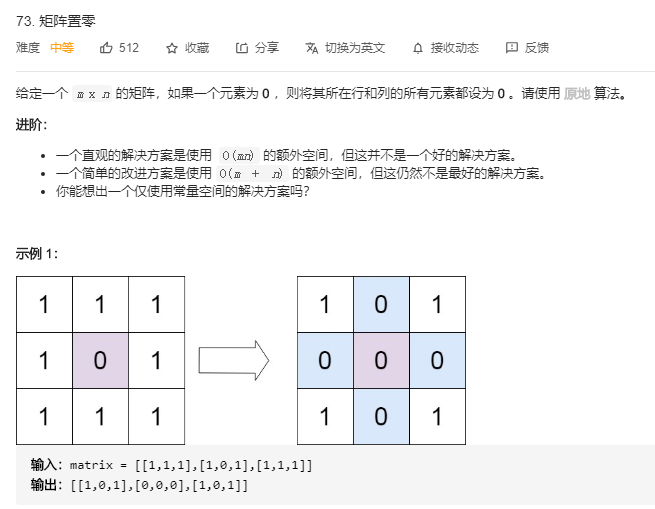
方法一:
void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { //先标识要置零的行和列 set<int> zero_row; set<int> zero_column; for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++){ for(int j=0;j<matrix[0].size();j++){ if(matrix[i][j]==0){ zero_row.insert(i); zero_column.insert(j); } } } //然后原地修改 set<int>::iterator itr; for (itr = zero_row.begin(); itr != zero_row.end(); itr++) { for(int i = 0;i<matrix[0].size();i++){ matrix[*itr][i] = 0; } } for (itr = zero_column.begin(); itr != zero_column.end(); itr++) { for(int i = 0;i<matrix.size();i++){ matrix[i][*itr] = 0; } } }
快的很,但是复杂度达不到O(1),为O(m+n)
方法二:我们只需要常数空间存储若干变量O(1)。
主要利用由于在原地修改,将要置零的行列信息存储到第一行或第一列,但是首先要用两个变量来存储首行或者首列要不要置零
void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { if(matrix.size()==0 || matrix[0].size()==0) return; bool rowFlag=false,colFlag=false; int rows=matrix.size(),cols=matrix[0].size(); //看第一列是否是有0 for(int i=0;i<rows;++i){ if(matrix[i][0] == 0){ colFlag=true; break; } } //看第一行是否有0 for(int i=0;i<cols;++i){ if(matrix[0][i]==0){ rowFlag=true; break; } } //遍历除第一行第一列以外的矩阵元素,如果有元素为0,则将对应的第一行第一列的位置置为0 for(int i=1;i<rows;++i){ for(int j=1;j<cols;++j){ if(matrix[i][j]==0){ matrix[i][0]=0; matrix[0][j]=0; } } } //同样遍历除第一行第一列以外的矩阵元素,如果matrix[i][j]所在位置的第一行第一列有任意一个位置为0 那么那个位置将被置为0 上一步的反馈 for(int i=1;i<rows;++i){ for(int j=1;j<cols;++j){ if(matrix[i][0]==0 || matrix[0][j]==0){ matrix[i][j]=0; } } } //看第一列是否有0 有则将该列置为0 if(colFlag){ for(int i=0;i<rows;++i) matrix[i][0] = 0; } //行同理 if(rowFlag){ for(int i=0;i<cols;++i) matrix[0][i] = 0; } }
实际上这两个方法内存消耗差不多,只有当矩阵中有非常多0的时候差别才大。
11. 字符串中第一个唯一字符

思路,和字符出现次数相关,使用hash表:
int firstUniqChar(string s) { unordered_map<char, int> m; for (auto &c : s) ++m[c];//初始值默认为0 for (auto &c : s) if (m[c] == 1) return s.find_first_of(c); return -1; }
12. 赎金信(一个字符串中是不是有足够的字符构成一个新的串)

杂志字符串中的每个字符只能在赎金信字符串中使用一次,就是说ransom中的每个字母出现至多和magazine中相等,才可能输出true. 涉及字母频率,
方法一:使用hash表
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine) { //首先对ransom中的字母个数做统计 unordered_map<char, int> mr; for(auto &c : ransomNote) ++mr[c]; //遍历maganize中的字母,如果count<需要的 则输出false unordered_map<char, int> mm; for(auto &b : magazine) ++mm[b]; for(auto itr = mr.begin(); itr != mr.end(); ++itr){ if((itr->second)>mm[itr->first]){ return false; } } return true; }
方法二:数组代替hash表, 由于少了个循环,更快了
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine) { vector<int> count(26); for(auto &c:magazine) ++count[c-'a']; for(auto &c:ransomNote) { if(count[c-'a']!=0) --count[c-'a']; else return false; } return true; }
13. 有效的字母异同位

方法一,hash表:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) { unordered_map<char, int> ms; for(auto &c : s) ++ms[c]; unordered_map<char, int> mt; for(auto &b : t) ++mt[b]; if(ms.size() != mt.size()) return false; for(auto itr = ms.begin(); itr != ms.end(); ++itr){ if((itr->second) != mt[itr->first]){ return false; } } return true; }
方法二:直接用sort函数
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) { sort(s.begin(),s.end()); sort(t.begin(),t.end()); if(s==t) return true; else return false; }
这段在python中只要一行:
return sorted(s)==sorted(t)
方法三:数组代替hash表
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) { int count[26]={0}; if(s.length()!=t.length()) return false; for(int i=0;s[i]!='\0';i++){ count[s[i]-'a']++; count[t[i]-'a']--; } for(int i=0;i<26;i++) if(count[i]!=0) return false; return true; }
14. 环形链表

- 快慢指针 快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,如果存在环,一定会在环中相遇
- 快指针始终一步一步靠近慢指针
- 一定会在环中相遇 =>有环
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { ListNode* fast = head; ListNode* slow = head;
// 循环条件注意 为了保证在环中相遇,使用fast做判断 while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) return true; } return false; }
15. 合并两个有序列表
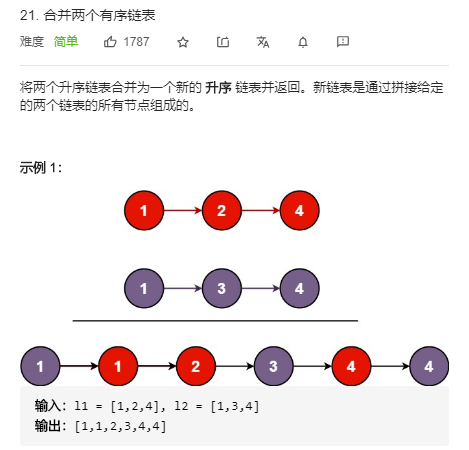
- 主要是要利用原有链表空间而不是要新建空间
方法一:递归, 很快啊
为什么可以用递归?官方题解
所有的步骤都是选一个较小的,同剩下元素合并的结果。
忽略边界情况,比如空链表等,则有如下操作:
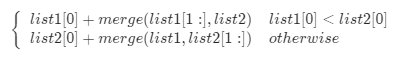
- 如果有链表为空,直接返回另一个
- 否则判断
l1和l2哪一个链表的头节点的值更小,递归的决定下一个添加到结果里的节点 - 如果两个链表有一个为空,递归结束。
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { if (l1 == nullptr) { return l2; } else if (l2 == nullptr) { return l1; } else if (l1->val < l2->val) { l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2); return l1; } else { l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next); return l2; } }
方法二:迭代
- 首先定义一个哑节点,空间复杂度O(1)
- 拿两个链表的当前遍历的值和哑节点做对比,如果需要插入,就更新哑节点和当前表示的next
- 循环条件直到有一个已经遍历到结尾,时间复杂度O(m+n)
- 将另一个当前的下一项加入即可(表达不清,看代码)
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode* retHead = new ListNode(-1); //作为哑节点 ListNode* prev = retHead; ListNode* ret = retHead; while(l1!=nullptr && l2!=nullptr){ if(l1->val < l2->val){ prev->next = l1; l1= l1->next; }else{ prev->next = l2; l2= l2->next; } prev = prev->next; } prev->next = l1 == nullptr ? l2 : l1; ret = retHead->next; delete retHead; return ret; }
16. 移除链表元素

此题删除链表中元素是很简单的,只需要让待删节点之前一个节点指向待删节点之后一个节点即可。 此题最大的问题就是,题目要求我们要返回新链表中的头结点,如果我们就采用仅仅复制头结点的方式(用H=head)然后用H进行操作,最后返回head。这样就会导致如果头结点也是我们需要删除的节点就会导致错误。
为了避免这种错误,创建一个新节点来作为整个链表的头结点。
迭代方法:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { //迭代方法 //先确定头 //ListNode* myhead = head if(head==NULL) return NULL; ListNode* ret = new ListNode(-1); ret->next = head; ListNode* pos = ret; ListNode* del_pos = NULL; while(pos->next != NULL){ //终止条件 if(pos->next->val == val){ del_pos = pos->next; pos->next = pos->next->next; delete del_pos; }else{ pos = pos->next; } } return ret->next; }
递归方法:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { //递归方法 if (!head) return head; head->next = removeElements(head->next, val); return head->val == val ? head->next : head; } };
17. 反转链表
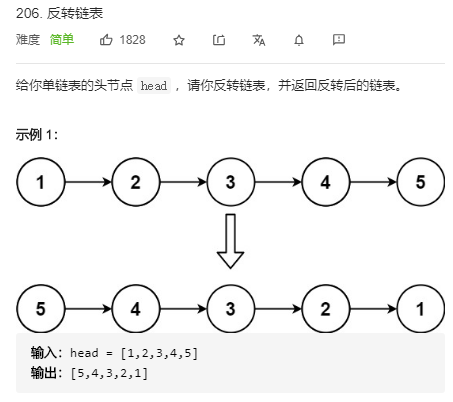

用双指针迭代:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { //利用双指针迭代 ListNode* pre = nullptr; ListNode* cur = head; ListNode* temp = new ListNode(); while(cur){ temp = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } };

- 终止条件是当前节点或者下一个节点==null why?
在head指向的结点为null或head指向的结点的下一个结点为null时停止,因为在这两种情况下,反转后的结果就是它自己
- 推公式reverseList的含义是:把拿到的链表进行反转,然后返回新的头结点newHead
(不需要明白是每一步怎么推的)
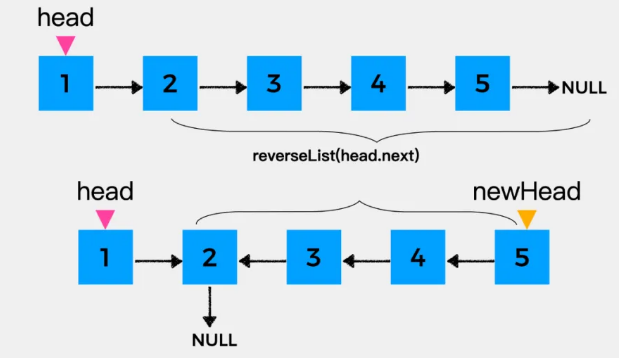
- 接着要做的就是反转结点1,也就是将head指向的结点作为其下一个结点的下一个结点head.next.next=head
- 最后,将head指向的结点的下一个结点置为null
class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { //递归解法 if (!head || !head->next) { return head; } // 想象递归已经层层返回,到了最后一步 // 以链表 1->2->3->4->5 为例,现在链表变成了 5->4->3->2->null,1->2->null(是一个链表,不是两个链表) // 此时 newHead是5,head是1 ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next); // 最后的操作是把链表 1->2->null 变成 2->1->null // head是1,head.next是2,head.next.next = head 就是2指向1,此时链表为 2->1->2 head->next->next = head; // 防止链表循环,1指向null,此时链表为 2->1->null,整个链表为 5->4->3->2->1->null head->next = nullptr; return newHead; } };
递归就是只要考虑当前节点和后面整体的关系,不要去考虑后面整体内部关系,把整体内部的关系交给递归处理。最后只需要返回最初设想的值…
18. 删除链表中的重复元素
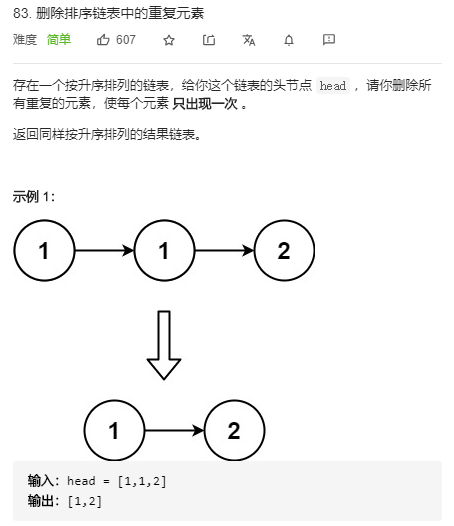
双指针,很快啊:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return head; ListNode* curr = head; ListNode* rear = head->next; while(rear){ if(curr->val == rear->val){ curr->next = rear->next; rear = rear->next; }else{ curr = rear; rear = rear->next; } } return head; } };
注意,c++加上垃圾回收意识就更好了。
class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return head; ListNode* curr = head; ListNode* rear = head->next; while(rear){ if(curr->val == rear->val){ ListNode* temp = rear; //相应地会增加一些开销就是了 curr->next = rear->next; rear = rear->next; delete(temp); }else{ curr = rear; rear = rear->next; } } return head; } };




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~